History
The group was originally organized to work on PeerGuardian, a program Leonard created in 2003 in response to the shutdown of the Audiogalaxy file sharing site. [1] The name Methlabs came from Leonard's handle, 'method'. In late 2004, the group added Blocklist.org, a website designed to allow users to interactively manage and block the IP addresses of certain organisations and companies.
Phoenix Labs was formed in September 2005 following a dispute between members of the Methlabs team. According to a Phoenix Labs press release, a "series of threats and incidents" forced most of the group out of the methlabs.org website. [2] The press release attributed this action to a team member with responsibility for finances and server control. Based on information from other participants, internet news sources identified this person as using the nickname "Cerberius", but Cerberius reportedly disputed their charges of domain hijacking and described the situation as a "revolt". Method and a few members of the group decided they could not get the methlabs.com domain back, and decided took suggestions for a new name on their IRC channel. A user named 'bizzyb0t' came up with the name "phoenixlabs.org" to represent the group being reborn "rising from the ashes".
Samba is a free software re-implementation of the SMB networking protocol, and was originally developed by Andrew Tridgell. Samba provides file and print services for various Microsoft Windows clients and can integrate with a Microsoft Windows Server domain, either as a Domain Controller (DC) or as a domain member. As of version 4, it supports Active Directory and Microsoft Windows NT domains.
SourceForge is a web service that offers software consumers a centralized online location to control and manage open-source software projects and research business software. It provides source code repository hosting, bug tracking, mirroring of downloads for load balancing, a wiki for documentation, developer and user mailing lists, user-support forums, user-written reviews and ratings, a news bulletin, micro-blog for publishing project updates, and other features.
A Domain Name System blocklist, Domain Name System-based blackhole list, Domain Name System blacklist (DNSBL) or real-time blackhole list (RBL) is a service for operation of mail servers to perform a check via a Domain Name System (DNS) query whether a sending host's IP address is blacklisted for email spam. Most mail server software can be configured to check such lists, typically rejecting or flagging messages from such sites.

Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol is an open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML, it enables the near-real-time exchange of structured data between two or more network entities. Designed to be extensible, the protocol offers a multitude of applications beyond traditional IM in the broader realm of message-oriented middleware, including signalling for VoIP, video, file transfer, gaming and other uses.
WASTE is a peer-to-peer and friend-to-friend protocol and software application developed by Justin Frankel at Nullsoft in 2003 that features instant messaging, chat rooms, and file browsing/sharing capabilities. The name WASTE is a reference to Thomas Pynchon's novel The Crying of Lot 49. In the novel, W.A.S.T.E. is an underground postal service.
An anonymous P2P communication system is a peer-to-peer distributed application in which the nodes, which are used to share resources, or participants are anonymous or pseudonymous. Anonymity of participants is usually achieved by special routing overlay networks that hide the physical location of each node from other participants.
The computer file hosts is an operating system file that maps hostnames to IP addresses. It is a plain text file. Originally a file named HOSTS.TXT was manually maintained and made available via file sharing by Stanford Research Institute for the ARPANET membership, containing the hostnames and address of hosts as contributed for inclusion by member organizations. The Domain Name System, first described in 1983 and implemented in 1984, automated the publication process and provided instantaneous and dynamic hostname resolution in the rapidly growing network. In modern operating systems, the hosts file remains an alternative name resolution mechanism, configurable often as part of facilities such as the Name Service Switch as either the primary method or as a fallback method.
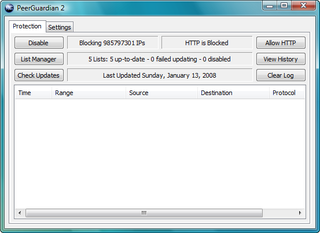
PeerGuardian is a free and open source program developed by Phoenix Labs (software). It is capable of blocking incoming and outgoing connections based on IP blacklists. The aim of its use was to block peers on the same torrent download from any visibility of your own peer connection using IP lists. The system is also capable of blocking custom ranges, depending upon user preferences.

The Pirate Bay is an online index of digital content of entertainment media and software. Founded in 2003 by Swedish think tank Piratbyrån, The Pirate Bay allows visitors to search, download, and contribute magnet links and torrent files, which facilitate peer-to-peer file sharing among users of the BitTorrent protocol.
MoBlock is free software for blocking connections to and from a specified range of hosts. Moblock is an IP address filtering program for Linux that is similar to PeerGuardian for Microsoft Windows. Its development has been stopped in favor of Phoenix Labs' official PeerGuardian Linux and parts of its code have been merged in PeerGuardian Linux.

VirusTotal is a website created by the Spanish security company Hispasec Sistemas. Launched in June 2004, it was acquired by Google in September 2012. The company's ownership switched in January 2018 to Chronicle, a subsidiary of Google.

In computing, a blacklist, disallowlist, blocklist, or denylist is a basic access control mechanism that allows through all elements, except those explicitly mentioned. Those items on the list are denied access. The opposite is a whitelist, allowlist, or passlist, in which only items on the list are let through whatever gate is being used. A greylist contains items that are temporarily blocked until an additional step is performed.

PeerBlock is a free and open-source personal firewall that blocks packets coming from, or going to, a maintained list of black listed hosts. PeerBlock is the Windows successor to the software PeerGuardian. It blocks incoming and outgoing connections to IP addresses that are included on blacklists, and to addresses specified by the user. PeerBlock mainly uses blacklists provided by iblocklist.com.
Torrent poisoning is intentionally sharing corrupt data or data with misleading file names using the BitTorrent protocol. This practice of uploading fake torrents is sometimes carried out by anti-infringement organisations as an attempt to prevent the peer-to-peer (P2P) sharing of copyrighted content, and to gather the IP addresses of downloaders.
WebRTC is a free and open-source project providing web browsers and mobile applications with real-time communication (RTC) via application programming interfaces (APIs). It allows audio and video communication and streaming to work inside web pages by allowing direct peer-to-peer communication, eliminating the need to install plugins or download native apps.
Internet censorship circumvention, also referred to as going over the wall or scientific browsing in China, is the use of various methods and tools to bypass internet censorship.
SmartScreen is a cloud-based anti-phishing and anti-malware component included in several Microsoft products:

A response policy zone (RPZ) is a mechanism to introduce a customized policy in Domain Name System servers, so that recursive resolvers return possibly modified results. By modifying a result, access to the corresponding host can be blocked.

Snowflake is a software package for assisting others in circumventing internet censorship by relaying data requests. Snowflake relay nodes are meant to be created by people in countries where Tor and Snowflake are not blocked. People under censorship then use a Snowflake client, packaged with the Tor Browser or Onion Browser, to access the Tor network, using Snowflake relays as proxy servers. Access to the Tor network can in turn give access to other blocked services. A Snowflake node can be created by either installing a browser extension, installing a stand-alone program, or browsing a webpage with an embedded Snowflake relay. The node runs whenever the browser or program is connected to the internet.







