See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Pedal boat. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Pedal boat may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Pedal boat. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

A hydrofoil is a lifting surface, or foil, that operates in water. They are similar in appearance and purpose to aerofoils used by aeroplanes. Boats that use hydrofoil technology are also simply termed hydrofoils. As a hydrofoil craft gains speed, the hydrofoils lift the boat's hull out of the water, decreasing drag and allowing greater speeds.

A kayak is a small, narrow watercraft which is typically propelled by means of a double-bladed paddle. The word kayak originates from the Greenlandic word qajaq.

Human-powered transport is the transport of person(s) and/or goods using human muscle power. Like animal-powered transport, human-powered transport has existed since time immemorial in the form of walking, running and swimming. Modern technology has allowed machines to enhance human-power.

Watercraft, also known as water vessels or waterborne vessels, are vehicles used in water, including ships, boats, hovercraft and submarines. Watercraft usually have a propulsive capability and hence are distinct from a simple device that merely floats, such as a log raft.

A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine that drives paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, where the first uses were wheelers driven by animals or humans.

A riverboat is a watercraft designed for inland navigation on lakes, rivers, and artificial waterways. They are generally equipped and outfitted as work boats in one of the carrying trades, for freight or people transport, including luxury units constructed for entertainment enterprises, such as lake or harbour tour boats. As larger water craft, virtually all riverboats are especially designed and constructed, or alternatively, constructed with special-purpose features that optimizes them as riverine or lake service craft, for instance, dredgers, survey boats, fisheries management craft, fireboats and law enforcement patrol craft.

Decavitator is a human-powered hydrofoil equipped with pedals and an air propeller that was built by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It holds the human-powered speed record on water. The vehicle was displayed hanging in the entry lobby of the Museum of Science, Boston until 2015. It is currently in storage at MIT.

HMCS Bras d'Or was a hydrofoil that served in the Canadian Forces from 1968 to 1971. During sea trials in 1969, the vessel exceeded 63 knots, making her the fastest unarmed warship in the world at the time.

A pedalo or paddle boat is a small human-powered watercraft propelled by the action of pedals turning a paddle wheel.
The Flyak is a hydrofoil adaptation to the conventional kayak. It uses twin hydrofoils designed to raise the hull out of the water to increase the speed. Speeds of up to 27.2 km/h can be achieved on calm water.
The Batboat, Batstrike, or Batsub is the fictional personal aqua-dynamic hydrofoil/submersible watercraft of the DC Comics superhero Batman.
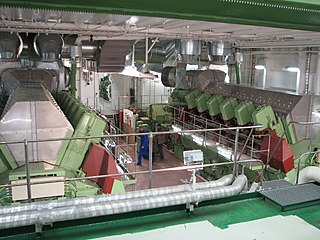
Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a ship or boat across water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or engine turning a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems.
Paddling with regard to watercraft is the act of manually propelling a boat using a paddle. The paddle, which consists of one or two blades joined to a shaft, is also used to steer the vessel. The paddle is not connected to the boat.

A human-powered hydrofoil is a small hydrofoil watercraft propelled entirely by the muscle power of its operator(s). Hydrofoils are the fastest water-based vehicles propelled solely by human power. They can reach speeds of up to 34 km/h, easily exceeding the world records set by competitive rowing which stand at about 20 km/h. This speed advantage is achieved since hydrofoils lack a submerged body to provide buoyancy, greatly reducing the drag force.

A paddle wheel is a form of waterwheel or impeller in which a number of paddles are set around the periphery of the wheel. It has several uses, some of which are:

The following outline is provided as an overview of canoeing and kayaking:

A hydrocycle is a bicycle-like watercraft. The concept was known in the 1870s under the title 'water velocipede' and the name was in use by the late 1890s.

Human-powered watercraft are watercraft propelled by human power.