Related Research Articles

A randomized controlled trial is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments.
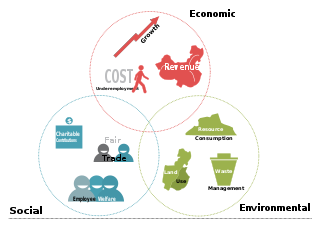
The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental and economic. Some organizations have adopted the TBL framework to evaluate their performance in a broader perspective to create greater business value. Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase in 1994.
Program evaluation is a systematic method for collecting, analyzing, and using information to answer questions about projects, policies and programs, particularly about their effectiveness and efficiency. In both the public and private sectors, stakeholders often want to know whether the programs they are funding, implementing, voting for, receiving or objecting to are producing the intended effect. While program evaluation first focuses around this definition, important considerations often include how much the program costs per participant, how the program could be improved, whether the program is worthwhile, whether there are better alternatives, if there are unintended outcomes, and whether the program goals are appropriate and useful. Evaluators help to answer these questions, but the best way to answer the questions is for the evaluation to be a joint project between evaluators and stakeholders.

Field experiments are experiments carried out outside of laboratory settings.
Disease management is defined as "a system of coordinated healthcare interventions and communications for populations with conditions in which patient self-care efforts are significant."
Social marketing has the primary goal of achieving "common good". Traditional commercial marketing aims are primarily financial, though they can have positive social effects as well. In the context of public health, social marketing would promote general health, raise awareness and induce changes in behaviour. Social marketing has been a large industry for some time in 2021 and was originally done with newspapers and billboards, but similar to commercial marketing has adapted to the modern world. The most common use of social marketing in today's society is through social media. However, to see social marketing as only the use of standard commercial marketing practices to achieve non-commercial goals is an oversimplified view.

Social impact assessment (SIA) is a methodology to review the social effects of infrastructure projects and other development interventions. Although SIA is usually applied to planned interventions, the same techniques can be used to evaluate the social impact of unplanned events, for example, disasters, demographic change, and epidemics. SIA is important in applied anthropology, as its main goal is to be able to deliver positive social outcomes and eliminate any possible negative or long term effects.
Evidence-based policy is an idea in public policy proposing that policy decisions should be based on, or informed by, rigorously established objective evidence. The implied contrast is with policymaking based on ideology, 'common sense,' anecdotes, and intuitions. It is the government equivalent of the effective altruism movement. Evidence-based policy uses a thorough research method, such as randomized controlled trials (RCT). Good data, analytical skills, and political support to the use of scientific information are typically seen as the crucial elements of an evidence-based approach.

A walking bus is a form of student transport for schoolchildren who, chaperoned typically by two adults, walk to school along a set route, with some similarities to a school bus route. Like a real bus, walking buses have a fixed route with designated "bus stops" and "pick up times" at which they pick up and "drop off" children.
Oportunidades is a government social assistance program in Mexico founded in 2002, based on a previous program called Progresa, created in 1997. It is designed to target poverty by providing cash payments to families in exchange for regular school attendance, health clinic visits, and nutrition support. Oportunidades is credited with decreasing poverty and improving health and educational attainment in regions where it has been deployed. Key features of Oportunidades include:

Natural resource management (NRM) is the management of natural resources such as land, water, soil, plants and animals, with a particular focus on how management affects the quality of life for both present and future generations (stewardship).

Household air pollution (HAP) is a significant form of indoor air pollution mostly relating to cooking and heating methods used in developing countries. Since much of the cooking is carried out with biomass fuel, in the form of wood, charcoal, dung, and crop residue, in indoor environments that lack proper ventilation, millions of people, primarily women and children face serious health risks. In total, about three billion people in developing countries are affected by this problem. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that cooking-related pollution causes 3.8 million annual deaths. The Global Burden of Disease study estimated the number of deaths in 2017 at 1.6 million. The problem is closely related to Energy poverty and cooking.
Impact evaluation assesses the changes that can be attributed to a particular intervention, such as a project, program or policy, both the intended ones, as well as ideally the unintended ones. In contrast to outcome monitoring, which examines whether targets have been achieved, impact evaluation is structured to answer the question: how would outcomes such as participants' well-being have changed if the intervention had not been undertaken? This involves counterfactual analysis, that is, "a comparison between what actually happened and what would have happened in the absence of the intervention." Impact evaluations seek to answer cause-and-effect questions. In other words, they look for the changes in outcome that are directly attributable to a program.
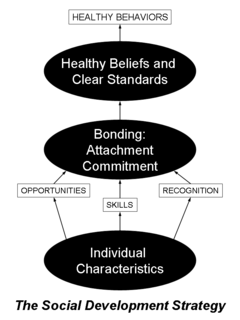
Communities That Care (CTC) is a program of the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) in the office of the United States Government's Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). CTC is a coalition-based prevention operating system that uses a public health approach to prevent youth problem behaviors such as violence, delinquency, school drop out and substance abuse. Using strategic consultation, training, and research-based tools, CTC is designed to help community stakeholders and decision makers understand and apply information about risk and protective factors, and programs that are proven to make a difference in promoting healthy youth development, in order to most effectively address the specific issues facing their community's youth.
Early intervention in psychosis is a clinical approach to those experiencing symptoms of psychosis for the first time. It forms part of a new prevention paradigm for psychiatry and is leading to reform of mental health services, especially in the United Kingdom and Australia.
A cluster-randomised controlled trial is a type of randomised controlled trial in which groups of subjects are randomised. Cluster randomised controlled trials are also known as cluster-randomised trials, group-randomised trials, and place-randomized trials. Cluster-randomised controlled trials are used when there is a strong reason for randomising treatment and control groups over randomising participants.

Social and behavior change communication (SBCC), often also only "BCC" or "Communication for Development (C4D)" is an interactive process of any intervention with individuals, group or community to develop communication strategies to promote positive behaviors which are appropriate to their settings and thereby solving the world's most pressing health problems. This in turn provides a supportive environment which will enable people to initiate, sustain and maintain positive and desirable behavior outcomes.

WASH is an acronym that stands for "water, sanitation and hygiene". It is used widely by non-governmental organizations and aid agencies in developing countries. The purposes of providing access to WASH services include achieving public health gains, improving human dignity in the case of sanitation, implementing the human right to water and sanitation, reducing the burden of collecting drinking water for women, reducing risks of violence against women, improving education and health outcomes at schools and health facilities, and reducing water pollution. Access to WASH services is also an important component of water security. Universal, affordable and sustainable access to WASH is a key issue within international development and is the focus of the first two targets of Sustainable Development Goal 6. Targets 6.1 and 6.2 aim at equitable and accessible water and sanitation for all. In 2017 it was estimated that 2.3 billion people live without basic sanitation facilities and 844 million people live without access to safe and clean drinking water.

Anthony Costello is a British paediatrician. Until 2015 Costello was Professor of International Child Health and Director of the Institute for Global Health at the University College London. Costello is most notable for his work on improving survival among mothers and their newborn infants in poor populations of developing countries. From 2015 to 2018 he was director of maternal, child and adolescent health at the World Health Organization in Geneva.
In medicine, a stepped-wedge trial is a type of randomised controlled trial (RCT). An RCT is a scientific experiment that is designed to reduce bias when testing a new medical treatment, a social intervention, or another testable hypothesis.
References
- ↑ Andersson N. Proof of impact and pipeline planning: directions and challenges for social audit in the health sector. BMC Health Services Research 2011;11(supp2):S16
- ↑ Hussey MA, Hughes JP: Design and analysis of stepped wedge cluster randomized trials. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2007, 28(2):182-191.