Related Research Articles

The Peloponnesian War was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time, until the decisive intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet, built with Persian subsidies, finally defeated Athens and started a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.
This article concerns the period 439 BC – 430 BC.
This article concerns the period 429 BC – 420 BC.
This decade witnessed the continuing decline of the Achaemenid Empire, fierce warfare amongst the Greek city-states during the Peloponnesian War, the ongoing Warring States period in Zhou dynasty China, and the closing years of the Olmec civilization in modern-day Mexico.

This is a timeline of ancient Greece from its emergence around 800 BC to its subjection to the Roman Empire in 146 BC.

Alcibiades was an Athenian statesman and general. The last of the Alcmaeonidae, he played a major role in the second half of the Peloponnesian War as a strategic advisor, military commander, and politician, but subsequently fell from prominence.

The Sicilian Expedition was an Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse and Corinth on the other. The expedition ended in a devastating defeat for the Athenian forces, severely impacting Athens.

The History of the Peloponnesian War is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War, which was fought between the Peloponnesian League and the Delian League. It was written by Thucydides, an Athenian historian who also served as an Athenian general during the war. His account of the conflict is widely considered to be a classic and regarded as one of the earliest scholarly works of history. The History is divided into eight books.
The Battle of Olpae was a battle of the Peloponnesian War in 426 BC, between armies led by Athens and Sparta.
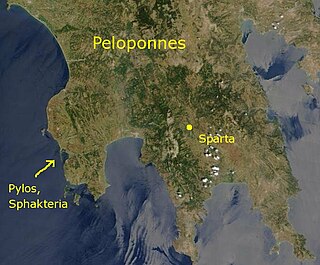
The naval Battle of Pylos took place in 425 BC during the Peloponnesian War at the peninsula of Pylos, on the present-day Bay of Navarino in Messenia, and was an Athenian victory over Sparta. An Athenian fleet had been driven ashore at Pylos by a storm, and, at the instigation of Demosthenes, the Athenian soldiers fortified the peninsula, and a small force was left there when the fleet departed again. The establishment of an Athenian garrison in Spartan territory frightened the Spartan leadership, and the Spartan army, which had been ravaging Attica under the command of Agis, ended their expedition and marched home, while the Spartan fleet at Corcyra sailed to Pylos.
The Battle of Sybota took place in 433 BC between Corcyra and Corinth. It was one of the immediate catalysts for the Peloponnesian War.
Eurymedon was one of the Athenian generals (strategoi) during the Peloponnesian War.

Demosthenes, son of Alcisthenes, was an Athenian general during the Peloponnesian War.

The Samian War was an Ancient Greek military conflict between Athens and Samos. The war was initiated by Athens's intervention in a dispute between Samos and Miletus. When the Samians refused to break off their attacks on Miletus as ordered, the Athenians easily drove out the oligarchic government of Samos and installed a garrison in the city, but the oligarchs soon returned, with Persian support.

Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years in Ancient Greece, marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining politics, artistic thought, scientific thought, theatre, literature and philosophy of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. Part of the broader era of classical antiquity, the classical Greek era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against the common enemy of the Persian Empire, which was conquered within 13 years during the wars of Alexander the Great, Philip's son.
Diodotus, son of Eucrates, was an opponent to the proposal of Cleon – leader of the radical, imperialist faction in Athens – in 427 BC to kill all adult Mytilenean males and to enslave their women and children after the defeat of Mytilene. He seems to represent the moderate faction in Athens.
The Thirty Years' Peace was a treaty signed between the ancient Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta in 446/445 BC. The treaty brought an end to the conflict commonly known as the First Peloponnesian War, which had been raging since c. 460 BC.

Korkyra was an ancient Greek city on the island of Corfu in the Ionian Sea that is adjacent to Epirus. It was a colony of Corinth that was founded in the Archaic period. Korkyra was acting as a port of call on the sailing routes, especially to reach the Italian coast or ventured farther north. According to Thucydides, the earliest recorded naval battle took place between Korkyra and Corinth, roughly 260 years before he was writing, and thus in the mid-7th century BC. He also writes that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers in 5th-century BC Greece, along with Athens and Corinth.
The Affair of Epidamnus, also known as the Epidamnian Affair, is cited by the Ancient Greek historian Thucydides as one of the major immediate causes for the Peloponnesian War. The conflict began as a minor coup by a democratic faction of the city-state of Epidamnus, but eventually escalated into a major conflict between the cities of Athens and Corcyra on one side and the city of Corinth on the other. The culminating Battle of Sybota subsequently led to the Potidaean Affair and the Megarian Decree, both also major contributors to the final outbreak of hostilities between Athens and Sparta, beginning the Peloponnesian War.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Thucydides, History of the Peloponnesian War/Book 3, 70. (2007, April 11). In Wikisource, The Free Library. Retrieved 10:37, August 19, 2007, from wikisource