Related Research Articles

Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise.

A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three phases: an inhalation, a forced exhalation against a closed glottis, and a violent release of air from the lungs following opening of the glottis, usually accompanied by a distinctive sound.
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an increased risk of lung infections. Complications may include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cirrhosis, neonatal jaundice, or panniculitis.

Rhinitis, also known as coryza, is irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the nose. Common symptoms are a stuffy nose, runny nose, sneezing, and post-nasal drip.
Beta2-adrenergic agonists, also known as adrenergic β2 receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that act on the β2 adrenergic receptor. Like other β adrenergic agonists, they cause smooth muscle relaxation. β2 adrenergic agonists' effects on smooth muscle cause dilation of bronchial passages, vasodilation in muscle and liver, relaxation of uterine muscle, and release of insulin. They are primarily used to treat asthma and other pulmonary disorders, such as Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alternated depending on whether someone is breathing in or out. It is termed "non-invasive" because it is delivered with a mask that is tightly fitted to the face or around the head, but without a need for tracheal intubation. While there are similarities with regard to the interface, NIV is not the same as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which applies a single level of positive airway pressure throughout the whole respiratory cycle; CPAP does not deliver ventilation but is occasionally used in conditions also treated with NIV.

Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.

Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleurae, pleural cavity, the nerves and muscles of respiration. Respiratory diseases range from mild and self-limiting, such as the common cold, influenza, and pharyngitis to life-threatening diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, tuberculosis, acute asthma, lung cancer, and severe acute respiratory syndromes, such as COVID-19. Respiratory diseases can be classified in many different ways, including by the organ or tissue involved, by the type and pattern of associated signs and symptoms, or by the cause of the disease.
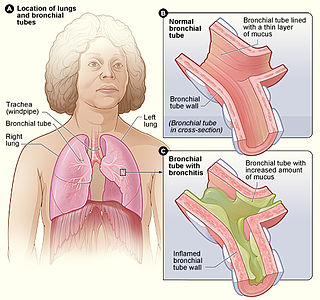
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi in the lungs that causes coughing. Symptoms include coughing up sputum, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Bronchitis can be acute or chronic.
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness is a state characterised by easily triggered bronchospasm.

Roflumilast, sold under the trade name Daxas among others, is a drug that acts as a selective, long-acting inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4). It has anti-inflammatory effects and is used as an orally administered drug for the treatment of inflammatory conditions of the lungs such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
An endotype is a subtype of a health condition, which is defined by a distinct functional or pathobiological mechanism. This is distinct from a phenotype, which is any observable characteristic or trait of a disease, such as development, biochemical or physiological properties without any implication of a mechanism. It is envisaged that patients with a specific endotype present themselves within phenotypic clusters of diseases.

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mucus. COPD progressively worsens, with everyday activities such as walking or dressing becoming difficult. While COPD is incurable, it is preventable and treatable.
The Dutch hypothesis provides one of several biologically plausible explanations for the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a progressive disease known to be aetiologically linked to environmental insults such as tobacco smoke.
Ravi Kalhan is the director of the Asthma and COPD Program at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and Northwestern Memorial Hospital.

Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces (pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the alveoli and they replace the spongy lung parenchyma. This reduces the total alveolar surface available for gas exchange leading to a reduction in oxygen supply for the blood. Emphysema usually affects the middle aged or older population because it takes time to develop with the effects of tobacco smoking, and other risk factors. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a genetic risk factor that may lead to the condition presenting earlier.
MFAP4 is an extracellular matrix protein encoded by the MFAP4 gene. It is part of the MFAP family of proteoglycans, which are involved in cell adhesion, intercellular interactions and the assembly and/or maintenance of elastic fibres.

Stephanie J. London is an American epidemiologist and physician-scientist specializing in environmental health, respiratory diseases, and genetic susceptibility. She is the deputy chief of the epidemiology branch at the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.

Smoker’s macrophages are alveolar macrophages whose characteristics, including appearance, cellularity, phenotypes, immune response, and other functions, have been affected upon the exposure to cigarettes. These altered immune cells are derived from several signaling pathways and are able to induce numerous respiratory diseases. They are involved in asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancer. Smoker’s macrophages are observed in both firsthand and secondhand smokers, so anyone exposed to cigarette contents, or cigarette smoke extract (CSE), would be susceptible to these macrophages, thus in turns leading to future complications.

Pulmonary drug delivery is a route of administration in which patients use an inhaler to inhale their medications and drugs are absorbed into the bloodstream via the lung mucous membrane. This technique is most commonly used in the treatment of lung diseases, for example, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Different types of inhalers include metered-dose inhalers (MDI), dry powder inhalers (DPI), soft mist inhalers (SMI) and nebulizers. The rate and efficacy of pulmonary drug delivery are affected by drug particle properties, breathing patterns and respiratory tract geometry.
References
- ↑ Scheuermann, Richard H.; Ceusters, Werner; Smith, Barry (2009-03-01). "Toward an Ontological Treatment of Disease and Diagnosis". Summit on Translational Bioinformatics. 2009: 116–120. PMC 3041577 . PMID 21347182.
- ↑ Russell, CD; Baillie, JK (April 2017). "Treatable traits and therapeutic targets: Goals for systems biology in infectious disease". Current Opinion in Systems Biology. 2: 140–146. doi:10.1016/j.coisb.2017.04.003. ISSN 2452-3100. PMC 7185428 . PMID 32363252.
- ↑ Miravitlles, Marc; Calle, Myriam; Soler-Cataluña, Juan José (2012-03-01). "Clinical Phenotypes of COPD: Identification, Definition and Implications for Guidelines". Archivos de Bronconeumología (English ed.). 48 (3): 86–98. doi:10.1016/j.arbr.2012.01.003. PMID 22196477.
- ↑ Bel, Elisabeth H. (January 2004). "Clinical phenotypes of asthma". Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine. 10 (1): 44–50. doi:10.1097/00063198-200401000-00008. PMID 14749605.