
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a federally funded research and development center in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, United States. Founded in 1943, the laboratory is now sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administered by UT–Battelle, LLC.
Tennessine is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Ts and atomic number 117. It is the second-heaviest known element and the penultimate element of the 7th period of the periodic table.

Molecular engineering is an emerging field of study concerned with the design and testing of molecular properties, behavior and interactions in order to assemble better materials, systems, and processes for specific functions. This approach, in which observable properties of a macroscopic system are influenced by direct alteration of a molecular structure, falls into the broader category of “bottom-up” design.

Peter V. Coveney is a Professor of Physical Chemistry, Honorary Professor of Computer Science, and the Director of the Centre for Computational Science (CCS) and Associate Director of the Advanced Research Computing Centre at University College London (UCL). He is also a Professor of Applied High Performance Computing at University of Amsterdam (UvA) and Professor Adjunct at the Yale School of Medicine, Yale University. He is a Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering and Member of Academia Europaea. Coveney is active in a broad area of interdisciplinary research including condensed matter physics and chemistry, materials science, as well as life and medical sciences in all of which high performance computing plays a major role. The citation about Coveney on his election as a FREng says: Coveney "has made outstanding contributions across a wide range of scientific and engineering fields, including physics, chemistry, chemical engineering, materials, computer science, high performance computing and biomedicine, much of it harnessing the power of supercomputing to conduct original research at unprecedented space and time scales. He has shown outstanding leadership across these fields, manifested through running multiple initiatives and multi-partner interdisciplinary grants, in the UK, Europe and the US. His achievements at national and international level in advocacy and enablement are exceptional".

Denis James Evans, is an Australian scientist who is an Emeritus Professor at the Australian National University and Honorary Professor at The University of Queensland. He is widely recognised for his contributions to nonequilibrium thermodynamics and nonequilibrium statistical mechanics and the simulation of nonequilibrium fluids.
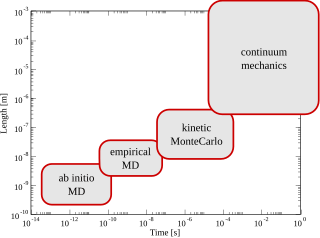
Multiscale modeling or multiscale mathematics is the field of solving problems that have important features at multiple scales of time and/or space. Important problems include multiscale modeling of fluids, solids, polymers, proteins, nucleic acids as well as various physical and chemical phenomena.

Thomas Zacharia is an Indian-born American computer scientist. He received his bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from National Institute of Technology, Karnataka in 1980 and a master's degree in Materials Science from the University of Mississippi in 1984. He obtained his doctoral degree from Clarkson University in 1987.

Michael Lawrence KleinNAS is Laura H. Carnell Professor of Science and director of the Institute for Computational Molecular Science in the college of science and technology at Temple University in Philadelphia, US. He was previously the Hepburn Professor of Physical Science in the Center for Molecular Modeling at the University of Pennsylvania. Currently, he serves as the dean of the college of science and technology and has since 2013.
Michael W. Deem is an American engineer, scientist, inventor, and entrepreneur. Deem received his B.S. in chemical engineering from the California Institute of Technology in 1991 and his Ph.D. in chemical engineering from the University of California at Berkeley in 1994. His thesis research was in statistical mechanics and disordered materials with David Chandler. He did postdoctoral research at Harvard University in physics with David R. Nelson. Deem joined the faculty at University of California, Los Angeles, in 1996 and rose to the rank of associate professor of chemical engineering. From 2002 to 2020 Deem was the John W. Cox Professor of Biochemical and Genetic Engineering and professor of physics and astronomy at Rice University in Houston, Texas. Deem was the founding director of the graduate program in systems, synthetic, and physical biology at Rice University, 2012-2014. From 2014 to 2017, Deem served as the chair of the bioengineering department at Rice University.

Keith E. Gubbins is a British-born American chemical engineer who is the W.H. Clark Distinguished University Professor of Chemical Engineering at North Carolina State University in Raleigh, North Carolina. He is perhaps best known as one of the originators of statistical associating fluid theory (SAFT).
Massively Parallel Monte Carlo (MPMC) is a Monte Carlo method package primarily designed to simulate liquids, molecular interfaces, and functionalized nanoscale materials. It was developed originally by Jon Belof and is now maintained by a group of researchers in the Department of Chemistry and SMMARTT Materials Research Center at the University of South Florida. MPMC has been applied to the scientific research challenges of nanomaterials for clean energy, carbon sequestration, and molecular detection. Developed to run efficiently on the most powerful supercomputing platforms, MPMC can scale to extremely large numbers of CPUs or GPUs. Since 2012, MPMC has been released as an open-source software project under the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 3, and the repository is hosted on GitHub.

