The Rainhill trials was an important competition run from the 6 to 14 October 1829, to test George Stephenson's argument that locomotives would have the best motive power for the then nearly-completed Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR). Ten locomotives were entered, of which five were able to compete, running along a 1 mile (1.6 km) length of level track at Rainhill, in Lancashire.

Stephenson's Rocket is an early steam locomotive of 0-2-2 wheel arrangement. It was built for and won the Rainhill Trials of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR), held in October 1829 to show that improved locomotives would be more efficient than stationary steam engines.

Timothy Hackworth was an English steam locomotive engineer who lived in Shildon, County Durham, England and was the first locomotive superintendent of the Stockton and Darlington Railway.

The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It was also the first railway to rely exclusively on locomotives driven by steam power, with no horse-drawn traffic permitted at any time; the first to be entirely double track throughout its length; the first to have a true signalling system; the first to be fully timetabled; and the first to carry mail.

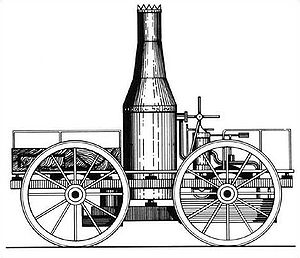
Sans Pareil is a steam locomotive built by Timothy Hackworth which took part in the 1829 Rainhill Trials on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, held to select a builder of locomotives. The name is French and means 'peerless' or 'without equal'.

Rainhill is a village and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of St Helens, Merseyside, England. The population at the 2011 census was 10,853.
John Urpeth Rastrick was one of the first English steam locomotive builders. In partnership with James Foster, he formed Foster, Rastrick and Company, the locomotive construction company that built the Stourbridge Lion in 1829 for export to the Delaware and Hudson Railroad in America. From the 1830s he concentrated on civil engineering with his major project from 1838 being the construction of the London and Brighton Railway.

Cycloped was an early horse-powered locomotive, built by Thomas Shaw Brandreth of Liverpool, which competed unsuccessfully in the Rainhill trials of October 1829.

An 0-2-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is one that has two coupled driving wheels followed by two trailing wheels, with no leading wheels. The configuration was briefly built by Robert Stephenson and Company for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway.

Novelty was an early steam locomotive built by John Ericsson and John Braithwaite to take part in the Rainhill Trials in 1829.

The Midland Railway 115 Class was the third of four classes of 4-2-2 steam locomotive, nicknamed "Spinners", designed by Samuel Waite Johnson. A total of 15 of the class were built between 1896 and 1899. They were capable of reaching speeds of up to 90 miles per hour (145 km/h). One engine, No. 673, is preserved in the National Collection.
R and W Hawthorn Ltd was a locomotive manufacturer in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, from 1817 until 1885.

Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell was an engineering company in Bolton, England. Set up in 1822, the partners became interested in the production of steam locomotives after the Rainhill Trials. The company's first engine was Union, a vertical boiler, 2-2-0 with horizontal cylinders for the Bolton and Leigh Railway of which Hick and Rothwell were promoters and original shareholders, followed by three more locomotives the following year for American railways.
Perseverance most commonly refers to:
The history of rail transport in Great Britain to 1830 covers the period up to the opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, the world's first intercity passenger railway operated solely by steam locomotives. The earliest form of railways, horse-drawn wagonways, originated in Germany in the 16th century. Soon wagonways were also built in Britain. However, the first use of steam locomotives was in Wales. The invention of wrought iron rails, together with Richard Trevithick's pioneering steam locomotive meant that Britain had the first modern railways in the world.
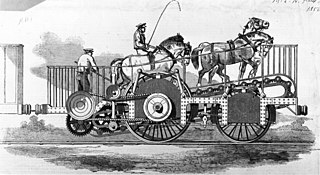
The Impulsoria was a locomotive constructed in 1850 that was powered via a gearbox by two to four horses on a treadmill following a design by Clemente Masserano. It undertook trials in London in 1850 and was exhibited at The Great Exhibition in 1851.

The Cape Government Railways 0-6-0T back-to-back of 1876 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope.
Events from the year 1829 in Scotland.
Timothy Burstall (1776–1860) was a British engineer and pioneer in the field of locomotive construction.