
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

Shackleton Glacier is a major Antarctic glacier, over 60 nautical miles long and from 5 to 10 nautical miles wide, descending from the Antarctic Plateau from the vicinity of Roberts Massif and flowing north through the Queen Maud Mountains to enter the Ross Ice Shelf between Mount Speed and Waldron Spurs. Discovered by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS) (1939–41) and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Sir Ernest Shackleton, British Antarctic explorer.

The Taylor Glacier is a glacier in Antarctica about 35 nautical miles long, flowing from the plateau of Victoria Land into the western end of Taylor Valley, north of the Kukri Hills. It flows to the south of the Asgard Range. The middle part of the glacier is bounded on the north by the Inland Forts and on the south by Beacon Valley.
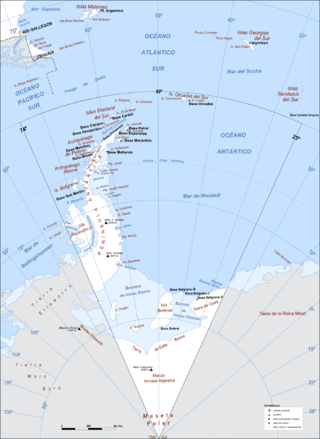
Argentine Antarctica is an area on Antarctica claimed by Argentina as part of its national territory. It consists of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel. This region overlaps with British and Chilean claims in Antarctica. None of these claims have widespread international recognition.
Reclus Peninsula is a 7 nautical miles peninsula on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It borders Charlotte Bay to its east.
Lennox-King Glacier is a large valley glacier, about 40 nautical miles (70 km) long that flows east into the Ross Ice Shelf.

Roperuelos del Páramo is a municipality located in the province of León, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2004 census (INE), the municipality has a population of 737 inhabitants.
Simpson Glacier is a glacier, 6 nautical miles, in the Admiralty Mountains, Antarctica. It flows northward to the coast between Nelson Cliff and Mount Cherry-Garrard where it forms the Simpson Glacier Tongue.
São Salvador do Tocantins is a municipality in the state of Tocantins in the Northern region of Brazil.

La Punta is a village and municipality in San Luis Province in central Argentina.
The Latady Mountains are a group of mountains rising west of Gardner Inlet and between Wetmore Glacier and Ketchum Glacier, in southeastern Palmer Land, Antarctica.

Bilgeri Glacier is a glacier flowing into Barilari Bay south of Huitfeldt Point and west of Byaga Point, on Velingrad Peninsula on the west coast of Graham Land in Antarctica. It was charted by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill, 1934–37, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 for Georg Bilgeri (1873–1934), Austrian pioneer exponent of skiing, inventor of the first spring ski binding, and author of one of the earliest skiing manuals.
Bowman Inlet is an ice-filled inlet between Kay Nunatak and Platt Point on the Hollick-Kenyon Peninsula, on the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula.
Channel Glacier is a through glacier, 1.5 nautical miles (3 km), extending in an east-west direction across Wiencke Island, between Nipple Peak and Wall Range, in the Palmer Archipelago. It was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache 1897–99. The name appears on a chart based on a 1927 survey by DI personnel on the Discovery.

Wiggins Glacier is a 10 nautical miles (18 km) long glacier on Kyiv Peninsula in Antarctica, flowing from Bruce Plateau to the west coast of Graham Land just south of Blanchard Ridge. Charted by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Charcot, and named Glacier du Milieu. Feeling that a more distinctive name was needed, the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1959 renamed the glacier for W.D.C. Wiggins, then Deputy Director of Overseas Surveys.
Planet Heights is a series of summits running along an ice-free ridge, extending 24 nautical miles (44 km) in a north-south direction between the southernmost extremity of the LeMay Range and George VI Sound in the east part of Alexander Island, Antarctica. Many landforms and nearby features are named in association with this mountain range; some of these include landforms named after astronomers, satellites, planets and other things related to astrology and astrophysics. The mountain range was first mapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, by Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1960. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) from association with the nearby glaciers named for planets of the Solar System. The only planet that is not featured in any of these glaciers is the planet Earth, as there are no glaciers named "Earth Glacier" and this glacier does not exist.
The Edgeworth Glacier is a glacier 12 nautical miles long, flowing south-southwestwards from the edge of Detroit Plateau below Wolseley Buttress to the ice shelf west of Sobral Peninsula, Graham Land, Antarctica.
Gould Glacier is a glacier, 12 miles (19 km) long, on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica, flowing south-east into Mill Inlet, to the west of Aagaard Glacier. It was first surveyed by the Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey in 1946–47, and named "East Gould Glacier". Together with "West Gould Glacier" it was reported to fill a transverse depression across Graham Land, but further survey in 1957 showed that there is no close topographical alignment between the two. The name Gould Glacier, after Rupert T. Gould, a British polar historian and cartographer, is now only applied to this glacier, and the west glacier is now called Erskine Glacier.
Sjögren Glacier is a glacier 15 nautical miles long in the south part of Trinity Peninsula, Antarctica. It flows southeast from Detroit Plateau to the south side of Mount Wild, where it enters Prince Gustav Channel.








