
Chaldea was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BC, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was located in the marshy land of the far southeastern corner of Mesopotamia and briefly came to rule Babylon. The Hebrew Bible uses the term כשדים (Kaśdim) and this is translated as Chaldaeans in the Greek Old Testament, although there is some dispute as to whether Kasdim in fact means Chaldean or refers to the south Mesopotamian Kaldu.

The Kingdom of Israel, or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an Israelite kingdom in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age, whose beginnings can be dated back to the first half of the 10th century BCE. The kingdom controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan. The regions of Samaria and Galilee underwent a period with large number of settlements during the 10th century BCE, with the capital in Shechem, and then in Tirzah. The kingdom was ruled by the Omride dynasty in the 9th century BCE, whose political center was the city of Samaria.

Omri was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the sixth king of Israel. He was a successful military campaigner who extended the northern kingdom of Israel. Other monarchs from the House of Omri are Ahab, Ahaziah, Joram, and Athaliah. Like his predecessor, king Zimri, who ruled for only seven days, Omri is the second king mentioned in the Bible without a statement of his tribal origin. One possibility, though unproven, is that he was of the tribe of Issachar.

Shalmaneser III was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Ashurnasirpal II in 859 BC to his own death in 824 BC.

The Medes were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, they occupied the mountainous region of northwestern Iran and the northeastern and eastern region of Mesopotamia in the vicinity of Ecbatana. Their consolidation in Iran is believed to have occurred during the 8th century BC. In the 7th century BC, all of western Iran and some other territories were under Median rule, but their precise geographic extent remains unknown.

Shalmaneser V was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Tiglath-Pileser III in 727 BC to his deposition and death in 722 BC. Though Shalmaneser V's brief reign is poorly known from contemporary sources, he remains known for the conquest of Samaria and the fall of the Kingdom of Israel, though the conclusion of that campaign is sometimes attributed to his successor, Sargon II, instead.

Hoshea was the nineteenth and last king of the northern Kingdom of Israel and son of Elah. William F. Albright dated his reign to 732–721 BCE, while E. R. Thiele offered the dates 732–723 BCE.

The Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III is a black limestone Neo-Assyrian sculpture with many scenes in bas-relief and inscriptions. It comes from Nimrud, in northern Iraq, and commemorates the deeds of King Shalmaneser III. It is on display at the British Museum in London, and several other museums have cast replicas.
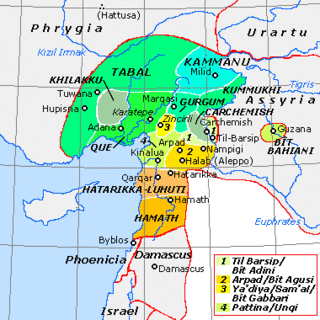
Tabal, later reorganised into Bīt-Burutaš or Bīt-Paruta, was a Luwian-speaking Syro-Hittite state which existed in southeastern Anatolia in the Iron Age.
Gindibu was a Qedarite Arab king

The Omride dynasty, Omrides or House of Omri were the ruling dynasty of the Kingdom of Samaria founded by King Omri. The dynasty's rule ended with the conquest of Samaria by the Neo-Assyrian Empire under Shalmaneser V, who annexed the territory as the Assyrian province of Samerina.
Cybistra or Kybistra, earlier known as Ḫubišna, was a town of ancient Cappadocia or Cilicia.
Shamshi-ilu (Šamši-ilu) was an influential court dignitary and commander in chief (turtanu) of the Assyrian army who rose in high prominence.
The Assyrian conquest of Aram concerns the series of conquests of largely Aramean, Phoenician, Sutean and Neo-Hittite states in the Levant by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. This region was known as Eber-Nari and Aram during the Middle Assyrian Empire and the Neo-Assyrian Empire.

The Assyrian captivity, also called the Assyrian exile, is the period in the history of ancient Israel and Judah during which several thousand Israelites from the Kingdom of Israel were dispossessed and forcibly relocated by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. One of many instances attesting Assyrian resettlement policy, this mass deportation of the Israelite nation began immediately after the Assyrian conquest of Israel, which was overseen by the Assyrian kings Tiglath-Pileser III and Shalmaneser V. The later Assyrian kings Sargon II and Sennacherib also managed to subjugate the Israelites in the neighbouring Kingdom of Judah following the Assyrian siege of Jerusalem in 701 BCE, but were unable to annex their territory outright. The Assyrian captivity's victims are known as the Ten Lost Tribes, and Judah was left as the sole Israelite kingdom until the Babylonian siege of Jerusalem in 587 BCE, which resulted in the Babylonian captivity of the Jewish people. Not all of Israel's populace was deported by the Assyrians; those who were not expelled from the former kingdom's territory eventually became known as the Samaritan people.

The Kurkh Monoliths are two Assyrian stelae of c. 852 BC & 879 BC that contain a description of the reigns of Ashurnasirpal II and his son Shalmaneser III. The Monoliths were discovered in 1861 by a British archaeologist John George Taylor, who was the British Consul-General stationed in the Ottoman Eyalet of Kurdistan, at a site called Kurkh, which is now known Üçtepe Höyük, in the district of Bismil, in the province of Diyarbakir of Turkey. Both stelae were donated by Taylor to the British Museum in 1863.

Kummuh was an Iron Age Neo-Hittite kingdom located on the west bank of the Upper Euphrates within the eastern loop of the river between Melid and Carchemish. Assyrian sources refer to both the land and its capital city by the same name. The city is identified with the classical-period Samosata, which has now been flooded under the waters of a newly built dam. Urartian sources refer to it as Kummaha. The name is also attested in at least one local royal inscription dating to the 8th century BCE. Other places that are mentioned in historical sources as lying within Kummuh are lands of Kištan and Halpi, and cities of Wita, Halpa, Parala, Sukiti and Sarita(?). Kummuh bordered the kingdoms of Melid to the north, Gurgum to the west and Carchemish to the south, while to the east it faced Assyria and later Urartu.

The timeline of ancient Assyria can be broken down into three main eras: the Old Assyrian period, Middle Assyrian Empire, and Neo-Assyrian Empire. Modern scholars typically also recognize an Early period preceding the Old Assyrian period and a post-imperial period succeeding the Neo-Assyrian period.

2 Kings 18 is the eighteenth chapter of the second part of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the Second Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. This chapter records the events during the reign of Hezekiah, the king of Judah, a part of the section comprising 2 Kings 18:1 to 20:21, with a parallel version in Isaiah 36–39.

2 Kings 17 is the seventeenth chapter of the second part of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the Second Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. This chapter records the events during the reigns of Hoshea the last king of Israel, the capture of Samaria and the deportation of the northern kingdom population by the Assyrians.













