Related Research Articles

A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels. The term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture. A colloid has a dispersed phase and a continuous phase. The dispersed phase particles have a diameter of approximately 1 nanometre to 1 micrometre.

In chemistry, electrophoresis is the motion of charged dispersed particles or dissolved charged molecules relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. As a rule, these are zwitterions.

In chemistry, a suspension is a heterogeneous mixture of a fluid that contains solid particles sufficiently large for sedimentation. The particles may be visible to the naked eye, usually must be larger than one micrometer, and will eventually settle, although the mixture is only classified as a suspension when and while the particles have not settled out.
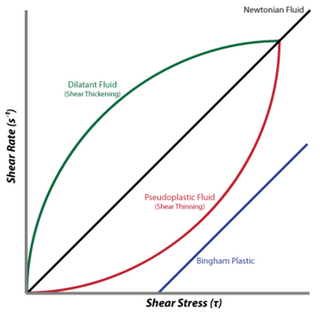
A dilatant material is one in which viscosity increases with the rate of shear strain. Such a shear thickening fluid, also known by the initialism STF, is an example of a non-Newtonian fluid. This behaviour is usually not observed in pure materials, but can occur in suspensions.
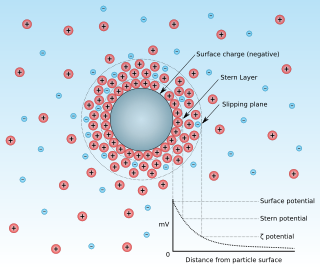
Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the slipping plane. This plane is the interface which separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface.
The DLVO theory explains the aggregation and kinetic stability of aqueous dispersions quantitatively and describes the force between charged surfaces interacting through a liquid medium. It combines the effects of the van der Waals attraction and the electrostatic repulsion due to the so-called double layer of counterions. The electrostatic part of the DLVO interaction is computed in the mean field approximation in the limit of low surface potentials - that is when the potential energy of an elementary charge on the surface is much smaller than the thermal energy scale, . For two spheres of radius each having a charge separated by a center-to-center distance in a fluid of dielectric constant containing a concentration of monovalent ions, the electrostatic potential takes the form of a screened-Coulomb or Yukawa potential,

In colloidal chemistry, flocculation is a process by which colloidal particles come out of suspension to sediment in the form of floc or flake, either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended, under the form of a stable dispersion and are not truly dissolved in solution.
A surface charge is an electric charge present on a two-dimensional surface. These electric charges are constrained on this 2-D surface, and surface charge density, measured in coulombs per square meter (C•m−2), is used to describe the charge distribution on the surface. The electric potential is continuous across a surface charge and the electric field is discontinuous, but not infinite; this is unless the surface charge consists of a dipole layer. In comparison, the potential and electric field both diverge at any point charge or linear charge.
Electrocoagulation (EC) is a technique used for wastewater treatment, wash water treatment, industrially processed water, and medical treatment. Electrocoagulation has become a rapidly growing area of wastewater treatment due to its ability to remove contaminants that are generally more difficult to remove by filtration or chemical treatment systems, such as emulsified oil, total petroleum hydrocarbons, refractory organics, suspended solids, and heavy metals. There are many brands of electrocoagulation devices available, and they can range in complexity from a simple anode and cathode to much more complex devices with control over electrode potentials, passivation, anode consumption, cell REDOX potentials as well as the introduction of ultrasonic sound, ultraviolet light and a range of gases and reactants to achieve so-called Advanced Oxidation Processes for refractory or recalcitrant organic substances.

The point of zero charge (pzc) is generally described as the pH at which the net electrical charge of the particle surface (i.e. adsorbent's surface) is equal to zero. This concept has been introduced in the studies dealing with colloidal flocculation to explain why pH is affecting the phenomenon.

