Related Research Articles

A parachute is a device used to slow the motion of an object through an atmosphere by creating drag or aerodynamic lift. A major application is to support people, for recreation or as a safety device for aviators, who can exit from an aircraft at height and descend safely to earth.

An aerospace manufacturer is a company or individual involved in the various aspects of designing, building, testing, selling, and maintaining aircraft, aircraft parts, missiles, rockets, or spacecraft. Aerospace is a high technology industry.
The Curtiss-Wright Corporation is a manufacturer and services provider headquartered in Davidson, North Carolina, with factories and operations in and outside the United States. Created in 1929 from the consolidation of Curtiss, Wright, and various supplier companies, the company was immediately the country's largest aviation firm and built more than 142,000 aircraft engines for the U.S. military during World War II.

The Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster (SRB) was the first solid-propellant rocket to be used for primary propulsion on a vehicle used for human spaceflight. A pair of them provided 85% of the Space Shuttle's thrust at liftoff and for the first two minutes of ascent. After burnout, they were jettisoned, and parachuted into the Atlantic Ocean, where they were recovered, examined, refurbished, and reused.

The X-38 is an experimental re-entry vehicle designed by NASA to research a possible emergency crew return vehicle (CRV) for the International Space Station (ISS). The 1995–2002 program also developed concepts for a crew return vehicle design that could be modified for other uses, such as a possible joint U.S. and international human spacecraft that could be launched on the French Ariane 5 booster.

A drogue parachute, also called drag chute, is a parachute designed for deployment from a rapidly moving object. It can be used for various purposes, such as to decrease speed, to provide control and stability, as a pilot parachute to deploy a larger parachute or a combination of these. Vehicles that have used drogue parachutes include multistage parachutes, aircraft, and spacecraft recovery systems.

A powered parachute, often abbreviated PPC, and also called a motorized parachute or paraplane, is a type of aircraft that consists of a parafoil with a motor and wheels.

The Martin X-23A PRIME (SV-5D) is a small lifting-body re-entry vehicle tested by the United States Air Force in the mid-1960s. Unlike ASSET, primarily used for structural and heating research, the X-23A PRIME was developed to study the effects of maneuvering during re-entry of Earth's atmosphere, including cross-range maneuvers up to 617 nmi from the ballistic track.

The ballute is a parachute-like braking device optimized for use at high altitudes and supersonic velocities.

The Ensign-Bickford Aerospace & Defense Company is a manufacturer of hardware and energetic systems for use in spacecraft, military, and industrial applications. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of Ensign-Bickford Industries.

Safran S.A. is a French multinational aerospace, defence and security corporation headquartered in Paris. It designs, develops and manufactures both commercial and military aircraft engines; launch vehicle, spacecraft and missile propulsion systems; as well as various other aerospace and military equipment and devices. The company was founded in 2005 through a merger between the aerospace engine manufacturer SNECMA and the electronics specialist SAGEM. Safran's subsequent acquisition of Zodiac Aerospace in 2018 significantly expanded its aeronautical activities.
Zodiac Aerospace was a French aerospace group, active from 1896 to 2018, that supplied systems and equipment for aircraft. In October 2018, it was acquired by French aerospace and defense company Safran.
Collins Aerospace is an American technology company that is one of the world's largest suppliers of aerospace and defense products. Headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina, it is a subsidiary of RTX Corporation.

The Kistler K-1 was a two-stage, fully reusable launch vehicle design created by Kistler Aerospace. It was to accommodate a wide range of missions, including payload delivery to low Earth orbit (LEO), payload delivery to high-energy orbits with a K-1 Active Dispenser, technology demonstration flights, microgravity missions, and commercial cargo resupply, recovery, and reboost services for the International Space Station (ISS).

IrvinGQ, formerly known as Airborne Systems, is an aerospace manufacturing company based in Llangeinor, Wales, United Kingdom. It specialises in the design, manufacture and supply of a range of parachutes and emergency, rescue and survival equipment for both the military and civilian markets.

Zodiac Nautic is a French company known for their inflatable boats.

The Space Rider is a planned uncrewed orbital lifting body spaceplane aiming to provide the European Space Agency (ESA) with affordable and routine access to space. Contracts for construction of the vehicle and ground infrastructure were signed in December 2020. Its maiden flight is currently scheduled for the third quarter of 2025.

RTX Corporation, formerly Raytheon Technologies Corporation, is an American multinational aerospace and defense conglomerate headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It is one of the largest aerospace and defense manufacturers in the world by revenue and market capitalization, as well as one of the largest providers of intelligence services. In 2023, the company's seat in Forbes Global 2000 was 79. RTX manufactures aircraft engines, avionics, aerostructures, cybersecurity solutions, guided missiles, air defense systems, satellites, and drones. The company is a large military contractor, getting much of its revenue from the U.S. government.
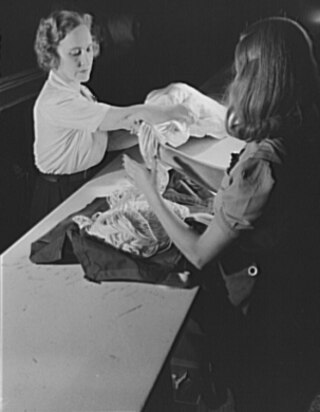
Adeline Gray, married names Johnson and Graf, was an early American parachutist. She is thought to have been one of the only female parachutists in the United States before the 1940s. Gray received her parachuting license at the age of 19 and afterwards appeared as part of a stunt parachuting team in barnstorming shows. She was also a licensed pilot by 21. Gray later worked as a parachute rigger and tester for DuPont and on June 6, 1942, became the first person to jump with a nylon parachute. Gray became moderately famous for this and appeared in advertisements for Camel cigarettes.
References
- ↑ | Mississippi Group Tour Escort Manual (pdf)
- ↑ | Bed & Breakfast Association of Mississippi (website); Visit Mississippi One Porch at a Time
- ↑ | Safran Aerosystems (corporate website), Contact Us
- ↑ Ofgang, Erik (22 May 2019). "How a Connecticut Company's Parachutes Helped Launch D-Day". CT Insider. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ↑ "Floyd Smith | The National Inventors Hall of Fame". www.invent.org. 28 November 2023. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ↑ Reuter, Jim. "Pioneer and the Parachute that goes UP" (PDF). Manchester History. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ↑ Ofgang, Erik (22 May 2019). "How a Connecticut Company's Parachutes Helped Launch D-Day". CT Insider. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ↑ | Mississippi Group Tour Escort Manual (pdf)
- ↑ | Bed & Breakfast Association of Mississippi (website); Visit Mississippi One Porch at a Time
- ↑ Speck, Emilee (6 February 2020). "What a catch: Florida fisherman reels in parachutes from SpaceX in-flight abort test". WKMG. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ↑ Pioneer Aerospace Standard Products by gina amoroso - Issuu. Pioneer Aerospace. 8 March 2012. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ↑ | Pioneer Aerospace (now defunct corporate website), Company History
- ↑ Safran shareholders meeting approves the merger of Zodiac Aerospace into Safran with 99.88% voting in favor
- ↑ "ASR Acquires Pioneer Aerospace". evtol.news.
- ↑ | Pioneer Aerospace (corporate website), Home
- ↑ "Pioneer Aerospace Corporation Files For Bankruptcy". BKData. November 1, 2023. Retrieved November 2, 2023.
- ↑ Foust, Jeff (30 November 2023). "SpaceX acquires parachute supplier". SpaceNews. Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- ↑ "SpaceX Acquires Parachute Maker Pioneer Aerospace for $2.2 Million". The Information. Retrieved 29 November 2023.