
Lidar is a surveying method that measures distance to a target by illuminating the target with pulsed laser light and measuring the reflected pulses with a sensor. Differences in laser return times and wavelengths can then be used to make digital 3-D representations of the target. The name lidar, now used as an acronym of light detection and ranging, was originally a portmanteau of light and radar. Lidar sometimes is called 3D laser scanning, a special combination of a 3D scanning and laser scanning. It has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications.

Evapotranspiration (ET) is the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land and ocean surface to the atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and waterbodies. Transpiration accounts for the movement of water within a plant and the subsequent loss of water as vapor through stomata in its leaves. Evapotranspiration is an important part of the water cycle. An element that contributes to evapotranspiration can be called an evapotranspirator.
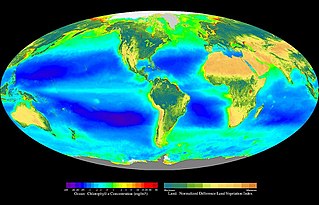
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are known as primary producers or autotrophs, and form the base of the food chain. In terrestrial ecoregions, these are mainly plants, while in aquatic ecoregions algae predominate in this role. Ecologists distinguish primary production as either net or gross, the former accounting for losses to processes such as cellular respiration, the latter not.

A truss is an assembly of beams or other elements that creates a rigid structure. In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so that the assemblage as a whole behaves as a single object". A "two-force member" is a structural component where force is applied to only two points. Although this rigorous definition allows the members to have any shape connected in any stable configuration, trusses typically comprise five or more triangular units constructed with straight members whose ends are connected at joints referred to as nodes.

A quadrat is a frame, traditionally square, used in ecology and geography to isolate a standard unit of area for study of the distribution of an item over a large area. Modern quadrats can for example be rectangular, circular, or irregular. The quadrat is suitable for sampling plants, slow-moving animals, and some aquatic organisms.

Solid fuel refers to various forms of solid material that can be burnt to release energy, providing heat and light through the process of combustion. Solid fuels can be contrasted with liquid fuels and gaseous fuels. Common examples of solid fuels include wood, charcoal, peat, coal, Hexamine fuel tablets, wood pellets, corn, wheat, rye, and other grains. Solid fuels are extensively used in rocketry as solid propellants. Solid fuels have been used throughout human history to create fire and solid fuel is still in widespread use throughout the world in the present day.

Anaerobic digestion is a collection of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels. Much of the fermentation used industrially to produce food and drink products, as well as home fermentation, uses anaerobic digestion.

Phytoliths are rigid, microscopic structures made of silica, found in some plant tissues and persisting after the decay of the plant. These plants take up silica from the soil, whereupon it is deposited within different intracellular and extracellular structures of the plant. Phytoliths come in varying shapes and sizes. Although some use "phytolith" to refer to all mineral secretions by plants, it more commonly refers to siliceous plant remains. In contrast, mineralized calcium secretions in cacti are composed of calcium oxalates.
Leaf area index (LAI) is a dimensionless quantity that characterizes plant canopies. It is defined as the one-sided green leaf area per unit ground surface area in broadleaf canopies. In conifers, three definitions for LAI have been used:
Phytosociology is the branch of science which deals with plant communities, their composition and development, and the relationships between the species within them. A phytosociological system is a system for classifying these communities.
Renewable Natural Gas (RNG), also known as Sustainable Natural Gas (SNG) or biomethane, is a biogas which has been upgraded to a quality similar to fossil natural gas and having a methane concentration of 90% or greater. A biogas is a gaseous form of methane obtained from biomass. By upgrading the quality to that of natural gas, it becomes possible to distribute the gas to customers via the existing gas grid within existing appliances. Renewable natural gas is a subset of synthetic natural gas or substitute natural gas (SNG).

Nonparametric regression is a category of regression analysis in which the predictor does not take a predetermined form but is constructed according to information derived from the data. Nonparametric regression requires larger sample sizes than regression based on parametric models because the data must supply the model structure as well as the model estimates.
The MEMO model is a Eulerian non-hydrostatic prognostic mesoscale model for wind-flow simulation. It was developed by the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in collaboration with the Universität Karlsruhe. The MEMO Model together with the photochemical dispersion model MARS are the two core models of the European zooming model (EZM). This model belongs to the family of models designed for describing atmospheric transport phenomena in the local-to-regional scale, frequently referred to as mesoscale air pollution models.

Barren vegetation describes an area of land where plant growth may be sparse, stunted, and/or contain limited biodiversity. Environmental conditions such as toxic or infertile soil, high winds, coastal salt-spray and climatic conditions are often key factors in poor plant growth and development. Barren vegetation can be categorized depending on the climate, geology and the geographic location of a specific area. Pine barrens, coastal barrens and serpentine barrens are some of the more distinct ecoregions for barren vegetation and are the most commonly researched by scientists. Often referred to as "heathlands", barrens can be excellent environments for unique biological diversity and taxonomic compositions.
Cephalometric analysis is the clinical application of cephalometry. It is analysis of the dental and skeletal relationships of a human skull. It is frequently used by dentists, orthodontists, and oral and maxillofacial surgeons as a treatment planning tool. Two of the more popular methods of analysis used in orthodontology are the Steiner analysis and the Downs analysis. There are other methods as well which are listed below.
Slash-and-char is an alternative to slash-and-burn that has a lesser effect on the environment. It is the practice of charring the biomass resulting from the slashing, instead of burning it. The resulting residue matter charcoal can be utilized as biochar to improve the soil fertility.

Ottovale coke works was a large industrial complex situated at Blaydon Burn, near Blaydon-on-Tyne, Gateshead, North East England. The complex comprised a coke works, tar works and a power station. Built on the site of Dockendale Hall in 1904, it was operated by the Priestman Collieries until the 1970s.
DPHM-RS is a semi-distributed hydrologic model developed at University of Alberta, Canada.












