
An automated teller machine (ATM) or cash machine is an electronic telecommunications device that enables customers of financial institutions to perform financial transactions, such as cash withdrawals, deposits, funds transfers, balance inquiries or account information inquiries, at any time and without the need for direct interaction with bank staff.

A personal identification number (PIN), or sometimes redundantly a PIN number or PIN code, is a numeric passcode used in the process of authenticating a user accessing a system.
A transaction account, also called a checking account, chequing account, current account, demand deposit account, or share draft account at credit unions, is a deposit account held at a bank or other financial institution. It is available to the account owner "on demand" and is available for frequent and immediate access by the account owner or to others as the account owner may direct. Access may be in a variety of ways, such as cash withdrawals, use of debit cards, cheques (checks) and electronic transfer. In economic terms, the funds held in a transaction account are regarded as liquid funds. In accounting terms, they are considered as cash.
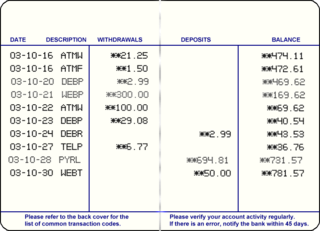
A passbook or bankbook is a paper book used to record bank or building society transactions on a deposit account.
Seven Bank, Ltd. is a Japanese bank. It is a subsidiary of Seven & I Holdings Co., Ltd.. Until October 11, 2005, it was IY Bank, taking its initials from Ito Yokado. Conducting its business primarily through the Internet, IY Bank has automatic teller machines in 7-Eleven convenience stores and Ito Yokado general-merchandise stores in Japan, and on April 27, 2005, opened its first branch with live staff. Customers with accounts at certain banks can process transactions at IY terminals at no cost; IY collects a handling fee from customers at other banks.
A Talking ATM is a type of automated teller machine (ATM) that provides audible instructions so that persons who cannot read an ATM screen can independently use the machine. All audible information is delivered privately through a standard headphone jack on the face of the machine or a separately attached telephone handset. Information is delivered to the customer either through pre-recorded sound files or via text-to-speech speech synthesis.

Payment cards are part of a payment system issued by financial institutions, such as a bank, to a customer that enables its owner to access the funds in the customer's designated bank accounts, or through a credit account and make payments by electronic acc transfer and access automated teller machines (ATMs). Such cards are known by a variety of names including bank cards, ATM cards, client cards, key cards or cash cards.

An ATM card is a payment card or dedicated payment card issued by a financial institution which enables a customer to access their financial accounts via its and others' automated teller machines (ATMs) and to make approved point of purchase retail transactions ATM cards are not credit cards or debit cards. ATM cards are payment card size and style plastic cards with a magnetic stripe and/or a plastic smart card with a chip that contains a unique card number and some security information such as an expiration date or CVVC (CVV). ATM cards are known by a variety of names such as bank card, MAC, client card, key card or cash card, among others. Other payment cards, such as debit cards and credit cards can also function as ATM cards. Charge and proprietary cards cannot be used as ATM cards. The use of a credit card to withdraw cash at an ATM is treated differently to a point of sale transaction, usually attracting interest charges from the date of the cash withdrawal. Interbank networks allow the use of ATM cards at ATMs of private operators and financial institutions other than those of the institution that issued the cards.

The Malaysian Electronic Payment System (MEPS) is an interbank network service provider in Malaysia. In August 2017, MEPS merged with Malaysian Electronic Clearing Corporation Sdn Bhd (MyClear) to form Payments Network Malaysia Sdn Bhd (PayNet).

A bank teller is an employee of a bank whose responsibilities include the handling of customer cash and negotiable instruments. In some places, this employee is known as a cashier or customer representative. Most teller jobs require experience with handling cash and a high school diploma. Most banks provide on-the-job training.
ATM usage fees are the fees that many banks and interbank networks charge for the use of their automated teller machines (ATMs). In some cases, these fees are assessed solely for non-members of the bank; in other cases, they apply to all users.
The Global ATM Alliance is a joint venture of several major international banks that allows customers of their banks to use their automated teller machine (ATM) card or debit card at another bank within the alliance with no international ATM access fees. Other fees, such as an international transaction or foreign currency fee, may still apply for some account holders. Participating banks include Australasia, Asia, Europe, Africa, North America, and South America.

A branch, banking center or financial center is a retail location where a bank, credit union, or other financial institution offers a wide array of face-to-face and automated services to its customers.

Automated cash handling is the process of dispensing, counting and tracking cash in a bank, retail, check cashing, payday loan / advance, casino or other business environment through specially designed hardware and software for the purposes of loss prevention, theft deterrence and reducing management time for oversight of cash drawer (till) operations.

National Financial Switch (NFS) is the largest network of shared automated teller machines (ATMs) in India. It was designed, developed and deployed by the Institute for Development and Research in Banking Technology (IDRBT) in 2004, with the goal of inter-connecting the ATMs in the country and facilitating convenience banking. It is run by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
Cashline is the name of the Automated Teller Machine (ATM) network run by the Royal Bank of Scotland. Its beginnings date back to 1967 when the Royal Bank installed its first ATM in its offices in the West End of Edinburgh. Initially the service offered only basic deposit services to a small select number of customers, but by 1977 the familiar cash withdrawal service to current account holders was launched under the Cashline name.

Automated teller machines (ATMs) are targets for fraud, robberies and other security breaches. In the past, the main purpose of ATMs was to deliver cash in the form of banknotes, and to debit a corresponding bank account. However, ATMs are becoming more complicated and they now serve numerous functions, thus becoming a high priority target for robbers and hackers.

Multicaixa (MCX) is the one and only brand name for debit cards issued in Angola, and also the brand name for the one and only interbank network of automated teller machines and point of sales terminals for electronic payments. While the ATMs and the POS terminals are owned by the supporting bank, the network is operated by EMIS, and the Multicaixa cards of any bank are accepted at the same terms at any Multicaixa ATM or POS terminal. This is regulated by the national law on Angolan payment systems, the BNA directive No. 9/2011 of 13 October on the regulation of bank payment cards, and various other laws and directives regulating the Angolan financial system. The ATMs accept Multicaixa debit cards and Visa credit cards. EMIS prepares the acceptance of other international credit card brands like MasterCard.

Tillie the All-Time Teller was one of the first ATMs, run by the First National Bank of Atlanta and considered to be one of the most successful ATMs in the banking industry. Tillie the All-Time Teller had a picture of a smiling blonde girl on the front of the machine to suggest it was user-friendly, had an apparent personality, and could greet people by name. Many banks hired women dressed as this person to show their customers how to use Tillie the All-Time Teller.

Dinarak is a mobile wallet, money transfer, electronic bill payment, funds disbursement service, licensed by the Central Bank of Jordan under the JoMoPay national switch and launched in late 2015 as Dinarak wallet as part of the Jordanian central bank's efforts to advocate financial inclusion for the un-banked segment of the Jordanian population. Dinarak allows users to deposit, withdraw, transfer money and pay for goods and services via their mobile phone. The service can be accessed by Dinarak mobile application.













