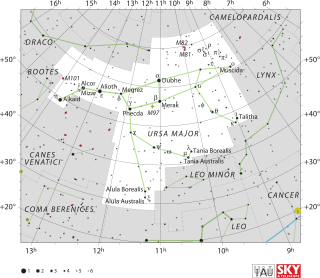
Ursa Major is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater she-bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations.

The Triangulum Galaxy is a spiral galaxy 2.73 million light-years (ly) from Earth in the constellation Triangulum. It is catalogued as Messier 33 or NGC 598. The Triangulum Galaxy is the third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, behind the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way. It is one of the most distant permanent objects that can be viewed with the naked eye.

Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, form part of the Hubble sequence. Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the bulge. These are often surrounded by a much fainter halo of stars, many of which reside in globular clusters.

Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees, and also the longest at over 100 degrees. Its southern end borders Libra and Centaurus and its northern end borders Cancer. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. Commonly represented as a water snake, it straddles the celestial equator.

The Pinwheel Galaxy is a face-on spiral galaxy 21 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 and was communicated that year to Charles Messier, who verified its position for inclusion in the Messier Catalogue as one of its final entries.
M101 or M-101 may refer to:

Messier 83 or M83, also known as the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy and NGC 5236, is a barred spiral galaxy approximately 15 million light-years away in the constellation borders of Hydra and Centaurus. Nicolas Louis de Lacaille discovered M83 on February 23, 1752 at the Cape of Good Hope. Charles Messier added it to his catalogue of nebulous objects in March 1781. It is one of the closest and brightest barred spiral galaxies in the sky, and is visible with binoculars. Its nickname of the Southern Pinwheel derives from its resemblance to the Pinwheel Galaxy (M101).
83 (eighty-three) is the natural number following 82 and preceding 84.
M83 or M-83 may refer to:
Messier 102 is a galaxy listed in the Messier Catalogue that cannot be unambiguously identified. Its original discoverer Pierre Méchain said that it was a duplicate observation of Messier 101, but more historical evidence favors that it is NGC 5866, although other galaxies have been suggested as possible identities. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) considers it to be the same as NGC 5866.

Messier 58 is an intermediate barred spiral galaxy with a weak inner ring structure located within the constellation Virgo, approximately 68 million light-years away from Earth. It was discovered by Charles Messier on April 15, 1779 and is one of four barred spiral galaxies that appear in Messier's catalogue. M58 is one of the brightest galaxies in the Virgo Cluster. From 1779 it was arguably the farthest known astronomical object until the release of the New General Catalogue in the 1880s and even more so the publishing of redshift values in the 1920s.

Messier 99 or M99, also known as NGC 4254, is a grand design spiral galaxy in the northern constellation Coma Berenices approximately 15,000,000 parsecs from the Milky Way. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain on 17 March 1781. The discovery was then reported to Charles Messier, who included the object in the Messier Catalogue of comet-like objects. It was one of the first galaxies in which a spiral pattern was seen. This pattern was first identified by Lord Rosse in the spring of 1846.

Messier 109 is a barred spiral galaxy exhibiting a weak inner ring structure around the central bar approximately 83.5 ± 24 million light-years away in the northern constellation Ursa Major. M109 can be seen south-east of the star Phecda.

Messier 110, or M110, also known as NGC 205, is a dwarf elliptical galaxy that is a satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy in the Local Group.
A pinwheel is a spinning children’s toy. Various other things which spin or have a similar shape have been given the name by analogy:

The Great Debate, also called the Shapley–Curtis Debate, was held on 26 April 1920 at the Smithsonian Museum of Natural History, between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis. It concerned the nature of so-called spiral nebulae and the size of the universe; Shapley believed that distant nebulae were relatively small and lay within the outskirts of Earth's home galaxy, while Curtis held that they were in fact independent galaxies, implying that they were exceedingly large and distant.
A black eye is an injury.

SN 2011fe, initially designated PTF 11kly, was a Type Ia supernova discovered by the Palomar Transient Factory (PTF) survey on 24 August 2011 during an automated review of images of the Messier 101 from the nights of 22 and 23 August 2011. It was located in Messier 101, the Pinwheel Galaxy, 21 million light years from Earth. It was observed by the PTF survey very near the beginning of its supernova event, when it was approximately 1 million times too dim to be visible to the naked eye. It is the youngest type Ia ever discovered. About 13 September 2011, it reached its maximum brightness of apparent magnitude +9.9 which equals an absolute magnitude of about -19, equal to 2.5 billion Suns. At +10 apparent magnitude around 5 September, SN 2011fe was visible in small telescopes. As of 30 September the supernova was at +11 apparent magnitude in the early evening sky after sunset above the northwest horizon. It had dropped to +13.7 as of 26 November 2011.

UGC 8837 is a dwarf galaxy located in the constellation of Ursa Major, 24 million light years away from Earth. It is a member of the M101 Group, a group containing several galaxies orbiting the largest, the Pinwheel Galaxy (M101).

UGC 9405 is a faint dwarf irregular galaxy situated in the constellation of Ursa Major. It is about 20.5 million light-years, or 6.3 megaparsecs, away from the Earth. It is listed as a member of the M101 Group, a group containing the several galaxies orbiting the largest, Pinwheel Galaxy (M101). However, due to its far distance from the Pinwheel Galaxy, its membership of the group is uncertain.












