
A centripetal force is a force that makes a body follow a curved path. The direction of the centripetal force is always orthogonal to the motion of the body and towards the fixed point of the instantaneous center of curvature of the path. Isaac Newton described it as "a force by which bodies are drawn or impelled, or in any way tend, towards a point as to a centre". In the theory of Newtonian mechanics, gravity provides the centripetal force causing astronomical orbits.

Ohm's law states that the electric current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the three mathematical equations used to describe this relationship:
In fluid mechanics, the Rayleigh number (Ra, after Lord Rayleigh) for a fluid is a dimensionless number associated with buoyancy-driven flow, also known as free (or natural) convection. It characterises the fluid's flow regime: a value in a certain lower range denotes laminar flow; a value in a higher range, turbulent flow. Below a certain critical value, there is no fluid motion and heat transfer is by conduction rather than convection. For most engineering purposes, the Rayleigh number is large, somewhere around 106 to 108.

The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is electrical conductance, measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm, while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S).

Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: self capacitance and mutual capacitance. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operation of the capacitor, an elementary linear electronic component designed to add capacitance to an electric circuit.
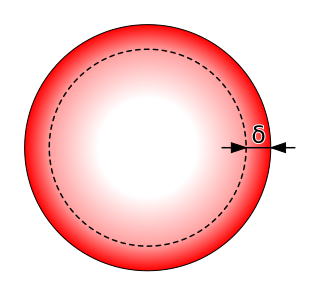
In electromagnetism, skin effect is the tendency of an alternating electric current (AC) to become distributed within a conductor such that the current density is largest near the surface of the conductor and decreases exponentially with greater depths in the conductor. It is caused by opposing eddy currents induced by the changing magnetic field resulting from the alternating current. The electric current flows mainly at the skin of the conductor, between the outer surface and a level called the skin depth. Skin depth depends on the frequency of the alternating current; as frequency increases, current flow becomes more concentrated near the surface, resulting in less skin depth. Skin effect reduces the effective cross-section of the conductor and thus increases its effective resistance. At 60 Hz in copper, skin depth is about 8.5 mm. At high frequencies, skin depth becomes much smaller.
A flexible alternating current transmission system (FACTS) is a system composed of static equipment used for the alternating current (AC) transmission of electrical energy. It is meant to enhance controllability and increase power transfer capability of the network. It is generally a power electronics-based system.
A resistor–capacitor circuit, or RC filter or RC network, is an electric circuit composed of resistors and capacitors. It may be driven by a voltage or current source and these will produce different responses. A first order RC circuit is composed of one resistor and one capacitor and is the simplest type of RC circuit.

A corona discharge is an electrical discharge caused by the ionization of a fluid such as air surrounding a conductor carrying a high voltage. It represents a local region where the air has undergone electrical breakdown and become conductive, allowing charge to continuously leak off the conductor into the air. A corona discharge occurs at locations where the strength of the electric field around a conductor exceeds the dielectric strength of the air. It is often seen as a bluish glow in the air adjacent to pointed metal conductors carrying high voltages, and emits light by the same mechanism as a gas discharge lamp. Corona discharges can also happen in weather, such as thunderstorms, where objects like ship masts or airplane wings have a charge significantly different from the air around them.
In electrical engineering, partial discharge (PD) is a localized dielectric breakdown (DB) of a small portion of a solid or fluid electrical insulation (EI) system under high voltage (HV) stress. While a corona discharge (CD) is usually revealed by a relatively steady glow or brush discharge (BD) in air, partial discharges within solid insulation system are not visible.

A p–n junction is a boundary or interface between two types of semiconductor materials, p-type and n-type, inside a single crystal of semiconductor. The "p" (positive) side contains an excess of holes, while the "n" (negative) side contains an excess of electrons in the outer shells of the electrically neutral atoms there. This allows electric current to pass through the junction only in one direction. The p- and n-type regions creating the junction are made by doping the semiconductor, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy.

A vibration in a string is a wave. Resonance causes a vibrating string to produce a sound with constant frequency, i.e. constant pitch. If the length or tension of the string is correctly adjusted, the sound produced is a musical tone. Vibrating strings are the basis of string instruments such as guitars, cellos, and pianos.
A temperature coefficient describes the relative change of a physical property that is associated with a given change in temperature. For a property R that changes when the temperature changes by dT, the temperature coefficient α is defined by the following equation:
The Transfer Length Method or the "Transmission Line Model" is a technique used in semiconductor physics and engineering to determine the specific contact resistivity between a metal and a semiconductor. TLM has been developed because with the ongoing device shrinkage in microelectronics the relative contribution of the contact resistance at metal-semiconductor interfaces in a device could not be neglected any more and an accurate measurement method for determining the specific contact resistivity was required.

In electromagnetism, charge density is the amount of electric charge per unit length, surface area, or volume. Volume charge density is the quantity of charge per unit volume, measured in the SI system in coulombs per cubic meter (C⋅m−3), at any point in a volume. Surface charge density (σ) is the quantity of charge per unit area, measured in coulombs per square meter (C⋅m−2), at any point on a surface charge distribution on a two dimensional surface. Linear charge density (λ) is the quantity of charge per unit length, measured in coulombs per meter (C⋅m−1), at any point on a line charge distribution. Charge density can be either positive or negative, since electric charge can be either positive or negative.
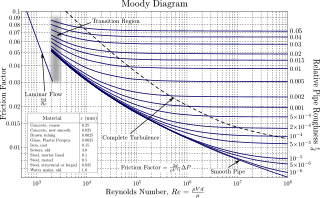
In engineering, the Moody chart or Moody diagram is a graph in non-dimensional form that relates the Darcy–Weisbach friction factor fD, Reynolds number Re, and surface roughness for fully developed flow in a circular pipe. It can be used to predict pressure drop or flow rate down such a pipe.
Quantum capacitance, also called chemical capacitance and electrochemical capacitance, is a quantity first introduced by Serge Luryi (1988), and is defined as the variation of electrical charge with respect to the variation of electrochemical potential , i.e., .
An RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.
The activating function is a mathematical formalism that is used to approximate the influence of an extracellular field on an axon or neurons. It was developed by Frank Rattay and is a useful tool to approximate the influence of functional electrical stimulation (FES) or neuromodulation techniques on target neurons. It points out locations of high hyperpolarization and depolarization caused by the electrical field acting upon the nerve fiber. As a rule of thumb, the activating function is proportional to the second-order spatial derivative of the extracellular potential along the axon.
Performance modelling is the abstraction of a real system into a simplified representation to enable the prediction of performance. The creation of a model can provide insight into how a proposed or actual system will or does work. This can, however, point towards different things to people belonging to different fields of work.












