
The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol, is an international organisation working to achieve safe and seamless air traffic management across Europe. Founded in 1960, Eurocontrol currently has 41 member states and is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. It has several local sites as well, including R&D activities in Brétigny-sur-Orge, France, the Institute of Air Navigation Training (IANS) in Luxembourg, and the Maastricht Upper Area Control Centre (MUAC) in Maastricht, the Netherlands. The organisation employs approximately two thousand people, and operates with an annual budget in excess of half a billion Euro.

The United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research (UNIDIR) was established in 1980 by the United Nations General Assembly to inform States and the global community on questions of international security, and to assist with disarmament efforts so as to facilitate progress toward greater security and economic and social development for all.
An ecomuseum is a museum focused on the identity of a place, largely based on local participation and aiming to enhance the welfare and development of local communities. Ecomuseums originated in France, the concept being developed by Georges Henri Rivière and Hugues de Varine, who coined the term ‘ecomusée’ in 1971. The term "éco" is a shortened form for "écologie", but it refers especially to a new idea of holistic interpretation of cultural heritage, in opposition to the focus on specific items and objects, performed by traditional museums.

The German Marshall Fund of the United States (GMF) is a nonpartisan American public policy think tank and grantmaking institution dedicated to promoting cooperation and understanding between North America and Europe.
The European Association of History Educators (EuroClio) was established in 1992 with the support of the Council of Europe. The NGO works as a European wide facilitator for innovation and progress in history Education. The organisation contributes not only to the development, but also on the actual implementation of regional, national and European long-term projects, which focus on establishing knowledge, experience and expertise in the countries by training and consulting teachers. EuroClio develops teaching materials, builds and maintains professional Networks and acts as advisor to governments, international organisations, NGOs, History Teacher Associations and other Organisations. EuroClio is supported by the Europe for Citizens Programme of the European Union and has, for many years, Official Participatory Status and is part of the EU Stake Holder's Network in Education and Training.

The International Association of students in Agricultural and related Sciences (IAAS) is an international non-profit and non-governmental student society headquartered in Leuven, Belgium. It was founded in 1957 in Tunis by 8 countries. At the moment it is one of the world's biggest student organizations and one of the leading agricultural student associations. IAAS gathers students studying, majoring or researching in agriculture and related areas like environmental sciences, forestry, food science, landscape architecture etc. Its committees are spread in universities in over 50 countries worldwide.

Landscape-scale conservation is a holistic approach to landscape management, aiming to reconcile the competing objectives of nature conservation and economic activities across a given landscape. Landscape-scale conservation may sometimes be attempted because of climate change. It can be seen as an alternative to site based conservation.

