Related Research Articles

Brian Wilson Kernighan is a Canadian computer scientist.
A spreadsheet is a computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in cells of a table. Each cell may contain either numeric or text data, or the results of formulas that automatically calculate and display a value based on the contents of other cells. The term spreadsheet may also refer to one such electronic document.

The Michigan Terminal System (MTS) is one of the first time-sharing computer operating systems. Developed in 1967 at the University of Michigan for use on IBM S/360-67, S/370 and compatible mainframe computers, it was developed and used by a consortium of eight universities in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom over a period of 33 years.
SIMSCRIPT is a free-form, English-like general-purpose simulation language conceived by Harry Markowitz and Bernard Hausner at the RAND Corporation in 1962. It was implemented as a Fortran preprocessor on the IBM 7090 and was designed for large discrete event simulations. It influenced Simula.

Business process modeling (BPM) in business process management and systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current business processes may be analyzed, improved, and automated. BPM is typically performed by business analysts, who provide expertise in the modeling discipline; by subject matter experts, who have specialized knowledge of the processes being modeled; or more commonly by a team comprising both. Alternatively, the process model can be derived directly from events' logs using process mining tools.
In software engineering, profiling is a form of dynamic program analysis that measures, for example, the space (memory) or time complexity of a program, the usage of particular instructions, or the frequency and duration of function calls. Most commonly, profiling information serves to aid program optimization, and more specifically, performance engineering.

Jack R. Edmonds is an American-born and educated computer scientist and mathematician who lived and worked in Canada for much of his life. He has made fundamental contributions to the fields of combinatorial optimization, polyhedral combinatorics, discrete mathematics and the theory of computing. He was the recipient of the 1985 John von Neumann Theory Prize.
A discrete-event simulation (DES) models the operation of a system as a (discrete) sequence of events in time. Each event occurs at a particular instant in time and marks a change of state in the system. Between consecutive events, no change in the system is assumed to occur; thus the simulation time can directly jump to the occurrence time of the next event, which is called next-event time progression.

Mark Burgess is an independent researcher and writer, formerly professor at Oslo University College in Norway and creator of the CFEngine software and company, who is known for work in computer science in the field of policy-based configuration management.

A. Alan B. Pritsker was an American engineer, pioneer in the field of Operations research, and one of the founders of the field of computer simulation. Over the course of a fifty-five-year career, he made numerous contributions to the field of simulation and to the larger fields of industrial engineering and operations research.
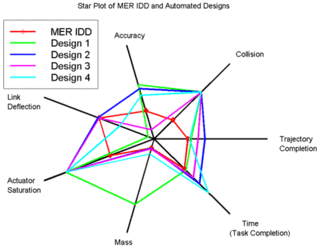
A radar chart is a graphical method of displaying multivariate data in the form of a two-dimensional chart of three or more quantitative variables represented on axes starting from the same point. The relative position and angle of the axes is typically uninformative, but various heuristics, such as algorithms that plot data as the maximal total area, can be applied to sort the variables (axes) into relative positions that reveal distinct correlations, trade-offs, and a multitude of other comparative measures.
Web-based simulation (WBS) is the invocation of computer simulation services over the World Wide Web, specifically through a web browser. Increasingly, the web is being looked upon as an environment for providing modeling and simulation applications, and as such, is an emerging area of investigation within the simulation community.

AnyLogic is a multimethod simulation modeling tool developed by The AnyLogic Company. It supports agent-based, discrete event, and system dynamics simulation methodologies. AnyLogic is cross-platform simulation software that works on Windows, macOS and Linux. AnyLogic is used to simulate: markets and competition, healthcare, manufacturing, supply chains and logistics, retail, business processes, social and ecosystem dynamics, defense, project and asset management, pedestrian dynamics and road traffic, IT, and aerospace.
GoldSim is dynamic, probabilistic simulation software developed by GoldSim Technology Group. This general-purpose simulator is a hybrid of several simulation approaches, combining an extension of system dynamics with some aspects of discrete event simulation, and embedding the dynamic simulation engine within a Monte Carlo simulation framework.

Danny Cohen was an Israeli American computer scientist specializing in computer networking. He was involved in the ARPAnet project and helped develop various fundamental applications for the Internet. He was one of the key figures behind the separation of TCP and IP ; this allowed the later creation of UDP.
Philip S. Yu is an American computer scientist and Professor in Information Technology at the University of Illinois at Chicago, known for his work in the field of data mining.

Parametric design is a design method where features are shaped according to algorithmic processes, in contrast to being designed directly. In this method, parameters and rules determine the relationship between design intent and design response. The term parametric refers to input parameters fed into the algorithms.
Thomas J. (Tom) Schriber is an American academic, and Professor of Technology and Operations at the Ross School of Business. He is particularly known for his work on "Simulation using General Purpose Simulation System (GPSS)."
GASP, GASP II and GASP IV are FORTRAN-based simulation languages. GASP stands for General Activity Simulation Program.
Richard Walter Conway is an American industrial engineer and computer scientist who is the Emerson Electric Company Professor of Manufacturing Management, Emeritus in the Johnson Graduate School of Management at Cornell University. Conway has spent his entire academic career, both as a student and a professor, at Cornell and has held faculty positions at Cornell in several different areas: industrial engineering, operations research, computer science, and management science. He is especially known for his work and publications in foundational questions about computer simulation methodology; in writing about production scheduling theory; in developing computer languages and language compilers, including the widely used PL/C dialect of IBM's PL/I language; in authoring or co-authoring textbooks about computer programming; and in developing simulation software for manufacturing. He was also the first director of the Office of Computing Services at Cornell.
References
- ↑ James R. Wilson; David Goldsman (October 2000). "A. Alan B. Pritsker".
- 1 2 Richard E. Nance (May 21, 2013). "Philip J. Kiviat".
- ↑ Tinsfeldt, Mette; Jensen, Per Anker (2014). "Value Adding Space Management in Higher Education". Proceedings of CIB Facilities Management Conference 2014: 369–380.
- ↑ Yu-Ting Wong; Kai-Yin Cheng; Sheng-Jie Luo; Bing-Yu Chen (2010). Visualizing Information Evolution (PDF). Proceedings of Computer Graphics Workshop 2010. Hsinchu, Taiwan: National Chiao Tung University.
- ↑ when used in Excel
- ↑ Kenneth W. Kolence (1973). "The Software Empiricist". ACM SIGMETRICS Performance Evaluation Review. 2 (2): 31–36. doi:10.1145/1113644.1113647. S2CID 18600391.
Dr. Philip J. Kiviat suggested .. a circular graph, using .. I recommend they be called "Kiviat Plots" or "Kiviat Graphs" to recognize ..
- 1 2 Ernie Page; John Tufarolo (December 19, 1997). "Philip J. Kiviat Interview".
- ↑ "American computer executive"