Pitcairn may refer to:
Pitcairn may refer to:

The Pitcairn Islands, officially the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, is a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean that form the sole British Overseas Territory in the Pacific Ocean. The four islands—Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno—are scattered across several hundred miles of ocean and have a combined land area of about 18 square miles (47 km2). Henderson Island accounts for 86% of the land area, but only Pitcairn Island is inhabited. The islands nearest to the Pitcairn Islands are Mangareva to the west and Easter Island to the east.
Henderson may refer to:

The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remnants of the former British Empire and do not form part of the United Kingdom itself. The permanently inhabited territories are internally self-governing, with the United Kingdom retaining responsibility for defence and foreign relations. Three of the territories are inhabited only by a transitory population of military or scientific personnel. All but one of the rest are listed by the UN Special Committee on Decolonization as non-self-governing territories. All fourteen have the British monarch as head of state.
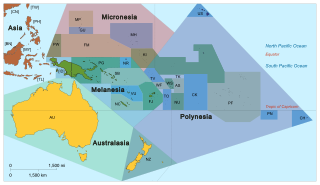
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania.

The coat of arms of the Pitcairn Islands is an official emblem of the British Overseas Territory of the Pitcairn Islands, alongside the flag of the Pitcairn Islands, and was granted by royal warrant on 4 November 1969. The flag, which consists of a Blue Ensign displaying the coat of arms, was granted on 2 April 1984.

The history of the Pitcairn Islands begins with the colonization of the islands by Polynesians in the 11th century. Polynesian people established a culture that flourished for four centuries and then vanished. They lived on Pitcairn and Henderson Islands, and on Mangareva Island 540 kilometres (340 mi) to the northwest, for about 400 years.

Oeno Island or Holiday Island a coral atoll in the South Pacific Ocean, part of the Pitcairn Islands overseas territory.

Ducie Island is an uninhabited atoll in the Pitcairn Islands. It lies east of Pitcairn Island, and east of Henderson Island, and has a total area of 1.5 square miles (3.9 km2), which includes the lagoon. It is 1.5 miles (2.4 km) long, measured northeast to southwest, and about 1 mile (1.6 km) wide. The island is composed of four islets: Acadia, Pandora, Westward and Edwards.

Asia-Pacific (APAC) is the part of the world near the western Pacific Ocean. The Asia-Pacific region varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, Russian Far East, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australasia and Pacific Islands.
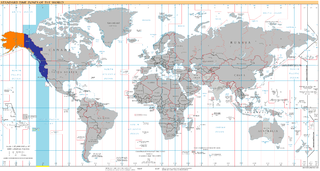
UTC−08:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −08:00. This time is used:
The indigenous peoples of Oceania are Aboriginal Australians, Papuans, and Austronesians. These indigenous peoples have a historical continuity with pre-colonial societies that developed on their territories. With the notable exceptions of Australia, New Zealand, Hawaii, New Caledonia, Guam, and Northern Mariana Islands, indigenous peoples make up the majority of the populations of Oceania.

The Sail and Life Training Society (SALTS), founded in 1974, is a non-profit Christian organization based in Victoria, British Columbia. SALTS provides sail training and life lessons for 1,700 young people each year on tall ships and provides a valued link to the area's maritime heritage. Currently, SALTS administrative offices are located on Herald Street in downtown Victoria, with a shop space located nearby in the Rock Bay area.
Halifax commonly refers to:
Hamilton may refer to:

HMS Briton was a 38-gun fifth-rate frigate of the British Royal Navy's Leda class. She was ordered on 28 September 1808 and her keel laid down at Chatham Dockyard in February 1810. Navy veteran Sir Thomas Staines was appointed her first captain on 7 May 1812 but did not join the ship until 17 June 1813 owing to his being at sea aboard HMS Hamadryad. After a period of cruising in the Bay of Biscay, the vessel set sail for South America where during the course of several missions she unexpectedly encountered the last member of the crew that had seized HMS Bounty from its captain Lieutenant William Bligh during the 1789 mutiny aboard the ship. With the coming of the Pax Britannica in 1815, Briton undertook various voyages before she was broken up in 1860.

John I. Tay was a Seventh-day Adventist missionary who was known for his pioneering work in the South Pacific. It was through his efforts that most of the inhabitants of Pitcairn Island were converted to Adventism, and that the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists purchased the Pitcairn schooner for missionary work in the South Pacific.

Edwin Sebastian Butz was a Seventh-day Adventist (SDA) missionary who was active in Oceania and in Australia.

Pitcairn was a schooner built in 1890 for the Seventh-day Adventist Church for use in missionary work in the South Pacific. After six missionary voyages, the schooner was sold in 1900 for commercial use, and renamed Florence S. She was lost by stranding on the island of Mindoro, Philippine Islands, on 17 October 1912.
Same-sex marriage in the Pitcairn Islands has been legal since 14 May 2015. An ordinance to permit same-sex marriages was passed unanimously by the Island Council on 1 April 2015, and received royal assent by Governor Jonathan Sinclair on 5 May.