In biochemistry, a polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to assemble DNA and RNA molecules, respectively, by copying a DNA template strand using base-pairing interactions or RNA by half ladder replication.

In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA . Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism.

In molecular biology, RNA polymerase, or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
DNA primase is an enzyme involved in the replication of DNA and is a type of RNA polymerase. Primase catalyzes the synthesis of a short RNA segment called a primer complementary to a ssDNA template. After this elongation, the RNA piece is removed by a 5' to 3' exonuclease and refilled with DNA.
A signal peptide is a short peptide present at the N-terminus of most newly synthesized proteins that are destined toward the secretory pathway. These proteins include those that reside either inside certain organelles, secreted from the cell, or inserted into most cellular membranes. Although most type I membrane-bound proteins have signal peptides, most type II and multi-spanning membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which biochemically resembles a signal sequence except that it is not cleaved. They are a kind of target peptide.
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code.
DD-Transpeptidase is a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the R-L-αα-D-alanyl moiety of R-L-αα-D-alanyl-D-alanine carbonyl donors to the γ-OH of their active-site serine and from this to a final acceptor. It is involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, namely, the transpeptidation that crosslinks the peptide side chains of peptidoglycan strands.
This is a list of topics in molecular biology. See also index of biochemistry articles.

Histone H2A is one of the five main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells.

Caspase recruitment domains, or caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), are interaction motifs found in a wide array of proteins, typically those involved in processes relating to inflammation and apoptosis. These domains mediate the formation of larger protein complexes via direct interactions between individual CARDs. CARDs are found on a strikingly wide range of proteins, including helicases, kinases, mitochondrial proteins, caspases, and other cytoplasmic factors.

A long terminal repeat (LTR) is a pair of identical sequences of DNA, several hundred base pairs long, which occur in eukaryotic genomes on either end of a series of genes or pseudogenes that form a retrotransposon or an endogenous retrovirus or a retroviral provirus. All retroviral genomes are flanked by LTRs, while there are some retrotransposons without LTRs. Typically, an element flanked by a pair of LTRs will encode a reverse transcriptase and an integrase, allowing the element to be copied and inserted at a different location of the genome. Copies of such an LTR-flanked element can often be found hundreds or thousands of times in a genome. LTR retrotransposons comprise about 8% of the human genome.

RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to typical DNA-dependent RNA polymerases, which all organisms use to catalyze the transcription of RNA from a DNA template.

The heat shock proteins HslV and HslU are expressed in many bacteria such as E. coli in response to cell stress. The hslV protein is a protease and the hslU protein is an ATPase; the two form a symmetric assembly of four stacked rings, consisting of an hslV dodecamer bound to an hslU hexamer, with a central pore in which the protease and ATPase active sites reside. The hslV protein degrades unneeded or damaged proteins only when in complex with the hslU protein in the ATP-bound state. HslV is thought to resemble the hypothetical ancestor of the proteasome, a large protein complex specialized for regulated degradation of unneeded proteins in eukaryotes, many archaea, and a few bacteria. HslV bears high similarity to core subunits of proteasomes.

The ykkC/yxkD leader is a conserved RNA structure found upstream of the ykkC and yxkD genes in Bacillus subtilis and related genes in other bacteria. The function of this family is unclear for many years although it has been suggested that it may function to switch on efflux pumps and detoxification systems in response to harmful environmental molecules. The Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis sequence AE013027 overlaps with that of purine riboswitch suggesting that the two riboswitches may work in conjunction to regulate the upstream gene which codes for TTE0584 (Q8RC62), a member of the permease family.
Tyrosine—tRNA ligase, also known as tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that is encoded by the gene YARS. Tyrosine—tRNA ligase catalyzes the chemical reaction

DEAD box proteins are involved in an assortment of metabolic processes that typically involve RNAs, but in some cases also other nucleic acids. They are highly conserved in nine motifs and can be found in most prokaryotes and eukaryotes, but not all. Many organisms, including humans, contain DEAD-box (SF2) helicases, which are involved in RNA metabolism.
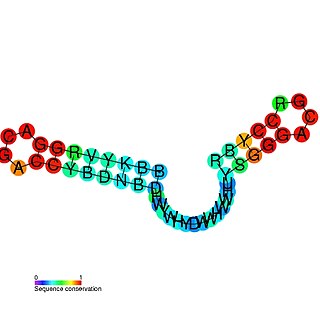
The mini-ykkC RNA motif was discovered as a putative RNA structure that is conserved in bacteria. The motif consists of two conserved stem-loops whose terminal loops contain the RNA sequence ACGR, where R represents either A or G. Mini-ykkC RNAs are widespread in Pseudomonadota, but some are predicted in other phyla of bacteria. It was expected that the RNAs are cis-regulatory elements, because they are typically located upstream of protein-coding genes.
C-terminal processing peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

The M23 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. M23 motif RNAs are found in Clostridia.














