
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure.
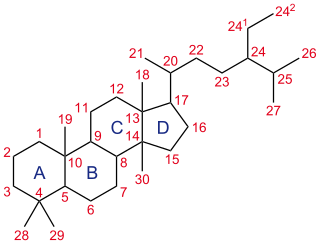
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Peptoids, or poly-N-substituted glycines, are a class of biochemicals known as biomimetics that replicate the behavior of biological molecules. Peptidomimetics are recognizable by side chains that are appended to the nitrogen atom of the peptide backbone, rather than to the α-carbons.

Beta-peptides (β-peptides) are peptides derived from β-amino acids, in which the amino group is attached to the β-carbon (i.e. the carbon two atoms away from the carboxylate group). The parent β-amino acid is β-alanine (H2NCH2CH2CO2H), a common natural substance, but most examples feature substituents in place of one or more C-H bonds. β-peptides usually do not occur in nature. β-peptide-based antibiotics are being explored as ways of evading antibiotic resistance. Early studies in this field were published in 1996 by the group of Dieter Seebach and that of Samuel Gellman.

Physalis is a genus of approximately 75 to 90 flowering plants in the nightshade family (Solanaceae), which are native to the Americas and Australasia. At least 46 species are endemic to Mexico. Cultivated and weedy species have been introduced worldwide. A defining feature of Physalis is a large, papery husk derived from the calyx, which partly or fully encloses the fruit. Many species bear edible fruit, and some species are cultivated.

Aromatase, also called estrogen synthetase or estrogen synthase, is an enzyme responsible for a key step in the biosynthesis of estrogens. It is CYP19A1, a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily, which are monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in steroidogenesis. In particular, aromatase is responsible for the aromatization of androgens into estrogens. The enzyme aromatase can be found in many tissues including gonads, brain, adipose tissue, placenta, blood vessels, skin, and bone, as well as in tissue of endometriosis, uterine fibroids, breast cancer, and endometrial cancer. It is an important factor in sexual development.

Physalis angulata is an erect herbaceous annual plant belonging to the nightshade family Solanaceae. Its leaves are dark green and roughly oval, often with tooth shapes around the edge. The flowers are five-sided and pale yellow; the yellow-orange fruits are borne inside a balloon-like calyx. It is native to the Americas, but is now widely distributed and naturalized in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide.
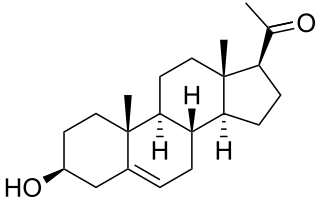
Pregnenolone (P5), or pregn-5-en-3β-ol-20-one, is an endogenous steroid and precursor/metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of most of the steroid hormones, including the progestogens, androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids. In addition, pregnenolone is biologically active in its own right, acting as a neurosteroid.

A selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM) is an agent that acts on the progesterone receptor (PR), the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. A characteristic that distinguishes such substances from full receptor agonists and full antagonists is that their action differs in different tissues, i.e. agonist in some tissues while antagonist in others. This mixed profile of action leads to stimulation or inhibition in tissue-specific manner, which further raises the possibility of dissociating undesirable adverse effects from the development of synthetic PR-modulator drug candidates.

Novobiocin, also known as albamycin or cathomycin, is an aminocoumarin antibiotic that is produced by the actinomycete Streptomyces niveus, which has recently been identified as a subjective synonym for S. spheroides a member of the class Actinomycetia. Other aminocoumarin antibiotics include clorobiocin and coumermycin A1. Novobiocin was first reported in the mid-1950s.
The retinoid X receptor (RXR) is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by 9-cis retinoic acid, which is discussed controversially to be of endogenous relevance, and 9-cis-13,14-dihydroretinoic acid, which is likely to be the major endogenous mammalian RXR-selective agonist.

Mibolerone, also known as dimethylnortestosterone (DMNT) and sold under the brand names Cheque Drops and Matenon, is a synthetic, orally active, and extremely potent anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) derivative which was marketed by Upjohn for use as a veterinary drug. It was indicated specifically as an oral treatment for prevention of estrus (heat) in adult female dogs.

Solamargine is a cytotoxic chemical compound that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae, such as potatoes, tomatoes, and eggplants. It has been also isolated from Solanum nigrum fungal endophyte Aspergillus flavus. It is a glycoalkaloid derived from the steroidal alkaloid solasodine.

Withanolides are a group of at least 300 naturally occurring steroids built on an ergostane skeleton. They occur as secondary metabolites primarily in genera of the Nightshade family, for example in the tomatillo.

Steroidal alkaloids have the basic steroidal skeleton with nitrogen-based functional groups attached to the skeleton. More specifically, they are distinguished by their tetracyclic cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene skeleton that marks their close relationship with sterols. They fall in two major categories: Solanum alkaloids and Veratrum alkaloids. A Steroidal alkaloid has also been found in Chonemorpha fragrans, 'chonemorphine' was used to treat intestinal infections in Wistar rats..
2,5-Diketopiperazine is an organic compound with the formula (NHCH2C(O))2. The compound features a six-membered ring containing two amide groups at opposite positions in the ring. It was first compound containing a peptide bond to be characterized by X-ray crystallography in 1938. It is the parent of a large class of 2,5-Diketopiperazines (2,5-DKPs) with the formula (NHCH2(R)C(O))2 (R = H, CH3, etc.). They are ubiquitous peptide in nature. They are often found in fermentation broths and yeast cultures as well as embedded in larger more complex architectures in a variety of natural products as well as several drugs. In addition, they are often produced as degradation products of polypeptides, especially in processed foods and beverages. They have also been identified in the contents of comets.

The Solanaceae, or the nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and ornamentals. Many members of the family contain potent alkaloids, and some are highly toxic, but many—including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell and chili peppers—are used as food. The family belongs to the order Solanales, in the asterid group and class Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons). The Solanaceae consists of about 98 genera and some 2,700 species, with a great diversity of habitats, morphology and ecology.
The inorganic imides are compounds containing an ion composed of nitrogen bonded to hydrogen with formula HN2−. Organic imides have the NH group, and two single or one double covalent bond to other atoms. The imides are related to the inorganic amides (H2N−), the nitrides (N3−) and the nitridohydrides (N3−•H−).
Calliphysalis carpenteri, or Carpenter's groundcherry, is a perennial plant in the family Solanaceae, the "nightshade" plants. Native to sandy soils on the coastal plain regions of southeastern North America from northern Florida to Louisiana and Arkansas, it was first described from specimens collected in West Feliciana Parish, Louisiana. Its species name honors the botanical contributions of early Louisiana naturalist William Marbury Carpenter (1811-1848).

Alkekengi officinarum, the bladder cherry, Chinese lantern, Japanese-lantern, strawberry groundcherry, winter cherry, alchechengi berry, or Klabuster cherry is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family Solanaceae. It is a close relative of the new world Calliphysalis carpenteri and a somewhat more distant relative to the members of the Physalis genus. This species is native to the regions covering Southern Europe to South Asia and Northeast Asia.















