
Omnipotence is the quality of having unlimited power. Monotheistic religions generally attribute omnipotence only to the deity of their faith. In the monotheistic religious philosophy of Abrahamic religions, omnipotence is often listed as one of a deity's characteristics, along with omniscience, omnipresence, and omnibenevolence. The presence of all these properties in a single entity has given rise to considerable theological debate, prominently including the problem of evil, the question of why such a deity would permit the existence of evil. It is accepted in philosophy and science that omnipotence can never be effectively understood.

The Hare Krishna mantra, also referred to reverentially as the Mahā-mantra, is a 16-word Vaishnava mantra which is mentioned in the Kali-Santarana Upanishad and which from the 15th century rose to importance in the Bhakti movement following the teachings of Chaitanya Mahaprabhu. This mantra is composed of two Sanskrit names of the Supreme Being, "Krishna" and "Rama".

Tawhid is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion's central and single most important concept, upon which a Muslim's entire religious adherence rests. It unequivocally holds that God as per Islam is One and Single.

Ōṁ is the sound of a sacred spiritual symbol in Indic religions. The meaning and connotations of Om vary between the diverse schools within and across the various traditions. It is part of the iconography found in ancient and medieval era manuscripts, temples, monasteries, and spiritual retreats in Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. As a syllable, it is often chanted either independently or before a spiritual recitation and during meditation in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism.

In the mythology of William Blake, Urizen is the embodiment of conventional reason and law. He is usually depicted as a bearded old man; he sometimes bears architect's tools, to create and constrain the universe; or nets, with which he ensnares people in webs of law and conventional society. Originally, Urizen represented one half of a two-part system, with him representing reason and Los, his opposition, representing imagination. In Blake's reworking of his mythic system, Urizen is one of the four Zoas that result from the division of the primordial man, Albion, and he continues to represent reason. He has an Emanation, or paired female equivalent, Ahania, who stands for Pleasure. In Blake's myth, Urizen is joined by many daughters with three representing aspects of the body. He is also joined by many sons, with four representing the four elements. These sons join in rebellion against their father but are later united in the Last Judgment. In many of Blake's books, Urizen is seen with four books that represent the various laws that he places upon humanity.
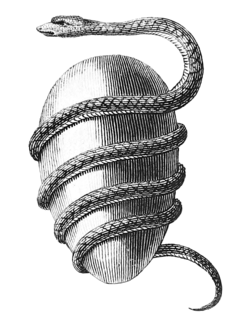
The world egg, cosmic egg or mundane egg is a mythological motif found in the cosmogonies of many cultures that is present in Proto-Indo-European culture and other cultures and civilizations. Typically, the world egg is a beginning of some sort, and the universe or some primordial being comes into existence by "hatching" from the egg, sometimes lain on the primordial waters of the Earth.

Vishnu Sahasranāmam, is a Sanskrit hymn which contains a list of 1,000 names of Vishnu, one of the main deities in Hinduism and the supreme God in Vaishnavism. It is one of the most sacred and popular stotras in Hinduism. The Vishnu Sahasranāma as found in the Anushasana Parva of the epic Mahabharata. It is the most popular version of the 1,000 names of Vishnu. Other versions exist in the Padma Purana, Skanda Purana and Garuda Purana. There is also a Sikh version, found in the text Sundar Gutka.

The Incal is a French graphic novel series written by Alejandro Jodorowsky and originally illustrated by Jean Giraud. The Incal, with first pages originally released as Une aventure de John Difool in Métal hurlant and published by Les Humanoïdes Associés, introduced Jodorowsky's "Jodoverse", a fictional universe in which his science fiction comics take place. It is an epic space opera blending fantastical intergalactic voyage, science, technology, political intrigues, conspiracies, messianism, mysticism, poetry, debauchery, love stories, and satire. The Incal includes and expands the concepts and artwork from the abandoned film project Dune directed by Jodorowsky and designed by Giraud from the early 1970s.

Ramcharitmanas, is an epic poem in the Awadhi language, composed by the 16th-century Indian bhakti poet Tulsidas. The word Ramcharitmanas literally means "Lake of the deeds of Rama". It is considered one of the greatest works of Hindu literature. The work has variously been acclaimed as "the living sum of Indian culture", "the tallest tree in the magic garden of medieval Indian poetry", "the greatest book of all devotional literature" and "the best and most trustworthy guide to the popular living faith of the Indian people".

