In economics and finance, present value (PV), also known as present discounted value, is the value of an expected income stream determined as of the date of valuation. The present value is usually less than the future value because money has interest-earning potential, a characteristic referred to as the time value of money, except during times of negative interest rates, when the present value will be equal or more than the future value. Time value can be described with the simplified phrase, "A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow". Here, 'worth more' means that its value is greater than tomorrow. A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because the dollar can be invested and earn a day's worth of interest, making the total accumulate to a value more than a dollar by tomorrow. Interest can be compared to rent. Just as rent is paid to a landlord by a tenant without the ownership of the asset being transferred, interest is paid to a lender by a borrower who gains access to the money for a time before paying it back. By letting the borrower have access to the money, the lender has sacrificed the exchange value of this money, and is compensated for it in the form of interest. The initial amount of borrowed funds is less than the total amount of money paid to the lender.

Saving is income not spent, or deferred consumption. In economics, a broader definition is any income not used for immediate consumption. Saving also involves reducing expenditures, such as recurring costs.

In finance and economics, interest is payment from a debtor or deposit-taking financial institution to a lender or depositor of an amount above repayment of the principal sum, at a particular rate. It is distinct from a fee which the borrower may pay to the lender or some third party. It is also distinct from dividend which is paid by a company to its shareholders (owners) from its profit or reserve, but not at a particular rate decided beforehand, rather on a pro rata basis as a share in the reward gained by risk taking entrepreneurs when the revenue earned exceeds the total costs.
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed. The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, the compounding frequency, and the length of time over which it is lent, deposited, or borrowed.
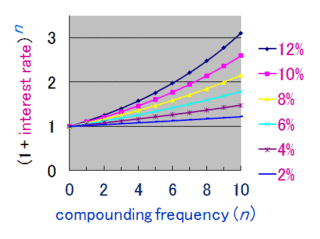
Compound interest is interest accumulated from a principal sum and previously accumulated interest. It is the result of reinvesting or retaining interest that would otherwise be paid out, or of the accumulation of debts from a borrower.
Future value is the value of an asset at a specific date. It measures the nominal future sum of money that a given sum of money is "worth" at a specified time in the future assuming a certain interest rate, or more generally, rate of return; it is the present value multiplied by the accumulation function. The value does not include corrections for inflation or other factors that affect the true value of money in the future. This is used in time value of money calculations.
Eurodollars are U.S. dollars held in time deposit accounts in banks outside the United States, which are not subject to the legal jurisdiction of the U.S. Federal Reserve. Consequently, such deposits are subject to much less regulation than deposits within the U.S. The term was originally applied to U.S. dollar accounts held in banks situated in Europe, but it expanded over the years to cover US dollar accounts held anywhere outside the U.S. Thus, a U.S. dollar-denominated deposit in Tokyo or Beijing would likewise be deemed a Eurodollar deposit. The offshore locations of the Eurodollar make it exposed to potential country risk and economic risk.

A certificate of deposit (CD) is a time deposit sold by banks, thrift institutions, and credit unions in the United States. CDs typically differ from savings accounts because the CD has a specific, fixed term before money can be withdrawn without penalty and generally higher interest rates. The bank expects the CDs to be held until maturity, at which time they can be withdrawn and interest paid.
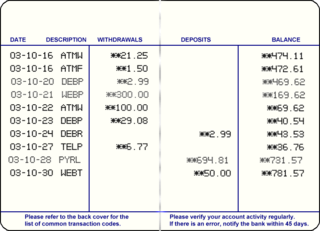
A savings account is a bank account at a retail bank. Common features include a limited number of withdrawals, a lack of cheque and linked debit card facilities, limited transfer options and the inability to be overdrawn. Traditionally, transactions on savings accounts were widely recorded in a passbook, and were sometimes called passbook savings accounts, and bank statements were not provided; however, currently such transactions are commonly recorded electronically and accessible online.

An overdraft occurs when something is withdrawn in excess of what is in a current account. For financial systems, this can be funds in a bank account. In these situations the account is said to be "overdrawn". In the economic system, if there is a prior agreement with the account provider for an overdraft, and the amount overdrawn is within the authorized overdraft limit, then interest is normally charged at the agreed rate. If the negative balance exceeds the agreed terms, then additional fees may be charged and higher interest rates may apply.
In finance, return is a profit on an investment. It comprises any change in value of the investment, and/or cash flows which the investor receives from that investment over a specified time period, such as interest payments, coupons, cash dividends and stock dividends. It may be measured either in absolute terms or as a percentage of the amount invested. The latter is also called the holding period return.
A tax sale is the forced sale of property by a governmental entity for unpaid taxes by the property's owner.

A mortgage loan or simply mortgage, in civil law jurisdictions known also as a hypothec loan, is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged. The loan is "secured" on the borrower's property through a process known as mortgage origination. This means that a legal mechanism is put into place which allows the lender to take possession and sell the secured property to pay off the loan in the event the borrower defaults on the loan or otherwise fails to abide by its terms. The word mortgage is derived from a Law French term used in Britain in the Middle Ages meaning "death pledge" and refers to the pledge ending (dying) when either the obligation is fulfilled or the property is taken through foreclosure. A mortgage can also be described as "a borrower giving consideration in the form of a collateral for a benefit (loan)".
The Public Provident Fund (PPF) is a voluntary savings-cum-tax-reduction social security instrument in India, introduced by the National Savings Institute of the Ministry of Finance in 1968. The scheme's main objective is to mobilize small savings for social security during uncertain times by offering an investment with reasonable returns combined with income tax benefits. The scheme is offered by the Central Government. Balance in the PPF account is not subject to attachment under any order or decree of court under the Government Savings Banks Act, 1873. However, Income Tax & other Government authorities can attach the account for recovering tax dues.
In the investment advisory industry, a management fee is a periodic payment that is paid by an investment fund to the fund's investment adviser for investment and portfolio management services. Often, the fee covers not only investment advisory services, but administrative services as well. Usually, the fee is calculated as a percentage of assets under management.

A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Single deposit is one-time lump sum investment. The Investment is made at the start of the period; grows over the period and matures at the end of the period. Examples of a single deposit are certificates of deposit or Fixed Deposits.
A fixed deposit (FD) is a tenured deposit account provided by banks or non-bank financial institutions which provides investors a higher rate of interest than a regular savings account, until the given maturity date. It may or may not require the creation of a separate account. The term fixed deposit is most commonly used in India and the United States. It is known as a term deposit or time deposit in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and as a bond in the United Kingdom.
A recurring deposit is a special kind of term deposit in India that is offered by Indian banks and India Post which helps people with regular incomes to deposit a fixed amount every month into their recurring deposit account and earn interest at the rate applicable to fixed deposits.
A stable value fund is a type of investment available in 401(k) plans and other defined contribution plans as well as some 529 or tuition assistance plans. Stable value funds are often made available in these plans under a name that intends to describe the nature of the fund. They offer principal preservation, predictable returns, and a rate higher than similar options without proportionately increasing risk. The funds are structured in various ways, but in general they are composed of high quality, diversified fixed income portfolios that are protected against interest rate volatility by contracts from banks and insurance companies. For example, a stable value fund may hold highly rated government or corporate debt, asset-backed securities, residential and commercial mortgage-backed securities, and cash equivalents. Stable value funds are designed to preserve principal while providing steady, positive returns, and are considered one of the lowest risk investment options offered in 401(k) plans. Stable value funds have recently been returning an annualized average of 2.72% as of October 2014, higher than the 0.08% offered by money-market funds, and are offered in 165,000 retirement plans.









