
PowerPC is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors.

Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. After the Sun acquisition by Oracle in 2010, it was renamed Oracle Solaris.

Portage is a package management system originally created for and used by Gentoo Linux and also by ChromeOS, Calculate, Sabayon, and Funtoo Linux among others. Portage is based on the concept of ports collections. Gentoo is sometimes referred to as a meta-distribution due to the extreme flexibility of Portage, which makes it operating-system-independent. The Gentoo/Alt project was concerned with using Portage to manage other operating systems, such as BSDs, macOS and Solaris. The most notable of these implementations is the Gentoo/FreeBSD project.

Pegasos is a MicroATX motherboard powered by a PowerPC 750CXe or PowerPC 7447 microprocessor, featuring three PCI slots, one AGP slot, two Ethernet ports, USB, DDR, AC'97 sound, and FireWire. Like the PowerPC Macintosh counterparts, it boots via Open Firmware.
MkLinux is an open-source software computer operating system begun by the Open Software Foundation Research Institute and Apple Computer in February 1996, to port Linux to the PowerPC platform, and Macintosh computers. The name refers to the Linux kernel being adapted to run as a server hosted on the Mach microkernel, version 3.0.
CodeWarrior is an integrated development environment (IDE) published by NXP Semiconductors for editing, compiling, and debugging software for several microcontrollers and microprocessors and digital signal controllers used in embedded systems.

Unix System V is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4. System V Release 4 (SVR4) was commercially the most successful version, being the result of an effort, marketed as Unix System Unification, which solicited the collaboration of the major Unix vendors. It was the source of several common commercial Unix features. System V is sometimes abbreviated to SysV.
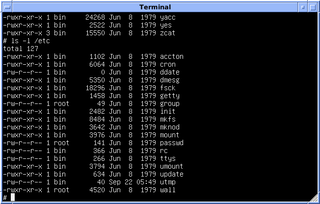
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1.
QuickTransit was a cross-platform virtualization program developed by Transitive Corporation. It allowed software compiled for one specific processor and operating system combination to be executed on a different processor and/or operating system architecture without source code or binary changes.

Metrowerks was a company that developed software development tools for various desktop, handheld, embedded, and gaming platforms. Its flagship product, CodeWarrior, comprised an IDE, compilers, linkers, debuggers, libraries, and related tools. In 1999 it was acquired by Motorola and in 2005 it was spun-off as part of Freescale, which continues to sell these tools. In 2015, Freescale Semiconductor was absorbed into NXP.

The Open Desktop Workstation, also referred to as ODW is a PowerPC based computer, by San Antonio-based Genesi. The ODW has an interchangeable CPU card allowing for a wide range of PowerPC microprocessors from IBM and Freescale Semiconductor.
The following is a timeline of virtualization development. In computing, virtualization is the use of a computer to simulate another computer. Through virtualization, a host simulates a guest by exposing virtual hardware devices, which may be done through software or by allowing access to a physical device connected to the machine.

Genesi is an international group of technology and consulting companies in the United States, Mexico and Germany. It is most widely known for designing and manufacturing ARM architecture and Power ISA-based computing devices. The Genesi Group consists of Genesi USA Inc., Genesi Americas LLC, Genesi Europe UG, Red Efika, bPlan GmbH and the affiliated non-profit organization Power2People.

Efika is a line of power efficient ARM architecture and Power ISA based computers manufactured by Genesi.
In order to compete with Intel's Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC), which had enabled the first Intel 486-based multiprocessor systems, in early 1995 AMD and Cyrix proposed as somewhat similar-in-purpose OpenPIC architecture supporting up to 32 processors. The OpenPIC architecture had at least declarative support from IBM and Compaq around 1995. No x86 motherboard was released with OpenPIC however. After the OpenPIC's failure in the x86 market, AMD licensed the Intel APIC Architecture for its AMD Athlon and later processors.
The Linux kernel can run on a variety of devices made by Apple, including devices where the unlocking of the bootloader is not possible with an official procedure, such as iPhones and iPads.