Zhang Zai (1020–1077) was a Chinese philosopher and politician. He is most known for laying out four ontological goals for intellectuals: to build up the manifestations of Heaven and Earth's spirit, to build up good life for the populace, to develop past sages' endangered scholarship, and to open up eternal peace.

Rasam is a clear and spicy South Indian soup. It is eaten with rice or consumed as a soup. In a traditional South Indian meal, it can be part of a course that includes sambar rice and curd rice. Rasam has a distinct taste in comparison to the sambar due to its own seasoning ingredients and is fluid in consistency. Chilled prepared versions are marketed commercially as well as rasam paste in bottles.
The Hanuman Chalisa is a Hindu devotional hymn (stotra) in praise of Hanuman. It was authored by Tulsidas in the Awadhi language, and is his best known text apart from the Ramcharitmanas. Apart from Awadhi, the Hanuman Chalisa is also available in various languages including Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu and Gujarati. The word "chālīsā" is derived from "chālīs", which means the number forty in Hindi, as the Hanuman Chalisa has 40 verses. A Gulshan Kumar-produced rendition of Hanuman Chalisa sung by Hariharan has received more than 2 billion views on YouTube as of November 2021, making it the first devotional song in the platform to achieve this feat.

The Book of Urizen is one of the major prophetic books of the English writer William Blake, illustrated by Blake's own plates. It was originally published as The First Book of Urizen in 1794. Later editions dropped the "First". The book takes its name from the character Urizen in Blake's mythology, who represents alienated reason as the source of oppression. The book describes Urizen as the "primeaval priest" and tells how he became separated from the other Eternals to create his own alienated and enslaving realm of religious dogma. Los and Enitharmon create a space within Urizen's fallen universe to give birth to their son Orc, the spirit of revolution and freedom.

In the Hindu epic Ramayana, Lavanasur was a Rakshasa (demon) who was killed by Shatrughna, youngest brother of Rama.

The Mahāvākyas are "The Great Sayings" of the Upanishads, as characterized by the Advaita school of Vedanta with mahā meaning great and vākya, a sentence. Most commonly, Mahāvākyas are considered four in number,
- Tat Tvam Asi - traditionally rendered as "That Thou Art", ; correctly translated as "That's how [thus] you are," with tat in Ch.U.6.12.3 referring to "the very nature of all existence as permeated by [the finest essence]"
- Aham Brahman Asmi - - "I am Brahman", or "I am Divine"
- Prajnanam Brahma - "Prajñāna is Brahman", or "Brahman is Prajñāna"
- Ayam Atma Brahma - "This Self (Atman) is Brahman"
The Beatles Concerto is an instrumental musical medley of tunes from songs by The Beatles, arranged and composed by John Rutter within a classical "Piano Concerto Form".

Kharaharapriya is a rāga in Carnatic music. It is the 22nd melakarta rāga in the 72 melakarta rāga system. It is possible that the name of the ragam was originally Harapriya but it was changed to conform to the Katapayadi formula. Kharaharapriya has a distinct melody and brings out the Karuna rasam, invoking pathos in the listeners. The Kafi thaat of Hindustani music is the equivalent of Kharaharapriya. Its Western equivalent is the Dorian mode.

Akan religion comprises the traditional beliefs and religious practices of the Akan people of Ghana and eastern Ivory Coast. Akan religion is referred to as Akom. Although most Akan people have identified as Christians since the early 20th century, Akan religion remains practiced by some and is often syncretized with Christianity. The Akan have many subgroups, so the religion varies greatly by region and subgroup. Similar to other traditional religions of West and Central Africa such as West African Vodun, Yoruba religion, or Odinani, Akan cosmology consists of a senior god who generally does not interact with humans and many gods who assist humans.
Lakshana – derived from the combination of words lakshya and kshana – means 'indication' or 'symptom'. It also means 'an auspicious mark', 'attribute' or 'quality'. In Tamil language, Lakshanam means "features". Sulakshana means good features.

The Narayana Upanishad is one of the minor Upanishads, listed as number 18 in the extended anthology of 108 Upanishads historically recited by Rama to Hanuman. It is listed as number 33 in the early 19th-century Henry Thomas Colebrooke anthology. It is written in Sanskrit language, attached to the Krishna (Black) Yajurveda, is one of 14 Vaishnava Upanishads, and it recommends the bhakti of Lord Narayana (Vishnu).
















