Audio signal processing is a subfield of signal processing that is concerned with the electronic manipulation of audio signals. As audio signals may be represented in either digital or analog format, processing may occur in either domain. Analog processors operate directly on the electrical signal, while digital processors operate mathematically on the digital representation of that signal.
Frequency modulation synthesis is a form of sound synthesis where the frequency of a waveform, called the carrier, is changed by modulating its frequency with a modulator. The frequency of an oscillator is altered "in accordance with the amplitude of a modulating signal."
Program, programme, or programming may refer to:
Phase modulation (PM) is a modulation pattern for conditioning communication signals for transmission. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. Phase modulation is one of the two principal forms of angle modulation, together with frequency modulation.

Robert Arthur Moog was an American engineer and pioneer of electronic music. He was the founder of Moog Music and the inventor of the first commercial synthesizer, the Moog synthesizer. This was followed by a more portable model, the Minimoog, described as the most famous and influential synthesizer in history.
A software synthesizer, also known as a softsynth, or software instrument is a computer program, or plug-in that generates digital audio, usually for music. Computer software that can create sounds or music is not new, but advances in processing speed now allow softsynths to accomplish the same tasks that previously required the dedicated hardware of a conventional synthesizer. Softsynths are usually cheaper and more portable than dedicated hardware, and easier to interface with other music software such as music sequencers.
Synthesis or synthesize may also refer to:

The Yamaha DX7 is a synthesizer manufactured by the Yamaha Corporation from 1983 to 1989. It was the first commercially successful digital synthesizer and became one of the bestselling synthesizers in history, selling over 200,000 units.

A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscillation frequency. Consequently, a VCO can be used for frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) by applying a modulating signal to the control input. A VCO is also an integral part of a phase-locked loop.

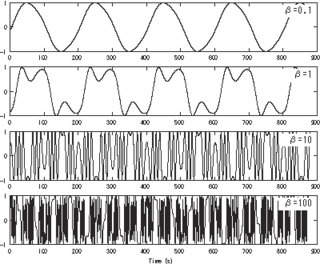
Low-frequency oscillation (LFO) is an electronic frequency which is usually below 20 Hz and creates a rhythmic pulse or sweep. This pulse or sweep is often used to modulate synthesizers, delay lines and other audio equipment in order to create effects used in the production of electronic music. Audio effects such as vibrato, tremolo and phasing are examples. The abbreviation LFO is also very often used to refer to low-frequency oscillators themselves.
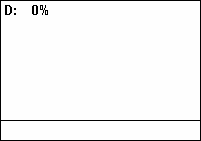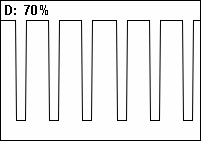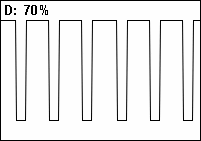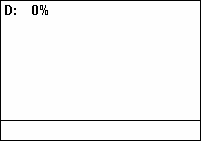
A pulse wave or pulse train is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform that includes square waves and similarly periodic but asymmetrical waves. It is a term common to synthesizer programming, and is a typical waveform available on many synthesizers. The exact shape of the wave is determined by the duty cycle of the oscillator. In many synthesizers, the duty cycle can be modulated for a more dynamic timbre.
The pulse wave is also known as the rectangular wave, the periodic version of the rectangular function.

The microKORG is a MIDI-capable virtual analog synthesizer/vocoder from Korg featuring DSP analog modelling. The synthesizer is built in such a way that it is essentially a Korg MS-2000 with programmable step arpeggiator, a less advanced vocoder, lack of motion sequencing, lack of an XLR microphone input, and in a smaller case with fewer real-time control knobs.

A synthesizer or synthesiser is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals that may be converted to sound. Synthesizers may imitate traditional musical instruments such as piano, flute, vocals, or natural sounds such as ocean waves; or generate novel electronic timbres. They are often played with a musical keyboard, but they can be controlled via a variety of other devices, including music sequencers, instrument controllers, fingerboards, guitar synthesizers, wind controllers, and electronic drums. Synthesizers without built-in controllers are often called sound modules, and are controlled via USB, MIDI or CV/gate using a controller device, often a MIDI keyboard or other controller.
A frequency synthesizer is an electronic circuit that generates a range of frequencies from a single reference frequency. Frequency synthesizers are used in many modern devices such as radio receivers, televisions, mobile telephones, radiotelephones, walkie-talkies, CB radios, cable television converter boxes satellite receivers, and GPS systems. A frequency synthesizer may use the techniques of frequency multiplication, frequency division, direct digital synthesis, frequency mixing, and phase-locked loops to generate its frequencies. The stability and accuracy of the frequency synthesizer's output are related to the stability and accuracy of its reference frequency input. Consequently, synthesizers use stable and accurate reference frequencies, such as those provided by crystal oscillators.
Italo dance, also known as nu Italo disco, nu-Italo or just Italo, is an offshoot of the Eurodance music genre, which was especially popular in Europe in the late 1990s to the early 2000s.

The CZ series is a family of low-cost phase distortion synthesizers produced by Casio in the mid-1980s. Eight models of CZ synthesizers were released: the CZ-101, CZ-230S, CZ-1000, CZ-2000S, CZ-2600S, CZ-3000, CZ-5000, and the CZ-1. Additionally, the home-keyboard model CT-6500 used 48 phase distortion presets from the CZ line. The CZ synthesizers' price at the time of their introduction made programmable synthesizers affordable enough to be purchased by garage bands. Yamaha soon introduced their own low-cost digital synthesizers, including the DX-21 (1985) and Yamaha DX100, in light of the CZ series' success.

The Teenage Engineering OP-1 is a synthesizer, sampler and sequencer designed and manufactured by the Stockholm-based company Teenage Engineering. The OP-1 is Teenage Engineering's first product; it was released in 2011 following an introduction at the NAMM Show. It is also considered their core product.
In sound and music, an envelope describes how a sound changes over time. Envelopes may relate to elements such as amplitude (volume), filters (frequencies), or pitch. For example, a piano key, when struck and held, creates a near-immediate initial sound which gradually decreases in volume to zero. Envelope generators are common features of synthesizers, samplers, and other electronic musical instruments.











