
Drawing is a form of visual art in which an artist uses instruments to mark paper or other two-dimensional surface. Drawing instruments include graphite pencils, pen and ink, various kinds of paints, inked brushes, colored pencils, crayons, charcoal, chalk, pastels, erasers, markers, styluses, and metals. Digital drawing is the act of drawing on graphics software in a computer. Common methods of digital drawing include a stylus or finger on a touchscreen device, stylus- or finger-to-touchpad, or in some cases, a mouse. There are many digital art programs and devices.

Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing, and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication.

Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine ; however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph. Except in the case of monotyping, all printmaking processes have the capacity to produce identical multiples of the same artwork, which is called a print. Each print produced is considered an "original" work of art, and is correctly referred to as an "impression", not a "copy". However, impressions can vary considerably, whether intentionally or not. Master printmakers are technicians who are capable of printing identical "impressions" by hand. Historically, many printed images were created as a preparatory study, such as a drawing. A print that copies another work of art, especially a painting, is known as a "reproductive print".

Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for storage or transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properties of image data to provide superior results compared with generic data compression methods which are used for other digital data.

A storyboard is a graphic organizer that consists of illustrations or images displayed in sequence for the purpose of pre-visualizing a motion picture, animation, motion graphic or interactive media sequence. The storyboarding process, in the form it is known today, was developed at Walt Disney Productions during the early 1930s, after several years of similar processes being in use at Walt Disney and other animation studios.

Digital art refers to any artistic work or practice that uses digital technology as part of the creative or presentation process. It can also refer to computational art that uses and engages with digital media.
Graphics are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of data, as in design and manufacture, in typesetting and the graphic arts, and in educational and recreational software. Images that are generated by a computer are called computer graphics.

Digital printing is a method of printing from a digital-based image directly to a variety of media. It usually refers to professional printing where small-run jobs from desktop publishing and other digital sources are printed using large-format and/or high-volume laser or inkjet printers.

A penciller is an artist who works on the creation of comic books, graphic novels, and similar visual art forms, with a focus on the initial pencil illustrations, usually in collaboration with other artists, who provide inks, colors and lettering in the book, under the supervision of an editor.

A category of fine art, graphic art covers a broad range of visual artistic expression, typically two-dimensional, i.e. produced on a flat surface. The term usually refers to the arts that rely more on line, color or tone, especially drawing and the various forms of engraving; it is sometimes understood to refer specifically to printmaking processes, such as line engraving, aquatint, drypoint, etching, mezzotint, monotype, lithography, and screen printing. Graphic art mostly includes calligraphy, photography, painting, typography, computer graphics, and bindery. It also encompasses drawn plans and layouts for interior and architectural designs.

Digital illustration or computer illustration is the use of digital tools to produce images under the direct manipulation of the artist, usually through a pointing device such as a graphics tablet or, less commonly, a mouse. It is distinguished from computer-generated art, which is produced by a computer using mathematical models created by the artist. It is also distinct from digital manipulation of photographs, in that it is an original construction "from scratch". Photographic elements such as background or texture may be incorporated into such works, but they are not necessarily the primary basis.

Hyperrealism is a genre of painting and sculpture resembling a high-resolution photograph. Hyperrealism is considered an advancement of photorealism by the methods used to create the resulting paintings or sculptures. The term is primarily applied to an independent art movement and art style in the United States and Europe that has developed since the early 1970s. Carole Feuerman is the forerunner in the hyperrealism movement along with Duane Hanson and John De Andrea.

Fun Home: A Family Tragicomic is a 2006 graphic memoir by the American cartoonist Alison Bechdel, author of the comic strip Dykes to Watch Out For. It chronicles the author's childhood and youth in rural Pennsylvania, United States, focusing on her complex relationship with her father. The book addresses themes of sexual orientation, gender roles, suicide, emotional abuse, dysfunctional family life, and the role of literature in understanding oneself and one's family.

Scanography, more commonly referred to as scanner photography, is the process of capturing digitized images of objects for the purpose of creating printable art using a flatbed "photo" scanner with a CCD array capturing device. Fine art scanography differs from traditional document scanning by using atypical objects, often three-dimensional, as well as from photography, due to the nature of the scanner's operation.
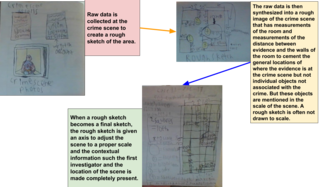
Forensic art is any art used in law enforcement or legal proceedings. Forensic art is used to assist law enforcement with the visual aspects of a case, often using witness descriptions and video footage.

Collage is a technique of art creation, primarily used in the visual arts, but in music too, by which art results from an assemblage of different forms, thus creating a new whole.

Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are digital photographs, traditional photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo retouching, using tools such as an airbrush to modify photographs or editing illustrations with any traditional art medium. Graphic software programs, which can be broadly grouped into vector graphics editors, raster graphics editors, and 3D modelers, are the primary tools with which a user may manipulate, enhance, and transform images. Many image editing programs are also used to render or create computer art from scratch. The term "image editing" usually refers only to the editing of 2D images, not 3D ones.
Art historical photo archives are collections of reproductions of works of art that document paintings, drawings, prints, sculpture, architecture and sometimes installation photos. They are essential resource tools for the study of art history. Image collections deepen understanding of specific objects of art and the careers of individual artists as they also provide the means for a comparative approach to the study of artists’ works, national schools and period styles. The documentation that accompanies the images can also reveal patterns of art collecting, art market fluctuations and the changeable nature of public opinion. Photo archives build their collections and gather documentation for the works of art they record through purchases, gifts and photography campaigns. Information about ownership, condition, attribution, and subject identification is recorded at the time of acquisition and is frequently updated.

The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics, photography, video, filmmaking, design, crafts and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual art, and textile arts also involve aspects of visual arts as well as arts of other types. Also included within the visual arts are the applied arts such as industrial design, graphic design, fashion design, interior design and decorative art.

Multi-image is the now largely obsolete practice and business of using 35mm slides (diapositives) projected by single or multiple slide projectors onto one or more screens in synchronization with an audio voice-over or music track. Multi-image productions are also known as multi-image slide presentations, slide shows and diaporamas and are a specific form of multimedia or audio-visual production.


















