
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania or Mecklenburg-West Pomerania, is a state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in population, 6th in area, and 16th in population density. Schwerin is the state capital and Rostock is the largest city. Other major cities include Neubrandenburg, Stralsund, Greifswald, Wismar and Güstrow.

Anklam [German pronunciation: [ˈaŋklam](listen)], formerly known as Tanglim and Wendenburg, is a town in the Western Pomerania region of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated on the banks of the Peene river, just 8 km from its mouth in the Kleines Haff, the western part of the Stettin Lagoon. Anklam has a population of 14,603 (2005) and was the capital of the former Ostvorpommern district. Since September 2011, it has been part of the district of Vorpommern-Greifswald.

The Bavarian Forest National Park is a national park in the Eastern Bavarian Forest immediately on Germany's border with the Czech Republic. It was founded on 7 October 1970 as the first national park in Germany. Since its expansion on 1 August 1997 it has covered an area of 24,250 hectares. Together with the neighbouring Czech Bohemian Forest the Bavarian Forest forms the largest contiguous area of forest in Central Europe.

The Peene is a river in Germany.
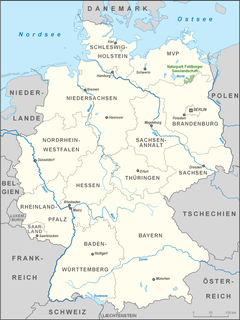
The Feldberg Lake District Nature Park lies in the southeast of the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in the district of Mecklenburgische Seenplatte. A large part of the nature park lies within the municipality of the same name, the Feldberger Seenlandschaft. In addition the municipalities of Wokuhl-Dabelow, Grünow, Carpin, Godendorf and parts of the towns of Woldegk and Neustrelitz fall within the nature park. The western end of the park is also a part of Müritz National Park.
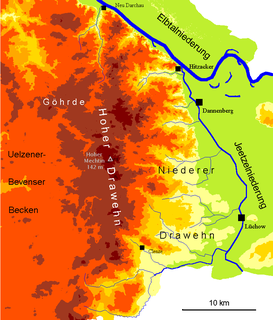
The Drawehn is a partly wooded and partly agricultural region of hills in the northeastern part of the German state of Lower Saxony, lying between the districts of Lüneburg and Uelzen in the west and Lüchow-Dannenberg in the east.

The Eifel National Park is the 14th national park in Germany and the first in North Rhine-Westphalia.

On 8 March 1988 the Bavarian State Ministry for State Development and the Environment designated an area of 1,280 square kilometres (490 sq mi) in the Steigerwald in North Bavaria, Germany, as the Steigerwald Nature Park. About half the area consists of protected landscapes. The nature park is run by the Steigerwald Tourist Association and Steigerwald Nature Park.

Pomeranian cuisine generally refers to dishes typical of the area that once formed the historic Province of Pomerania in northeast Germany and which included Stettin and Further Pomerania. It is characterised by ingredients produced by Pomeranian farms, such as swede (Wruken) and sugar beet, by poultry rearing, which has produced the famous Pomeranian goose, by the wealth of fish in the Baltic Sea, rivers and inland lakes of the Pomeranian Lake District, and the abundance of quarry in Pomeranian forests. Pomeranian cuisine is hearty. Several foodstuffs have a particularly important role to play here in the region: potatoes, known as Tüften, prepared in various ways and whose significance is evinced by the existence of a West Pomeranian Potato Museum, Grünkohl and sweet and sour dishes produced, for example, by baking fruit.

