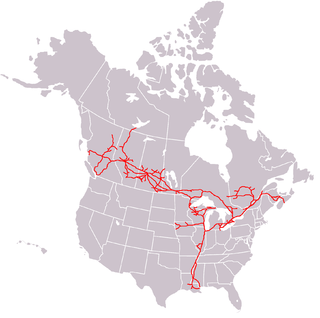
The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.

Nickel Centre was a town in Ontario, Canada, which existed from 1973 to 2000.

Capreol is a community in the Ontario city of Greater Sudbury. Situated on the Vermilion River, Capreol is the city's northernmost populated area.

The Reversing Falls are a series of rapids on the Saint John River located in Saint John, New Brunswick, Canada, where the river runs through a narrow gorge before emptying into the Bay of Fundy.

The River Tawe is a 30 miles (48 km) long river in South Wales. Its headwaters flow initially east from its source below Llyn y Fan Fawr south of Moel Feity in the Black Mountains, the westernmost range of the Brecon Beacons National Park, before the river turns south and then southwest to its estuary at Swansea. Its main tributaries are the right bank Upper and Lower Clydach Rivers and the Afon Twrch. The total area of the catchment is some 246 km2 (95 sq mi). The Tawe passes through a number of towns and villages including Ystradgynlais, Ystalyfera, Pontardawe, and Clydach and meets the sea at Swansea Bay below Swansea. The Tawe Valley is more commonly known as the Swansea Valley.

Unorganized North Algoma District is an unorganized area in northeastern Ontario, Canada, comprising all areas in Algoma District, north of the Sault Ste. Marie to Elliot Lake corridor, which are not part of an incorporated municipality or a First Nation. It covers 44,077.03 km2 (17,018.24 sq mi) of land, and had a population of 6050 in 2021. Many of these communities were/are stations on the Algoma Central Railway or were logging/mining towns.
The New York and Ottawa Railway was a railway connecting Tupper Lake in northeastern New York to Ottawa, Ontario, via Ramsayville, Russell, Embrun, Finch and Cornwall. It became part of the New York Central Railroad system in 1913, although it was under the larger company's possession since the end of 1904. It had started out as the Northern Adirondack Railroad and evolved into the Northern New York Railroad, the New York and Ottawa Railroad, and was last known as the New York and Ottawa Railway before being merged into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Other lines that were a part of this route are described below.
Severn Bridge is a small community in the Town of Gravenhurst, of the District of Muskoka in the province of Ontario, Canada. It is located approximately 160 kilometres north of Toronto, on the Severn River, roughly halfway between Orillia and Gravenhurst. Its population was around 300 in 1992. It was founded in the nineteenth century. The village is served by important road, rail, water links and its postal services and rural route are handled in Washago, Ontario.
The Birmingham District is a geological area in the vicinity of Birmingham, Alabama, where the raw materials for making steel, limestone, iron ore, and coal are found together in abundance. The district includes Red Mountain, Jones Valley, and the Warrior and Cahaba coal fields in Central Alabama.

The Phoenix Iron Works, located in Phoenixville, Pennsylvania, was a manufacturer of iron and related products during the 19th century and early 20th century. Phoenix Iron Company was a major producer of cannon for the Union Army during the American Civil War. The company also produced the Phoenix column, an advance in construction material. Company facilities are a core component of the Phoenixville Historic District, a National Register of Historic Places site that was in 2006 recognized as a historic landmark by ASM International.

Pointe du Bois is a small community located northeast of Winnipeg, Manitoba, in an unincorporated section of Census Division No. 1. Pointe du Bois has a Manitoba Hydro generating station. The area provides great fishing for pickerel, Northern pike and smallmouth bass. In April 2013 its owner, Manitoba Hydro announced that it will close the community by 2015 and level it to the ground at a later date. The crown corporation cites the high cost of maintaining municipal infrastructure as the primary reason for its decision.

Originally called the High Bridge, the Hi-Line Bridge is a historic railroad bridge located over the Sheyenne River in Valley City, North Dakota. The bridge is 3,860 feet (1,180 m) long and 162 feet (49 m) above the river. Construction work began on July 5, 1906, and it was ready for service on May 8, 1908. At the time it was the longest bridge for its height in the world. It currently remains one of the longest and highest single track railroad viaducts in the United States, and was designated as a National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Civil Engineers in 2005.
There are various Black Lakes in Nova Scotia, Canada. They vary widely in size, depth and usability. Many counties, such as Cumberland, Halifax, Inverness, and Pictou Counties have more than one Black Lake so named, while other counties mentioned in this article have only one named Black Lake.
The Seboeis River is a river in Penobscot County, Maine. The river is the outflow of Snowshoe Lake in Maine Township 7, Range 7, WELS; Snowshoe Lake is fed via a short stream from Grand Lake Seboeis. The river runs 28.1 miles (45.2 km) south — through White Horse Lake, Seboeis Deadwater, Upper Seboeis River Gorge, and Gagnon Flat — to its confluence with the East Branch of the Penobscot River in T.3 R.7 WELS.

Allan's Mill was a watermill located on both banks of the Speed River in Guelph, Ontario, Canada. Part of the site is now listed under the Ontario Heritage Act.

The Midland Bridge is a road bridge over the River Avon in Bath, Somerset, England, now carrying the B3118 road. It was originally built in 1870 by the Midland Railway Company to allow access to and from their goods station at Sydenham Field on the south bank of the river Avon, the opposite bank to the passenger Green Park terminus station and the city centre.

The Caledonian Railway Bridge is a bridge crossing the River Clyde at Broomielaw in Scotland. It is adjacent to Glasgow Central Station.

The Pickerel River is a river in the Canadian province of Ontario. Essentially a secondary arm of the larger French River system, the river extends from its headwaters in the Loring and Restoule area of the Almaguin Highlands in the northern part of Parry Sound District to Georgian Bay. Smaller channels near Wanikewin and Hartley Bay also connect the river directly to the main watercourse of the French River.

Wilmington is an industrial area east of the River Hull in Kingston upon Hull, England.

Quirke Lake is body of water located in Ontario, Canada. It is located in the Quirke Lake basin, a geological basin the northern part of the Huronian Supergroup. The lake is proximate to five decommissioned uranium mines.















