Related Research Articles

Weird Tales is an American fantasy and horror fiction pulp magazine founded by J. C. Henneberger and J. M. Lansinger in late 1922. The first issue, dated March 1923, appeared on newsstands February 18. The first editor, Edwin Baird, printed early work by H. P. Lovecraft, Seabury Quinn, and Clark Ashton Smith, all of whom went on to be popular writers, but within a year, the magazine was in financial trouble. Henneberger sold his interest in the publisher, Rural Publishing Corporation, to Lansinger, and refinanced Weird Tales, with Farnsworth Wright as the new editor. The first issue to list Wright as editor was dated November 1924. The magazine was more successful under Wright, and despite occasional financial setbacks, it prospered over the next 15 years. Under Wright's control, the magazine lived up to its subtitle, "The Unique Magazine", and published a wide range of unusual fiction.

Your Sinclair, or YS as it was commonly abbreviated, was a commercially published and printed British computer magazine for the Sinclair range of computers, mainly the ZX Spectrum. It was in circulation between 1984 and 1993.

The Strand Magazine was a monthly British magazine founded by George Newnes, composed of short fiction and general interest articles. It was published in the United Kingdom from January 1891 to March 1950, running to 711 issues, though the first issue was on sale well before Christmas 1890. Its immediate popularity is evidenced by an initial sale of nearly 300,000. Sales increased in the early months, before settling down to a circulation of almost 500,000 copies a month, which lasted well into the 1930s.

The Freeman was an American libertarian magazine, formerly published by the Foundation for Economic Education (FEE). It was founded in 1950 by John Chamberlain, Henry Hazlitt, and Suzanne La Follette. The magazine was purchased by a FEE-owned company in 1954, and FEE took over direct control of the magazine in 1956.

Planet Stories was an American pulp science fiction magazine, published by Fiction House between 1939 and 1955. It featured interplanetary adventures, both in space and on some other planets, and was initially focused on a young readership. Malcolm Reiss was editor or editor-in-chief for all of its 71 issues. Planet Stories was launched at the same time as Planet Comics, the success of which probably helped to fund the early issues of Planet Stories. Planet Stories did not pay well enough to regularly attract the leading science fiction writers of the day, but occasionally obtained work from well-known authors, including Isaac Asimov and Clifford D. Simak. In 1952 Planet Stories published Philip K. Dick's first sale, and printed four more of his stories over the next three years.

Michael Philip Batt is an English singer-songwriter, musician, arranger, record producer, director, and conductor. He was formerly the Deputy Chairman of the British Phonographic Industry.
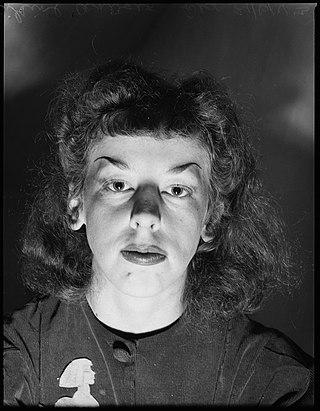
Rosaleen Miriam Norton, who used the name of "Thorn", was an Australian artist and occultist, in the latter capacity adhering to a form of pantheistic / Neopagan Witchcraft largely devoted to the Greek god Pan. She lived much of her later life in the bohemian area of Kings Cross, Sydney, leading her to be termed the "Witch of Kings Cross" in some of the tabloids, and from where she led her own coven of witches.

The Railway Magazine is a monthly British railway magazine, aimed at the railway enthusiast market, that has been published in London since July 1897. As of 2010 it was, for three years running, the railway magazine with the largest circulation in the United Kingdom, having a monthly average sale during 2009 of 34,715. It was published by IPC Media until October 2010, with ISSN 0033-8923, and in 2007 won IPC's 'Magazine of the Year' award. Since November 2010, The Railway Magazine has been published by Mortons of Horncastle.

Joshua Abraham Norton was a resident of San Francisco, California, who in 1859 declared himself "Emperor of these United States" in a proclamation that he signed "Norton I., Emperor of the United States". Commonly known as Emperor Norton, he took the secondary title "Protector of Mexico" in 1866.

Smith's Weekly was an Australian tabloid newspaper published from 1919 to 1950. It was an independent weekly published in Sydney, but read all over Australia.

Zero Tolerance is an extreme music magazine, launched in September 2004 by Lisa Macey and Leon Macey and published by Obdurate Ltd. in the United Kingdom. Published bi-monthly, it can be found on newsstands in the UK, Europe and North America - and is available on newsstands in Australia and specialist retailers in New Zealand and Taiwan. The magazine features a covermount CD. The magazine's tagline is "Extreme Views on Extreme Music by Extreme People".