The ACP–EU Joint Parliamentary Assembly was created to bring together the elected representatives of the European Union and the elected representatives of the African, Caribbean and Pacific states that have signed the Cotonou Agreement.
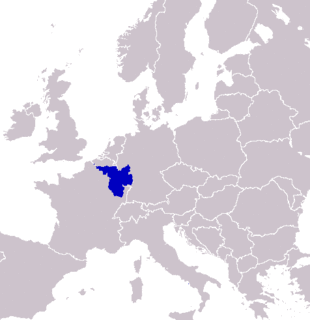
SaarLorLux or Saar-Lor-Lux, a portmanteau of Saarland, Lorraine and Luxembourg, is a euroregion of five regional authorities located in four European states. The term has also been applied to cooperations of several of these authorities or of their subdivisions, administrations, organisations, clubs and people. Member regions represent different political structures: the sovereign state of Luxembourg; Belgium's Walloon region, comprising the French and German speaking parts of Belgium; Lorraine, a region of France; the French départements Moselle and Meurthe-et-Moselle; and the German federated states of Saarland and Rhineland-Palatinate.
The European Policy Institutes Network (EPIN) is a network of 31 think tanks from most EU member states and beyond. Its main focus is on current EU and European political and policy debates. EPIN aims to contribute to the debate on the future of Europe through up to the minute, expert analysis and commentary and through providing easy access to understanding the different national debates. EPIN is coordinated by the Centre for European Policy Studies in Brussels, Belgium.
The International Panorama Council (IPC) is a nongovernmental, not-for-profit organization, subject to Swiss law. It is a global network involving museum directors, managers, artists, restorers and historians who deal with the historical or the contemporary art and media forms of the panorama. The organization comprises members from all over the world who are either representatives of museums and research institutes or private researchers and enthusiasts. The organization was founded in 1992 as the European Panorama Conference in Szeged, Hungary, and renamed in 1998 in Altoetting, Germany, at the International Panorama Conference. Since 2003 the organization is called International Panorama Council. IPC has been a Membership Association since 2010. It is governed by a member-elected Executive Board whose Secretary-General acts as the operational center for the Board’s members.
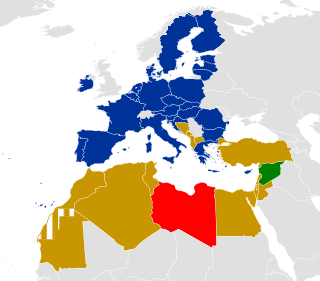
The Union for the Mediterranean is an intergovernmental organization of 42 member states from Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: the 27 EU member states and 15 Mediterranean partner countries from North Africa, Western Asia and Southern Europe. It was founded on 13 July 2008 at the Paris Summit for the Mediterranean, with an aim of reinforcing the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (Euromed) that was set up in 1995 as the Barcelona Process. Its general secretariat is located in Barcelona, Spain.
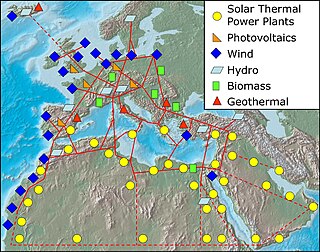
The European super grid is a possible future super grid that would ultimately interconnect the various European countries and the regions around Europe's borders – including North Africa, Kazakhstan, and Turkey – with a high-voltage direct current (HVDC) power grid.
The Platform of European Memory and Conscience is an educational project of the European Union bringing together government institutions and NGOs from EU countries active in research, documentation, awareness raising and education about the crimes of totalitarian regimes. Its membership includes 68 government agencies and NGOs from 15 EU member states and 8 non-EU countries including Ukraine, Albania, Georgia, Iceland, Moldova, the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada. Its members include the Institute of National Remembrance, the Berlin-Hohenschönhausen Memorial, the Stasi Records Agency and the Victims of Communism Memorial Foundation. The platform has offices in Prague and Brussels (formerly). The President of the platform is Łukasz Kamiński, former President of the Polish Institute of National Remembrance.
The Congo Basin Forest Partnership (CBFP) is a non-profit initiative to promote the conservation and responsible management of the Congo Basin's tropical forests. The project aims to improve the techniques and information sharing of involved organizations. It is led by the United States and sponsored by more than 40 international governments and investors.

The Wilfried Martens Centre for European Studies is a think tank and political foundation of the European People's Party (EPP). The Centre strives to impact policy, influence European public opinion, and to be a key platform of cooperation for its centre-right partners. The president of the Martens Centre is former Slovak prime minister Mikuláš Dzurinda.

Coastal & Marine Union (EUCC) is a nonprofit organization with a membership of around 500 institutions, NGOs and experts, in 40 countries. Its network at large involves about 2500 professionals involved in coastal and marine management issues. Founded in 1989 with the aim of promoting coastal management by bridging the gap between scientists, environmentalists, site managers, planners and policy makers, it has grown into the largest network of coastal practitioners and experts in Europe, with 13 National Branches, an International Secretariat in Leiden, and offices in Barcelona (Spain), Biarritz (France), Warnemünde (Germany), Szczecin (Poland), Klaipeda (Lithuania) and Sliema (Malta). EUCC's working area is Europe and its neighbouring regions, especially the Black Sea and the Mediterranean.

EUNIS is the European University Information Systems organization. Their mission is to help member institutions develop their IT landscape by sharing IT knowledge and experience and working together. The association counts more than 2,000 people from 120 different European Institutions and 18 National/Regional Organizations across 36 Countries.
The European Business History Association (EBHA) is an Academic association devoted to business history in Europe. It holds annual congresses and a bi-annual doctoral summer school. It is registered as a Scottish charity. Its constitution states its objectives as "to advance the education of the public concerning all aspects of the history of business and management in Europe and in the environment in which they operate and to promote research into all such aspects". Its aim is the organisation of conferences and seminars, the publication of a newsletter and other materials, the encouragement of research in all aspects of business history, and specifically the promotion of collaborative projects based in several European countries such as The Performance of European Business in the 20th Century project per instance. The association was established to enhance inter-European contacts and promote extra-European links among business historians, to encourage the exchange of business history graduate students and to promote teaching and interest in all such aspects.

The International Scientific Committee on Cultural Landscapes (ISCCL) is a committee of scientific experts on cultural landscapes that works, as a part of the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS), to develop international guidance on cultural landscape documentation and management, and to prepare expert recommendations for prospective World Heritage nominations. The committee functions as a joint effort with members from both ICOMOS and the International Federation of Landscape Architects (IFLA).