Particle agglomeration refers to the formation of assemblages in a suspension and represents a mechanism leading to the functional destabilization of colloidal systems. During this process, particles dispersed in the liquid phase stick to each other, and spontaneously form irregular particle assemblages, flocs, or agglomerates. This phenomenon is also referred to as coagulation or flocculation and such a suspension is also called unstable. Particle agglomeration can be induced by adding salts or other chemicals referred to as coagulant or flocculant.
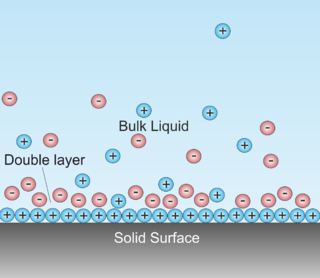
In surface science, a double layer is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The DL refers to two parallel layers of charge surrounding the object. The first layer, the surface charge, consists of ions which are adsorbed onto the object due to chemical interactions. The second layer is composed of ions attracted to the surface charge via the Coulomb force, electrically screening the first layer. This second layer is loosely associated with the object. It is made of free ions that move in the fluid under the influence of electric attraction and thermal motion rather than being firmly anchored. It is thus called the "diffuse layer".
Sedimentation potential occurs when dispersed particles move under the influence of either gravity or centrifugation or electricity in a medium. This motion disrupts the equilibrium symmetry of the particle's double layer. While the particle moves, the ions in the electric double layer lag behind due to the liquid flow. This causes a slight displacement between the surface charge and the electric charge of the diffuse layer. As a result, the moving particle creates a dipole moment. The sum of all of the dipoles generates an electric field which is called sedimentation potential. It can be measured with an open electrical circuit, which is also called sedimentation current.
Colloid-facilitated transport designates a transport process by which colloidal particles serve as transport vector of diverse contaminants in the surface water and in underground water circulating in fissured rocks (limestone, sandstone, granite, ...). The transport of colloidal particles in surface soils and in the ground can also occur, depending on the soil structure, soil compaction, and the particles size, but the importance of colloidal transport was only given sufficient attention during the 1980 years. Radionuclides, heavy metals, and organic pollutants, easily sorb onto colloids suspended in water and that can easily act as contaminant carrier.
Adsorption of polyelectrolytes on solid substrates is a surface phenomenon where long-chained polymer molecules with charged groups bind to a surface that is charged in the opposite polarity. On the molecular level, the polymers do not actually bond to the surface, but tend to "stick" to the surface via intermolecular forces and the charges created by the dissociation of various side groups of the polymer. Because the polymer molecules are so long, they have a large amount of surface area with which to contact the surface and thus do not desorb as small molecules are likely to do. This means that adsorbed layers of polyelectrolytes form a very durable coating. Due to this important characteristic of polyelectrolyte layers they are used extensively in industry as flocculants, for solubilization, as supersorbers, antistatic agents, as oil recovery aids, as gelling aids in nutrition, additives in concrete, or for blood compatibility enhancement to name a few.
The Stöber process is a chemical process used to prepare silica particles of controllable and uniform size for applications in materials science. It was pioneering when it was reported by Werner Stöber and his team in 1968, and remains today the most widely used wet chemistry synthetic approach to silica nanoparticles. It is an example of a sol-gel process wherein a molecular precursor is first reacted with water in an alcoholic solution, the resulting molecules then joining together to build larger structures. The reaction produces silica particles with diameters ranging from 50 to 2000 nm, depending on conditions. The process has been actively researched since its discovery, including efforts to understand its kinetics and mechanism – a particle aggregation model was found to be a better fit for the experimental data than the initially hypothesized LaMer model. The newly acquired understanding has enabled researchers to exert a high degree of control over particle size and distribution and to fine-tune the physical properties of the resulting material in order to suit intended applications.

Particle deposition is the spontaneous attachment of particles to surfaces. The particles in question are normally colloidal particles, while the surfaces involved may be planar, curved, or may represent particles much larger in size than the depositing ones. Deposition processes may be triggered by appropriate hydrodynamic flow conditions and favorable particle-surface interactions. Depositing particles may just form a monolayer which further inhibits additional particle deposition, and thereby one refers to surface blocking. Initially attached particles may also serve as seeds for further particle deposition, which leads to the formation of thicker particle deposits, and this process is termed as surface ripening or fouling. While deposition processes are normally irreversible, initially deposited particles may also detach. The latter process is known as particle release and is often triggered by the addition of appropriate chemicals or a modification in flow conditions.
Polyelectrolytes are charged polymers capable of stabilizing colloidal emulsions through electrostatic interactions. Their effectiveness can be dependent on molecular weight, pH, solvent polarity, ionic strength, and the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB). Stabilized emulsions are useful in many industrial processes, including deflocculation, drug delivery, petroleum waste treatment, and food technology.

Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density. For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.
Dispersion Technology Inc is a scientific instrument manufacturer located in Bedford Hills, New York. It was founded in 1996 by Philip Goetz and Dr. Andrei Dukhin. The company develops and sells analytical instruments intended for characterizing concentrated dispersions and emulsions, complying with the International Standards for acoustic particle sizing ISO 20998 and electroacoustic zeta potential measurement ISO 13099.
References
- ↑ "Peptization and Charge on Colloidal Particles - ChemistryUP". 2021-01-11. Retrieved 2022-12-03.
- ↑ Y. Li, T. J. White; Lim, S. H.; Lim, S.H (2004). "Low-temperature synthesis and microstructural control of titania nano-particles". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 177 (4–5): 1372–1381. Bibcode:2004JSSCh.177.1372L. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2003.11.016.