Dr. Philip 'Flip' Nissen Froelich, Jr. is an American academic oceanographic scientist, whose research uses biogeochemistry dynamics to address human impacts on the world's oceans.
Dr. Philip 'Flip' Nissen Froelich, Jr. is an American academic oceanographic scientist, whose research uses biogeochemistry dynamics to address human impacts on the world's oceans.
Froelich graduated from Duke University in 1968. [1] He obtained a Ph.D. from the University of Rhode Island in 1979. [2]
He is a Francis Eppes Professor of Oceanography at Florida State University, where he is involved in the interdisciplinary Biogeochemical Dynamics Program. He is also affiliated with the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory. [3]

The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, nonprofit research and higher education facility dedicated to the study of marine science and engineering.

The Scripps Institution of Oceanography (SIO) is the center for oceanography and Earth science at the University of California, San Diego. Its main campus is located in La Jolla, with additional facilities in Point Loma.

Philip EMEA Gwalior
The Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science is the University of Miami's academic and research institution for the study of oceanography, atmospheric, and earth sciences. The Rosenstiel School is located 8 miles (13 km) east from the University of Miami's main Coral Gables campus on Virginia Key in Miami, Florida, United States.
The Florida Institute of Oceanography (FIO), located on the campus of the University of South Florida St. Petersburg, is an entity of the State University System of Florida that works collaboratively with 32 institutions and agencies from across the state that support marine research.
Robert Edward Ulanowicz is an American theoretical ecologist and philosopher of Polish descent who in his search for a unified theory of ecology has formulated a paradigm he calls Process Ecology. He was born September 17, 1943, in Baltimore, Maryland.

R/P FLIP was an open ocean research platform owned by the U.S. Office of Naval Research (ONR) and operated by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. The platform was 108 meters (355 ft) long and was designed to partially flood and pitch backward 90°, resulting in only the front 17 meters (55 ft) of the platform pointing up out of the water, with bulkheads becoming decks. When flipped, most of the buoyancy for the platform was provided by water at depths below the influence of surface waves, hence FLIP was stable and mostly immune to wave action, similar to a spar buoy. At the end of a mission, compressed air was pumped into the ballast tanks in the flooded section and the platform, which had no propulsion, returned to its horizontal position so it could be towed to a new location. The platform was frequently mistaken for a capsized ocean transport ship.

Walter Heinrich Munk was an American physical oceanographer. He was one of the first scientists to bring statistical methods to the analysis of oceanographic data. Munk worked on a wide range of topics, including surface waves, geophysical implications of variations in the Earth's rotation, tides, internal waves, deep-ocean drilling into the sea floor, acoustical measurements of ocean properties, sea level rise, and climate change. His work won awards including the National Medal of Science, the Kyoto Prize, and induction to the French Legion of Honour.

Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute is a non-profit oceanographic institution operated by Florida Atlantic University in Fort Pierce, Florida, United States. Founded in 1971 as non-profit research organization, the institution was transferred to FAU in 2007.

The Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences of McGill University is the largest university atmospheric-oceanic sciences group in Canada. In 2012, it has 11 Faculty and 6 Associate Faculty members, 5 support staff, 14 research associates and postdoctoral fellows, and 31 graduate students. It is known worldwide, in particular for weather radar research and Arctic studies. It has operated the second oldest weather observatory in Canada since 1862.
Doron Nof was an American oceanographer. He was the Distinguished Nansen Professor of Physical Oceanography at Florida State University.

Melvin Ernest Stern was a U.S. academic oceanographer who focused on fluid dynamics. He served as the Ekman Professor of Oceanography at Florida State University and was an elected member of both the National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts & Sciences. Dr. Stern was the first researcher in the world to mathematically describe salt fingering, a phenomenon produced by Double diffusive convection.

John Broward Culpepper was a leader in university education in Florida. He was designated a Great Floridan in 2000.

Michael Selwyn Longuet-Higgins FRS was a British mathematician and oceanographer at the Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics (DAMTP), Cambridge University, England and Institute for Nonlinear Science, University of California, San Diego, USA. He was the younger brother of H. Christopher Longuet-Higgins.
Adrian Edmund Gill FRS was an Australian meteorologist and oceanographer best known for his textbook Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics. Gill was born in Melbourne, Australia, and worked at Cambridge, serving as Senior Research Fellow from 1963 to 1984. His father was Edmund Gill, geologist, palaeontologist and curator at the National Museum of Victoria.
Gilbert L. Voss was an American conservationist and oceanographer. He was one of the main persons behind the establishment of John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park in Key Largo, Florida and he spoke out successfully against several proposed real estate developments that might have threatened the ecology of the Florida Keys.

Mark Whitney Hulsbeck is an American professional aquanaut. He serves as an Oceanographic Operations Field Manager and research diver for the Aquarius Reef Base, the world's only undersea research laboratory, operated by Florida International University. Hulsbeck is nicknamed "Otter".
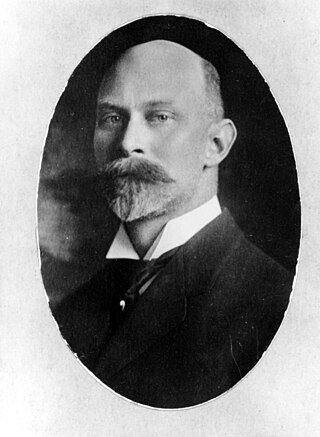
Thomas Wayland Vaughan was an American geologist and oceanographer. He worked with the United States Geological Survey and United States National Museum, investigating the geology of the West Indies, Panama Canal Zone, and the eastern coast of North America. In 1924 Vaughan became director of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and held the post until his retirement in 1936. His research work concentrated on the study of corals and coral reefs, the investigation of larger foraminifera, and oceanography.

Nancy Helen Marcus was an American biologist and oceanographer. During her graduate studies, Marcus became known as an expert on copepod ecology and evolutionary biology. She began her career as a postdoctoral fellow at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution where she studied copepod dormancy and its implications for marine aquaculture. She continued her field research as a professor of oceanography and later as the director of the Florida State University Marine Laboratory (FSU). During this time, Marcus was elected as a Fellow of the Association for Women in Science and the American Association for the Advancement of Science and served as the president of the Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography. As the president, she led efforts to increase education activities and increase the endowment fund.