Related Research Articles

In genetics, the phenotype is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting the phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book The Extended Phenotype suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddisfly larva cases and beaver dams as "extended phenotypes".

Nematomorpha are a phylum of parasitoid animals superficially similar to nematode worms in morphology, hence the name. Most species range in size from 50 to 100 millimetres, reaching 2 metres (79 in) in extreme cases, and 1 to 3 millimetres in diameter. Horsehair worms can be discovered in damp areas, such as watering troughs, swimming pools, streams, puddles, and cisterns. The adult worms are free-living, but the larvae are parasitic on arthropods, such as beetles, cockroaches, mantises, orthopterans, and crustaceans. About 351 freshwater species are known and a conservative estimate suggests that there may be about 2000 freshwater species worldwide. The name "Gordian" stems from the legendary Gordian knot. This relates to the fact that nematomorphs often coil themselves in tight balls that resemble knots.
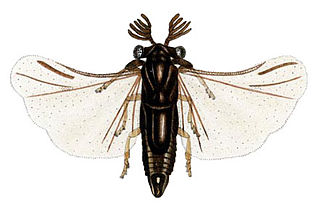
The Strepsiptera are an order of insects with eleven extant families that include about 600 described species. They are endoparasites of other insects, such as bees, wasps, leafhoppers, silverfish, and cockroaches. Females of most species never emerge from the host after entering its body, finally dying inside it. The early-stage larvae do emerge because they must find an unoccupied living host, and the short-lived males must emerge to seek a receptive female in her host. They are believed to be most closely related to beetles, from which they diverged 300–350 million years ago, but do not appear in the fossil record until the mid-Cretaceous around 100 million years ago.

The Extended Phenotype is a 1982 book by the evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins, in which the author introduced a biological concept of the same name. The book’s main idea is that phenotype should not be limited to biological processes such as protein biosynthesis or tissue growth, but extended to include all effects that a gene has on its environment, inside or outside the body of the individual organism.
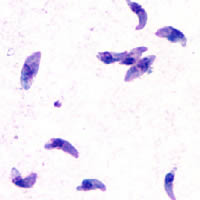
Toxoplasma gondii is a parasitic protozoan that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, T. gondii is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids are the only known definitive hosts in which the parasite may undergo sexual reproduction.

The parrotbills are a family, Paradoxornithidae, of passerine birds that are primarily native to East, Southeast and South Asia, with a single species in western North America, though feral populations exist elsewhere. They are generally small birds that inhabit reedbeds, forests and similar habitats. The traditional parrotbills feed mainly on seeds, e.g. of grasses, to which their robust bill, as the name implies, is well-adapted. Members of the family are usually non-migratory.

The three-spined stickleback is a fish native to most inland and coastal waters north of 30°N. It has long been a subject of scientific study for many reasons. It shows great morphological variation throughout its range, ideal for questions about evolution and population genetics. Many populations are anadromous and very tolerant of changes in salinity, a subject of interest to physiologists. It displays elaborate breeding behavior and it can be social making it a popular subject of inquiry in fish ethology and behavioral ecology. Its antipredator adaptations, host-parasite interactions, sensory physiology, reproductive physiology, and endocrinology have also been much studied. Facilitating these studies is the fact that the three-spined stickleback is easy to find in nature and easy to keep in aquaria.

Brood parasitism is a subclass of parasitism and phenomenon and behavioural pattern of certain animals, brood parasites, that rely on others to raise their young. The strategy appears among birds, insects and fish. The brood parasite manipulates a host, either of the same or of another species, to raise its young as if it were its own, usually using egg mimicry, with eggs that resemble the host's.

Spinochordodes tellinii is a parasitic nematomorph hairworm whose larvae develop in grasshoppers and crickets. This parasite is able to influence its host's behavior: once the parasite is grown, it causes its grasshopper host to jump into water, where the grasshopper will likely drown. The parasite then leaves its host; the adult worm lives and reproduces in water. S. tellinii does not influence its host to actively seek water over large distances, but only when it is already close to water.

Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompasses all types of environmentally induced changes that may or may not be permanent throughout an individual's lifespan.
An obligate parasite or holoparasite is a parasitic organism that cannot complete its life-cycle without exploiting a suitable host. If an obligate parasite cannot obtain a host it will fail to reproduce. This is opposed to a facultative parasite, which can act as a parasite but does not rely on its host to continue its life-cycle. Obligate parasites have evolved a variety of parasitic strategies to exploit their hosts. Holoparasites and some hemiparasites are obligate.
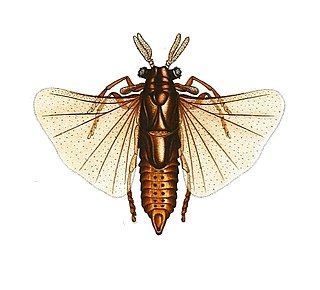
Xenos vesparum is a parasitic insect species of the order Strepsiptera that are endoparasites of paper wasps in the genus Polistes that was first described in 1793. Like other members of this family, X. vesparum displays a peculiar lifestyle, and demonstrates extensive sexual dimorphism.

Schistocephalus solidus is a tapeworm of fish, fish-eating birds and rodents. This hermaphroditic parasite belongs to the Eucestoda subclass, of class Cestoda. This species has been used to demonstrate that cross-fertilization produces a higher infective success rate than self-fertilization.

Parasitic castration is the strategy, by a parasite, of blocking reproduction by its host, completely or in part, to its own benefit. This is one of six major strategies within parasitism.
Host–parasite coevolution is a special case of coevolution, where a host and a parasite continually adapt to each other. This can create an evolutionary arms race between them. A more benign possibility is of an evolutionary trade-off between transmission and virulence in the parasite, as if it kills its host too quickly, the parasite will not be able to reproduce either. Another theory, the Red Queen hypothesis, proposes that since both host and parasite have to keep on evolving to keep up with each other, and since sexual reproduction continually creates new combinations of genes, parasitism favours sexual reproduction in the host.
Behavior-altering parasites are parasites with two or more hosts, capable of causing changes in the behavior of one of their hosts to enhance their transmission, sometimes directly affecting the hosts' decision-making and behavior control mechanisms. They do this by making the intermediate host, where they may reproduce asexually, more likely to be eaten by a predator at a higher trophic level which becomes the definitive host where the parasite reproduces sexually; the mechanism is therefore sometimes called parasite increased trophic facilitation or parasite increased trophic transmission. Examples can be found in bacteria, protozoa, viruses, and animals. Parasites may also alter the host behaviour to increase protection of the parasites or their offspring; the term bodyguard manipulation is used for such mechanisms.
Experimental Parasitology is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of parasitology. It is published by Elsevier and was established in 1951. The main topics covered are the physiology, immunology, biochemistry, and molecular biology of eukaryotic parasites, and the interaction between the parasite and its host, including chemotherapy against parasites. The editors-in-chief are Anton Aebischer and Bernd Kalinna.
Bassettia pallida is a species of gall wasp found in the Southern United States. This species was described by American entomologist William Harris Ashmead in 1896. B. pallida reproduces asexually in galls it induces on oak trees. The parasite Euderus set, a eulophid wasp, has B. pallida as a host and manipulates its behavior.

Parasites appear frequently in biology-inspired fiction from ancient times onwards, with a flowering in the nineteenth century. These include intentionally disgusting alien monsters in science fiction films, often with analogues in nature. Authors and scriptwriters have, to some extent, exploited parasite biology: lifestyles including parasitoid, behaviour-altering parasite, brood parasite, parasitic castrator, and many forms of vampire are found in books and films. Some fictional parasites, like Count Dracula and Alien's Xenomorphs, have become well known in their own right.
Mark Erno Hauber is an American ornithologist and Endowed Professor at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. His research considers the development of avian recognition systems.
References
- ↑ Encyclopedia of evolutionary biology . 14 April 2016. ISBN 978-0-12-800426-5.
- ↑ Grécias, Lucie; Valentin, Julie; Aubin-Horth, Nadia (15 March 2018). "Testing the parasite mass burden effect on alteration of host behaviour in the Schistocephalus-stickleback system" (PDF). The Journal of Experimental Biology. 221 (6): jeb174748. doi: 10.1242/jeb.174748 . PMID 29444843.