Oriental Stories, later retitled The Magic Carpet Magazine, was an American pulp magazine published by Popular Fiction and edited by Farnsworth Wright. It was launched in 1930 under the title Oriental Stories as a companion to Popular Fiction's Weird Tales, and carried stories with far eastern settings, including some fantasy. Contributors included Robert E. Howard, Frank Owen, and E. Hoffman Price. The magazine was not successful, and in 1932 publication was paused after the Summer issue. It was relaunched in 1933 under the title The Magic Carpet Magazine, with an expanded editorial policy that now included any story set in an exotic location, including other planets.

Fantastic Adventures was an American pulp fantasy and science fiction magazine, published from 1939 to 1953 by Ziff-Davis. It was initially edited by Raymond A. Palmer, who was also the editor of Amazing Stories, Ziff-Davis's other science fiction title. The first nine issues were in bedsheet format, but in June 1940 the magazine switched to a standard pulp size. It was almost cancelled at the end of 1940, but the October 1940 issue enjoyed unexpectedly good sales, helped by a strong cover by J. Allen St. John for Robert Moore Williams' Jongor of Lost Land. By May 1941 the magazine was on a regular monthly schedule. Historians of science fiction consider that Palmer was unable to maintain a consistently high standard of fiction, but Fantastic Adventures soon developed a reputation for light-hearted and whimsical stories. Much of the material was written by a small group of writers under both their own names and house names. The cover art, like those of many other pulps of the era, focused on beautiful women in melodramatic action scenes. One regular cover artist was H.W. McCauley, whose glamorous "MacGirl" covers were popular with the readers, though the emphasis on depictions of attractive and often partly clothed women did draw some objections.

Super Science Stories was an American pulp science fiction magazine published by Popular Publications from 1940 to 1943, and again from 1949 to 1951. Popular launched it under their Fictioneers imprint, which they used for magazines, paying writers less than one cent per word. Frederik Pohl was hired in late 1939, at 19 years old, to edit the magazine; he also edited Astonishing Stories, a companion science fiction publication. Pohl left in mid-1941 and Super Science Stories was given to Alden H. Norton to edit; a few months later Norton rehired Pohl as an assistant. Popular gave Pohl a very low budget, so most manuscripts submitted to Super Science Stories had already been rejected by the higher-paying magazines. This made it difficult to acquire good fiction, but Pohl was able to acquire stories for the early issues from the Futurians, a group of young science fiction fans and aspiring writers.
Gavin Greenlees was an Australian poet. He was born in Melbourne, Victoria, but later spent most of his time in Sydney, where he became known as a bohemian figure.

Nevill Drury was an English-born Australian editor and publisher, as well as the author of over 40 books on subjects ranging from shamanism and western magical traditions to art, music, and anthropology. His books have been published in 26 countries and in 19 languages.
Rolling Stone Australia is the Australian edition of the United States' Rolling Stone magazine devoted to music, politics, and popular culture, published monthly. The Australian version of Rolling Stone was initially published in 1970 as a supplement in Revolution magazine published by Monash University student Phillip Frazer. It was launched as a fully fledged magazine in 1972 by Frazer and was the longest-surviving international edition of Rolling Stone until its last issue appeared in January 2018.

Analog Science Fiction and Fact is an American science fiction magazine published under various titles since 1930. Originally titled Astounding Stories of Super-Science, the first issue was dated January 1930, published by William Clayton, and edited by Harry Bates. Clayton went bankrupt in 1933 and the magazine was sold to Street & Smith. The new editor was F. Orlin Tremaine, who soon made Astounding the leading magazine in the nascent pulp science fiction field, publishing well-regarded stories such as Jack Williamson's Legion of Space and John W. Campbell's "Twilight". At the end of 1937, Campbell took over editorial duties under Tremaine's supervision, and the following year Tremaine was let go, giving Campbell more independence. Over the next few years Campbell published many stories that became classics in the field, including Isaac Asimov's Foundation series, A. E. van Vogt's Slan, and several novels and stories by Robert A. Heinlein. The period beginning with Campbell's editorship is often referred to as the Golden Age of Science Fiction.
The Criterion was a British literary magazine published from October 1922 to January 1939. The Criterion was, for most of its run, a quarterly journal, although for a period in 1927–28 it was published monthly. It was created by the poet, dramatist, and literary critic T. S. Eliot who served as its editor for its entire run.

Decoration and Glass, was an English-language trade journal, issued from 1935 to 1949, and published in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia.
References
- Nevill Drury, Pan's Daughter: The Magical World of Rosaleen Norton
- Contents list for v4 #2, August–September 1945