Labour economics seeks to understand the functioning and dynamics of the markets for wage labour.

In commerce, supply-chain management (SCM), the management of the flow of goods and services, involves the movement and storage of raw materials, of work-in-process inventory, and of finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. Interconnected or interlinked networks, channels and node businesses combine in the provision of products and services required by end customers in a supply chain. Supply-chain management has been defined as the "design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring of supply-chain activities with the objective of creating net value, building a competitive infrastructure, leveraging worldwide logistics, synchronizing supply with demand and measuring performance globally." SCM practice draws heavily from the areas of industrial engineering, systems engineering, operations management, logistics, procurement, information technology, and marketing and strives for an integrated approach. Marketing channels play an important role in supply-chain management. Current research in supply-chain management is concerned with topics related to sustainability and risk management, among others. Some suggest that the “people dimension” of SCM, ethical issues, internal integration, transparency/visibility, and human capital/talent management are topics that have, so far, been underrepresented on the research agenda.

In economics, a commodity is an economic good or service that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them. Most commodities are raw materials, basic resources, agricultural, or mining products, such as iron ore, sugar, or grains like rice and wheat. Commodities can also be mass-produced unspecialized products such as chemicals and computer memory.
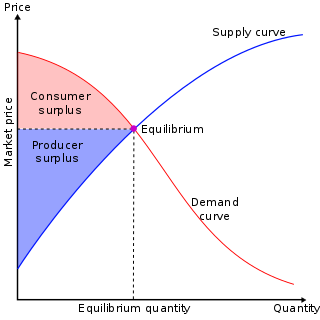
In mainstream economics, economic surplus, also known as total welfare or Marshallian surplus, refers to two related quantities. Consumer surplus or consumers' surplus is the monetary gain obtained by consumers because they are able to purchase a product for a price that is less than the highest price that they would be willing to pay. Producer surplus or producers' surplus is the amount that producers benefit by selling at a market price that is higher than the least that they would be willing to sell for; this is roughly equal to profit.

Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics is the management of the flow of things between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet requirements of customers or corporations. The resources managed in logistics may include tangible goods such as materials, equipment, and supplies, as well as food and other consumable items. The logistics of physical items usually involves the integration of information flow, materials handling, production, packaging, inventory, transportation, warehousing, and often security.

In business and finance, supply chain is a system of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. Supply chain activities involve the transformation of natural resources, raw materials, and components into a finished product that is delivered to the end customer. In sophisticated supply chain systems, used products may re-enter the supply chain at any point where residual value is recyclable. Supply chains link value chains.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. There is always at least one constraint, and TOC uses a focusing process to identify the constraint and restructure the rest of the organization around it. TOC adopts the common idiom "a chain is no stronger than its weakest link". This means that processes, organizations, etc., are vulnerable because the weakest person or part can always damage or break them or at least adversely affect the outcome.
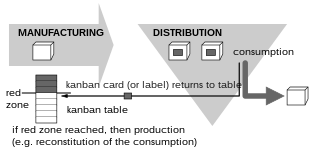
Kanban (看板) is a scheduling system for lean manufacturing and just-in-time manufacturing (JIT). Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, developed kanban to improve manufacturing efficiency. Kanban is one method to achieve JIT. The system takes its name from the cards that track production within a factory. For many in the automotive sector, kanban is known as the "Toyota nameplate system" and as such the term is not used by some other automakers.
In economics and consumer theory, a Giffen good is a product that people consume more of as the price rises and vice versa—violating the basic law of demand in microeconomics. For any other sort of good, as the price of the good rises, the substitution effect makes consumers purchase less of it, and more of substitute goods; for most goods, the income effect reinforces this decline in demand for the good. But a Giffen good is so strongly an inferior good in the minds of consumers that this contrary income effect more than offsets the substitution effect, and the net effect of the good's price rise is to increase demand for it.
In economics, overproduction, oversupply, excess of supply or glut refers to excess of supply over demand of products being offered to the market. This leads to lower prices and/or unsold goods along with the possibility of unemployment.
Pinch or pinching may refer to:
Purchasing refers to a business or organization attempting to acquire goods or services to accomplish its goals. Although there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process, processes can vary greatly between organizations. Typically the word “purchasing” is not used interchangeably with the word “procurement”, since procurement typically includes expediting, supplier quality, and transportation and logistics (T&L) in addition to purchasing.

The business terms push and pull originated in logistics and supply chain management, but are also widely used in marketing, and is also a term widely used in the hotel distribution business. Walmart is an example of a company that uses the push vs. pull strategy.
Monetary inflation is a sustained increase in the money supply of a country. Depending on many factors, especially public expectations, the fundamental state and development of the economy, and the transmission mechanism, it is likely to result in price inflation, which is usually just called "inflation", which is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services.
Contraceptive security (CS) is a situation in which people are able to reliably choose, obtain, and use quality contraceptives for family planning and the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. The term refers primarily to efforts undertaken in developing countries to ensure contraceptive availability as an integral part of family planning programs.
Pinch point may refer to:
Inflation rate in India was 3.78% as of August 2015, as per the Indian Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. This represents a modest reduction from the previous annual figure of 9.6% for June 2011. Inflation rates in India are usually quoted as changes in the Wholesale Price Index (WPI), for all commodities

Socially necessary labour time in Marx's critique of political economy is what regulates the exchange value of commodities in trade and consequently constrains producers in their attempt to economise on labour. It does not 'guide' them, as it can only be determined after the event and is thus inaccessible to forward planning.







