
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins.

The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.

The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The word thenar comes from Ancient Greek θέναρ (thenar) 'palm of the hand'.
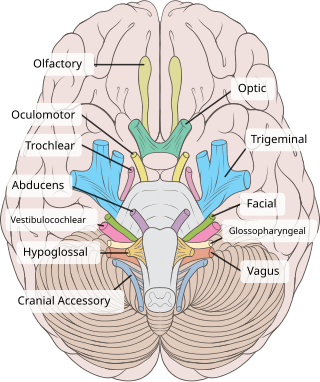
The trochlear nerve, also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates a single muscle - the superior oblique muscle of the eye. Unlike most other cranial nerves, the trochlear nerve is exclusively a motor nerve.

In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (lit. triplet nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name (trigeminal, from Latin tri- 'three', and -geminus 'twin') derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it.

The lesser occipital nerve is a cutaneous spinal nerve of the cervical plexus. It arises from second cervical (spinal) nerve (C2). It innervates the skin of the back of the upper neck and of the scalp posterior to the ear.

In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication.

A dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by afferent nerve fibres from the dorsal root of any given spinal nerve. There are 8 cervical nerves , 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves and 5 sacral nerves. Each of these nerves relays sensation from a particular region of skin to the brain.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

A myotome is the group of muscles that a single spinal nerve innervates. Similarly a dermatome is an area of skin that a single nerve innervates with sensory fibers. Myotomes are separated by myosepta. In vertebrate embryonic development, a myotome is the part of a somite that develops into muscle.

A nerve plexus is a plexus of intersecting nerves. A nerve plexus is composed of afferent and efferent fibers that arise from the merging of the anterior rami of spinal nerves and blood vessels. There are five spinal nerve plexuses, except in the thoracic region, as well as other forms of autonomic plexuses, many of which are a part of the enteric nervous system. The nerves that arise from the plexuses have both sensory and motor functions. These functions include muscle contraction, the maintenance of body coordination and control, and the reaction to sensations such as heat, cold, pain, and pressure. There are several plexuses in the body, including:

The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head.

The upper (superior) subscapular nerve is the first branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The upper subscapular nerve contains axons from the ventral rami of the C5 and C6 cervical spinal nerves. It innervates the superior portion of the subscapularis muscle. The inferior portion of the subscapularis is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve.

The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is the upper-most and largest of the cervical sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. It probably formed by the union of four sympathetic ganglia of the cervical spinal nerves C1–C4. It is the only ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. The SCG innervates numerous structures of the head and neck.

The superior ganglion of the vagus nerve is a sensory ganglion of the peripheral nervous system. It is located within the jugular foramen, where the vagus nerve exits the skull. It is smaller than and proximal to the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve.
A nerve root is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as:

The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve, posterior ramus of spinal nerve, or posterior primary division is the posterior division of a spinal nerve. The dorsal rami provide motor innervation to the deep muscles of the back, and sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior portion of the head, neck and back.
Cutaneous innervation refers to an area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve.

Posterior ramus syndrome, also referred to as thoracolumbar junction syndrome, Maigne syndrome and dorsal ramus syndrome is caused by the unexplained activation of the primary division of a posterior ramus of a spinal nerve. This nerve irritation causes referred pain in a well described tri-branched pattern. The diagnosis is made clinically with the variable presence of four criteria.
