Emily Ann Carter is the Gerhard R. Andlinger Professor in Energy and the Environment and a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering, the Andlinger Center for Energy and the Environment, and the Program in Applied and Computational Mathematics at Princeton University. She has been on the faculty at Princeton since 2004, including as serving as Princeton's Dean of the School of Engineering and Applied Science from 2016 to 2019. She moved to UCLA to serve as executive vice chancellor and provost and a distinguished professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, before returning to Princeton in December 2021. Carter is a theorist and computational scientist whose work combines quantum mechanics, solid-state physics, and applied mathematics.

Biman Bagchi is an Indian scientist currently serving as a SERB-DST National Science Chair Professor and Honorary Professor at the Solid State and Structural Chemistry Unit of the Indian Institute of Science. He is a theoretical physical chemist and biophysicist known for his research in the area of statistical mechanics; particularly in the study of phase transition and nucleation, solvation dynamics, mode-coupling theory of electrolyte transport, dynamics of biological macromolecules, protein folding, enzyme kinetics, supercooled liquids and protein hydration layer. He is an elected fellow of the Indian National Science Academy, the Indian Academy of Sciences, The World Academy of Sciences and an International honorary member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. Along with several scientific articles, he has authored three books, (i) Molecular Relaxation in Liquids, (ii) Water in Biological and Chemical Processes: From Structure and Dynamics to Function, and (iii) Statistical Mechanics for Chemistry and Materials Science.

Sergei V. Kalinin is a corporate fellow at the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences (CNMS) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). He is also the Weston Fulton Professor at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the University of Tennessee-Knoxville.
Kenneth M. Merz Jr. is an American biochemist and molecular biologist currently the Joseph Zichis Chair and a distinguished university professor at Michigan State University and editor-in-chief of American Chemical Society's Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. A highly cited expert in his field, his research interests are in computational chemistry and biology and computer-aided drug design (CADD). His group has been involved in developing the widely using AMBER suite of programs for simulating chemical and biological systems and the QUICK program for quantum chemical calculations.
Franz-Josef Ulm is a structural engineer, an engineering scientist and a professor since 1999. He is Professor of Civil & Environmental Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the Faculty Director of the Concrete Sustainability Hub (CSHub@MIT). He is credited for discovering the nanogranular structure of Calcium-Silicate-Hydrates (C-S-H), the binding phase of concrete, and for the development of concepts of nanoengineering of concrete which combine advanced nanomechanics experiments with molecular simulation results. He speaks up for an environmental sustainable engineering, with “greener” concrete with lower CO2 footprint, to reduce the carbon footprint of concrete; to enhance concrete's resilience; and reduce its impact on global warming.

Clarice Evone Phelps (née Salone) is an American nuclear chemist researching the processing of radioactive transuranic elements at the US Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). She was part of ORNL's team that collaborated with the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research to discover tennessine. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recognizes her as the first African-American woman to be involved with the discovery of a chemical element.

James L. Skinner is an American theoretical chemist. He is the Joseph O. and Elizabeth S. Hirschfelder Professor Emeritus at the University Wisconsin-Madison. He is also a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of the Welch Foundation. Most recently, Skinner was the Crown Family Professor of Molecular Engineering, professor of chemistry, director of the Water Research Initiative and deputy dean for faculty affairs of the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago. Skinner is recognized for his contributions to the fields of theoretical chemistry, nonequilibrium statistical mechanics, linear and nonlinear spectroscopy of liquids, amorphous and crystalline solids, surfaces, proteins, and supercritical fluids. Skinner is the co-author of over 230 peer-reviewed research articles.
Clare McCabe is an American chemical engineer who is Cornelius Vanderbilt Chair of Engineering and professor of engineering at Vanderbilt University. She was elected Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 2019. Her research makes use of molecular modelling to understand the properties of biological systems, fluids and nanomaterials.
Judith A. Harrison is an American physical chemist and tribologist who is known for pioneering numerical methods that incorporate chemical reactions into modeling studies. She is a professor in the Department of Chemistry at the United States Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland.












