The Personal Emergency Link (PE Link) was established by Senior Citizen Home Safe Association to launch a 24-hour personal emergency link to help the needy in Hong Kong.
The Personal Emergency Link (PE Link) was established by Senior Citizen Home Safe Association to launch a 24-hour personal emergency link to help the needy in Hong Kong.
During an unexpected cold spell in 1996, more than a hundred unattended elderly who lived alone died. In response, the Association were dedicated to render emergency relief and total care service to all elderly and chronic invalids by setting up the PE Link.[ citation needed ]

An epidemic is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in excess of 15 cases per 100,000 people for two consecutive weeks is considered an epidemic.

A firefighter is a rescuer extensively trained in firefighting, primarily to extinguish hazardous fires that threaten life, property, and the environment as well as to rescue people and in some cases or jurisdictions also animals from dangerous situations. Male firefighters are sometimes referred to as firemen.
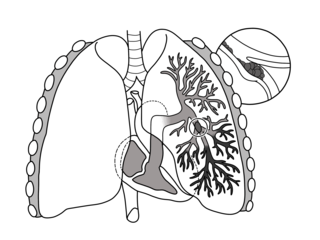
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing in, and coughing up blood. Symptoms of a blood clot in the leg may also be present, such as a red, warm, swollen, and painful leg. Signs of a PE include low blood oxygen levels, rapid breathing, rapid heart rate, and sometimes a mild fever. Severe cases can lead to passing out, abnormally low blood pressure, obstructive shock, and sudden death.

A nursing home is a facility for the residential care of elderly or disabled people. Nursing homes may also be referred to as skilled nursing facility (SNF), long-term care facilities, old people's homes, assisted living facilitiescare homes, rest homes, convalescent homes or convalescent care. Often, these terms have slightly different meanings to indicate whether the institutions are public or private, and whether they provide mostly assisted living, or nursing care and emergency medical care. Nursing homes are used by people who do not need to be in a hospital, but cannot be cared for at home. The nursing home facility nurses have the responsibilities of caring for the patients' medical needs and also the responsibility of being in charge of other employees, depending on their ranks. Most nursing homes have nursing aides and skilled nurses on hand 24 hours a day.

Emergency management is the organization and management of the resources and responsibilities for dealing with all humanitarian aspects of emergencies. The aim is to prevent and reduce the harmful effects of all hazards, including disasters.
A panic alarm is an electronic device designed to assist in alerting somebody in emergency situations where a threat to persons or property exists.
PED, Ped-, or ped may refer to:
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Nursing assessment is the gathering of information about a patient's physiological, psychological, sociological, and spiritual status by a licensed Registered Nurse. Nursing assessment is the first step in the nursing process. A section of the nursing assessment may be delegated to certified nurses aides. Vitals and EKG's may be delegated to certified nurses aides or nursing techs. It differs from a medical diagnosis. In some instances, the nursing assessment is very broad in scope and in other cases it may focus on one body system or mental health. Nursing assessment is used to identify current and future patient care needs. It incorporates the recognition of normal versus abnormal body physiology. Prompt recognition of pertinent changes along with the skill of critical thinking allows the nurse to identify and prioritize appropriate interventions. An assessment format may already be in place to be used at specific facilities and in specific circumstances.

Droperidol is an antidopaminergic drug used as an antiemetic and as an antipsychotic. Droperidol is also often used as a rapid sedative in intensive-care treatment, and where "agitation aggression or violent behavior" are present.

The Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) is a numerical hazard rating that incorporates the use of labels with color developed by the American Coatings Association as a compliance aid for the OSHA Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard.
A medical alarm is an alarm system designed to signal the presence of a hazard requiring urgent attention and to summon emergency medical personnel. Other terms for a medical alarm are Personal Emergency Response System (PERS) or medical alert.
In the Catholic Church, an association of the Christian faithful or simply association of the faithful is a group of baptized persons, clerics or laity or both together, who, according to the 1983 Code of Canon Law, jointly foster a more perfect life or promote public worship or Christian teaching, or who devote themselves to other works of the apostolate.
Johanniter-Unfall-Hilfe e.V., commonly referred to as Die Johanniter, is a voluntary humanitarian organisation affiliated with the Brandenburg Bailiwick of the Order of St John, the German Protestant descendant of the Knights Hospitaller. The organisation was founded in 1952 in Hanover under the leadership of Rudolf Christoph Freiherr von Gersdorff. One of the main reasons for its creation was the rise in injuries and deaths from road traffic accidents. JUH participates in international aid efforts together with its sister organisations in other countries as part of the Johanniter International partnership; it also works with the German Malteser Hilfsdienst, affiliated to the Catholic Sovereign Military Order of Malta. As of 2017 the organisation had 37,000 active volunteers and youth members and around 1,300,000 registered members.
Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are paraprofessionals who assist individuals with physical disabilities, mental impairments, and other health care needs with their activities of daily living (ADLs). UAPs also provide bedside care—including basic nursing procedures—all under the supervision of a registered nurse, licensed practical nurse or other health care professional. UAPs must demonstrate their ability and competence before gaining any expanded responsibilities in a clinical setting. While providing this care, UAPs offer compassion and patience and are part of the patient's healthcare support system. Communication between UAPs and registered nurses (RNs) is key as they are working together in their patients' best interests. The scope of care UAPs are responsible for is delegated by RNs or other clinical licensed professionals.
Lifeline Systems, Inc. was founded in Boston, MA in 1974 by gerontologist Andrew S. Dibner and his wife, sociologist Susan S. Dibner.
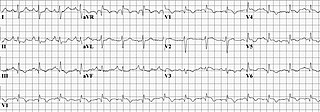
Right heart strain is a medical finding of right ventricular dysfunction where the heart muscle of the right ventricle (RV) is deformed. Right heart strain can be caused by pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary embolism, RV infarction, chronic lung disease, pulmonic stenosis, bronchospasm, and pneumothorax.
ISO 22395:2018Security and resilience -- Community resilience -- Guidelines for supporting vulnerable persons in an emergency, is an international standard developed by ISO/TC 292 Security and resilience and published by the International Organization for Standardization in October 2018. This document is a voluntary guidance standard for supporting vulnerable persons in an emergency.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Peru is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was reported to have spread to Peru on 6 March 2020, when a 25-year-old man who had travelled to Spain, France, and the Czech Republic tested positive. On 15 March 2020, President Martín Vizcarra announced a country-wide lockdown, closing borders, restricting domestic travel, and forbidding nonessential business operations, excluding health facilities, food vendors, pharmacies, and financial institutions. The country currently experiences the highest COVID-19 pandemic death rate in the world.