Phoenician may refer to:
- Phoenicia, an ancient civilization
- Phoenician alphabet
- Phoenicianism, a form of Lebanese nationalism
- Phoenician language
- List of Phoenician cities
Phoenician may refer to:
Cassiopeia or Cassiopea may refer to:
Phoenix most often refers to:
Tarshish occurs in the Hebrew Bible with several uncertain meanings, most frequently as a place far across the sea from Phoenicia and the Land of Israel. Tarshish was said to have exported vast quantities of important metals to Phoenicia and Israel. The same place name occurs in the Akkadian inscriptions of Assyrian king Esarhaddon and also on the Phoenician inscription of the Nora Stone in Sardinia; its precise location was never commonly known, and was eventually lost in antiquity. Legends grew up around it over time so that its identity has been the subject of scholarly research and commentary for more than two thousand years.
In Greek mythology, Syrus or Syros may refer to a person or an animal:
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Tyrus may refer to:–
MIM or Mim may refer to:
Ptolemais may refer to:

Phoenicianism is a nationalist and right-wing political viewpoint and identity in Lebanon that sees the ancient Phoenician civilization as the primary ethnic and cultural foundation of the modern Lebanese people, as opposed to later Arab immigration. This perspective opposes Pan-Arabism and resists Syrian influences in Lebanon's political and cultural spheres.
Phoenicus or Phoinikous may refer to:
Heliopolis may refer to:
Tell may refer to:
Marat may refer to:
Carne or Carné is a surname, and may refer to
Phoenicia, or Phœnicia, was an ancient civilization in the north of Canaan in parts of Lebanon, Syria, and Palestine.
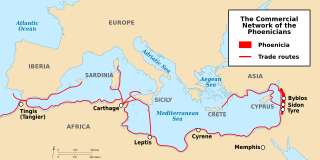
The culture of the ancient Phoenicians was one of the first to have had a significant effect on the history of wine. Phoenicia was a civilization centered in current day Lebanon. Between 1550 BC and 300 BC, the Phoenicians developed a maritime trading culture that expanded their influence from the Levant to North Africa, the Greek Isles, Sicily, and the Iberian Peninsula. Through contact and trade, they spread not only their alphabet but also their knowledge of viticulture and winemaking, including the propagation of several ancestral varieties of the Vitis vinifera species of wine grapes.

Phoenicia, or Phœnicia, was an ancient Semitic thalassocratic civilization originating in the coastal strip of the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenicians expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel in modern Israel covering the entire coast of modern Lebanon. Beyond their homeland, the Phoenicians extended through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula.
Syria Phoenicia may refer to:
PHNX or phnx may refer to:

Carne or Carnos was an ancient Phoenician city opposite to the island-city Arados, north of Tartus. Carne was the port of Arados on the mainland, the only port city of its dependencies.