The Mecklenburg Switzerland and Lake Kummerow Nature Park lies in the northern part of the Mecklenburg Lake District in the districts of Mecklenburgische Seenplatte and Rostock in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern between the towns of Dargun, Demmin, Teterow, Malchin and Waren (Müritz). It was created in 1997. The total area of the nature park is 673 km². 19 percent of this area is covered by woodland, ca. 10 percent by lakes and rivers, the rest is cultural landscape. There are 3 large lakes in the naturepark: Lake Malchin, Lake Kummerow and Lake Teterow. The Peene is the largest river in the park. The features that make it special are the large lakes, the riverin landscapes, the centuries-old oaks, the castles, the manor houses and their rural estates. The nature park is well known as a stopover for Nordic ducks. It is easily reached from the A 19, motorway junctions Krakow am See and Güstrow, or the A 20, junctions Tessin and Bad Sülze. The head office of the nature park administration is in Basedow.

The Heilige Hallen are one of the oldest beech woods in Germany and are found in the district of Mecklenburgische Seenplatte in Mecklenburg, 3.5 kilometres west of Feldberg. In the mid 19th century, Grand Duke George of Strelitz, impressed by the giant, columnar trees, ordered that this woodland should be protected and looked after for all time. The 25 hectare core area of the forest has been a nature reserve since the 24 February 1938. Because several of the already 350‑year‑old, up‑to‑53‑metre‑high trees have exceeded their natural life span, the wood today has a large amount of dead wood. In 1993 the area of the reserve was increased from 25 to 65.5 hectares.

The Stubnitz is a hilly, forested landscape region on the east coast of the Jasmund peninsula on the German Baltic Sea island of Rügen. It covers an area of about 2,400 ha and runs from the town of Sassnitz to the municipality of Lohme, Today, it is almost entirely part of the 3,000 ha Jasmund National Park. The name Stubnitz is probably of Slavic origin; but the literature gives a wide variety of meanings – from Stufenland to Waldung mit Bienenkellern.
The Goor-Muglitz Nature Reserve is a nature reserve, covering an area of 157 hectares, in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. It lies on the island of Rügen on the northern coastline of the Bay of Greifswald. It was granted protected status on 12 September 1990 as part of the creation of the Southeast Rügen Biosphere Reserve. The conservation aim of the two-part nature reserve is, on the one hand, the preservation and development of a deciduous forest of old trees in the Goor forest and the preservation of Freetz Lowland and, on the other hand, the protection of a steep wooded slope near Muglitz, which is interspersed with wild fruit trees. The areas are in conservation zone 2 of the biosphere reserve. The rocky shallow areas of the bay are also a protected area.

The Red Moor is a raised bog in the Hessian part of the Rhön Mountains in Germany. It lies within the eponymous nature reserve in the Rhön Biosphere Reserve and is part of the Europe-wide conservation system, Natura 2000. The Red Moor has an area of 50 hectares and is the second largest raised bog in the High Rhön after the Black Moor (66.4 hectares). For 175 years, until 1984, peat was cut here. The interior of the raised bog is severely damaged, especially as a result of the many years of peat cutting. Its perimeters are however still largely undisturbed areas that are better and more typically developed than the Black Moor, 8 kilometres away. In 1979 large-scale renaturalisation measures began.

The Swabian-Franconian Forest is a mainly forested, deeply incised upland region, 1,187 km² in area and up to 586.4 m above sea level (NHN), in the northeast of Baden-Württemberg. It forms natural region major unit number 108 within the Swabian Keuper-Lias Land. Its name is derived from the fact that, in medieval times, the border between the duchies of Franconia and Swabia ran through this forested region. In addition, the Swabian dialect in the south transitions to the East Franconian dialect in the north here.

The Buocher Höhe is a wooded region and hill range up to 519.6 m above sea level (NN), around the village of Buoch in the county of Rems-Murr-Kreis in the German state of Baden-Württemberg.

Karl Lorenz Rettich was a German landscape artist and draftsman.

Taubergießen is a floodplain wetland on the southern Upper Rhine in the natural area Offenburg Rhine plain. Taubergießen was declared Naturschutzgebiet in 1979 and, with 1,697 hectares, is one of the largest protected areas in Baden-Württemberg. It has a north-south extension of more than 12 km. The largest width is about 2.5 km.
Walther Schoenichen was a German biologist and a prominent proponent of nature conservation within Nazi Germany.



















