
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.

Paranthropus is a genus of extinct hominin which contains two widely accepted species: P. robustus and P. boisei. However, the validity of Paranthropus is contested, and it is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Australopithecus. They are also referred to as the robust australopithecines. They lived between approximately 2.9 and 1.2 million years ago (mya) from the end of the Pliocene to the Middle Pleistocene.
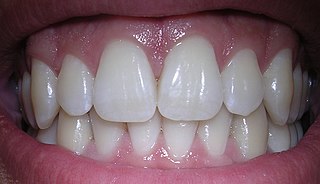
Human teeth function to mechanically break down items of food by cutting and crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digesting. As such, they are considered part of the human digestive system. Humans have four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, which each have a specific function. The incisors cut the food, the canines tear the food and the molars and premolars crush the food. The roots of teeth are embedded in the maxilla or the mandible and are covered by gums. Teeth are made of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness.

Tooth enamel is one of the four major tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface.

Ameloblasts are cells present only during tooth development that deposit tooth enamel, which is the hard outermost layer of the tooth forming the surface of the crown.
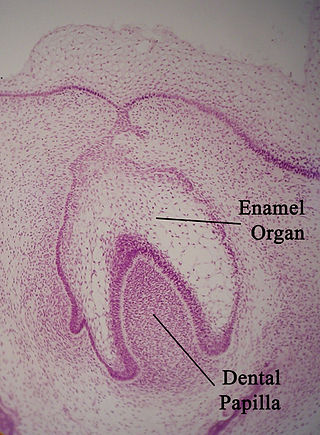
The enamel organ, also known as the dental organ, is a cellular aggregation seen in a developing tooth and it lies above the dental papilla. The enamel organ which is differentiated from the primitive oral epithelium lining the stomodeum. The enamel organ is responsible for the formation of enamel, initiation of dentine formation, establishment of the shape of a tooth's crown, and establishment of the dentoenamel junction.
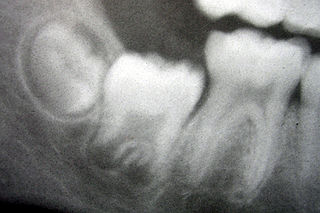
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stages of fetal development. Primary (baby) teeth start to form between the sixth and eighth week of prenatal development, and permanent teeth begin to form in the twentieth week. If teeth do not start to develop at or near these times, they will not develop at all, resulting in hypodontia or anodontia.
Amelogenesis is the formation of enamel on teeth and begins when the crown is forming during the advanced bell stage of tooth development after dentinogenesis forms a first layer of dentin. Dentin must be present for enamel to be formed. Ameloblasts must also be present for dentinogenesis to continue.

Paranthropus robustus is a species of robust australopithecine from the Early and possibly Middle Pleistocene of the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa, about 2.27 to 0.87 million years ago. It has been identified in Kromdraai, Swartkrans, Sterkfontein, Gondolin, Cooper's, and Drimolen Caves. Discovered in 1938, it was among the first early hominins described, and became the type species for the genus Paranthropus. However, it has been argued by some that Paranthropus is an invalid grouping and synonymous with Australopithecus, so the species is also often classified as Australopithecus robustus.
Enamel lamellae are a type of hypomineralized structure in teeth that extend either from the dentinoenamel junction (DEJ) to the surface of the enamel, or vice versa. In essence, they are prominent linear enamel defects, but are of no clinical consequence. These structures contain proteins, proteoglycans, and lipids.

Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is deficient in quantity, caused by defective enamel matrix formation during enamel development, as a result of inherited and acquired systemic condition(s). It can be identified as missing tooth structure and may manifest as pits or grooves in the crown of the affected teeth, and in extreme cases, some portions of the crown of the tooth may have no enamel, exposing the dentin. It may be generalized across the dentition or localized to a few teeth. Defects are categorized by shape or location. Common categories are pit-form, plane-form, linear-form, and localised enamel hypoplasia. Hypoplastic lesions are found in areas of the teeth where the enamel was being actively formed during a systemic or local disturbance. Since the formation of enamel extends over a long period of time, defects may be confined to one well-defined area of the affected teeth. Knowledge of chronological development of deciduous and permanent teeth makes it possible to determine the approximate time at which the developmental disturbance occurred. Enamel hypoplasia varies substantially among populations and can be used to infer health and behavioural impacts from the past. Defects have also been found in a variety of non-human animals.

Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is a congenital disorder which presents with a rare abnormal formation of the enamel or external layer of the crown of teeth, unrelated to any systemic or generalized conditions. Enamel is composed mostly of mineral, that is formed and regulated by the proteins in it. Amelogenesis imperfecta is due to the malfunction of the proteins in the enamel as a result of abnormal enamel formation via amelogenesis.

Kohlschütter–Tönz syndrome (KTS), also called amelo-cerebro-hypohidrotic syndrome, is a rare inherited syndrome characterized by epilepsy, psychomotor delay or regression, intellectual disability, and yellow teeth caused by amelogenesis imperfecta. It is a type A ectodermal dysplasia.

Tooth pathology is any condition of the teeth that can be congenital or acquired. Sometimes a congenital tooth disease is called a tooth abnormality. These are among the most common diseases in humans The prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of these diseases are the base to the dentistry profession, in which are dentists and dental hygienists, and its sub-specialties, such as oral medicine, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and endodontics. Tooth pathology is usually separated from other types of dental issues, including enamel hypoplasia and tooth wear.

Tricho–dento–osseous syndrome (TDO) is a rare, systemic, autosomal dominant genetic disorder that causes defects in hair, teeth, and bones respectively. This disease is present at birth. TDO has been shown to occur in areas of close geographic proximity and within families; most recent documented cases are in Virginia, Tennessee, and North Carolina. The cause of this disease is a mutation in the DLX3 gene, which controls hair follicle differentiation and induction of bone formation. All patients with TDO have two co-existing conditions called enamel hypoplasia and taurodontism in which the abnormal growth patterns of the teeth result in severe external and internal defects. The hair defects are characterized as being rough, course, with profuse shedding. Hair is curly and kinky at infancy but later straightens. Dental defects are characterized by dark-yellow/brownish colored teeth, thin and/or possibly pitted enamel, that is malformed. The teeth can also look normal in color, but also have a physical impression of extreme fragility and thinness in appearance. Additionally, severe underbites where the top and bottom teeth fail to correctly align may be present; it is common for the affected individual to have a larger, more pronounced lower jaw and longer bones. The physical deformities that TDO causes become more noticeable with age, and emotional support for the family as well as the affected individual is frequently recommended. Adequate treatment for TDO is a team based approach, mostly involving physical therapists, dentists, and oromaxillofacial surgeons. Genetic counseling is also recommended.

Medieval Bioarchaeology is the study of human remains recovered from medieval archaeological sites. Bioarchaeology aims to understand populations through the analysis of human skeletal remains and this application of bioarchaeology specifically aims to understand medieval populations. There is an interest in the Medieval Period when it comes to bioarchaeology, because of how differently people lived back then as opposed to now, in regards to not only their everyday life, but during times of war and famine as well. The biology and behavior of those that lived in the Medieval Period can be analyzed by understanding their health and lifestyle choices.
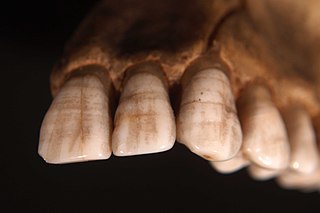
Linear enamel hypoplasia (LEH) is a failure of the tooth enamel to develop correctly during growth, leaving bands of reduced enamel on a tooth surface. It is the most common type of enamel hypoplasia reported in clinical and archaeological samples, with other types including plane-form enamel hypoplasia and pitting enamel hypoplasia.

Plane-form enamel hypoplasia is often seen as the most severe type of enamel hypoplasia, and results from enamel matrix formation stopping, resulting in areas of crown with little or no dental enamel deposition. A relatively short period of severe stress can potentially lead to a very large defect. Plane-form enamel hypoplasia can be caused by a variety of factors, including severe illness/malnutrition, as well as specific conditions such as amelogenesis imperfecta and congenital syphilis. In severe cases enamel can be completely missing from areas of the crown, exposing the underlying dentine.
Chalky Teeth is a colloquialism used to describe teeth that are abnormal in some way. The term usually refers to tooth enamel that is visibly different in colour, consistency or shape (morphology). Hence, by analogy to blackboard chalk, "chalky enamel" is discoloured, opaque, soft, porous and prone to degradation or staining – unlike normal enamel which is translucent, hard and impermeable. Chalky teeth and derivative terms have received widespread exposure as a metaphor for malformed teeth with elevated risk of tooth decay. A public "Chalky Teeth Campaign" highlights the major socioeconomic burdens of this medico-dental problem and desirability of research into prevention. The gritty sensation elicited by oxalate-rich foods such as spinach may also be described as "chalky teeth'.
Near Eastern bioarchaeology covers the study of human skeletal remains from archaeological sites in Cyprus, Egypt, Levantine coast, Jordan, Turkey, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, United Arab Emirates, Oman, and Yemen.

















