Related Research Articles

Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei, usually deuterium and tritium, combine to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers active or main-sequence stars and other high-magnitude stars, where large amounts of energy are released.

A stellarator is a plasma device that relies primarily on external magnets to confine a plasma. Scientists researching magnetic confinement fusion aim to use stellarator devices as a vessel for nuclear fusion reactions. The name refers to the possibility of harnessing the power source of the stars, such as the Sun. It is one of the earliest fusion power devices, along with the z-pinch and magnetic mirror.

Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2023, no device has reached net power.

Inertial electrostatic confinement, or IEC, is a class of fusion power devices that use electric fields to confine the plasma rather than the more common approach using magnetic fields found in magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) designs. Most IEC devices directly accelerate their fuel to fusion conditions, thereby avoiding energy losses seen during the longer heating stages of MCF devices. In theory, this makes them more suitable for using alternative aneutronic fusion fuels, which offer a number of major practical benefits and makes IEC devices one of the more widely studied approaches to fusion.

A levitated dipole is a type of nuclear fusion reactor design using a superconducting torus which is magnetically levitated inside the reactor chamber. The name refers to the magnetic dipole that forms within the reaction chamber, similar to Earth's or Jupiter's magnetospheres. It is believed that such an apparatus could contain plasma more efficiently than other fusion reactor designs. The concept of the levitated dipole as a fusion reactor was first theorized by Akira Hasegawa in 1987.
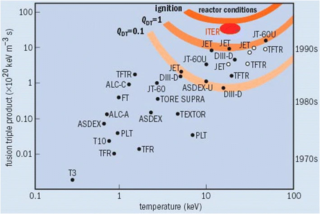
The Lawson criterion is a figure of merit used in nuclear fusion research. It compares the rate of energy being generated by fusion reactions within the fusion fuel to the rate of energy losses to the environment. When the rate of production is higher than the rate of loss, the system will produce net energy. If enough of that energy is captured by the fuel, the system will become self-sustaining and is said to be ignited.

The Tokamak Fusion Test Reactor (TFTR) was an experimental tokamak built at Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) circa 1980 and entering service in 1982. TFTR was designed with the explicit goal of reaching scientific breakeven, the point where the heat being released from the fusion reactions in the plasma is equal or greater than the heating being supplied to the plasma by external devices to warm it up.

Aneutronic fusion is any form of fusion power in which very little of the energy released is carried by neutrons. While the lowest-threshold nuclear fusion reactions release up to 80% of their energy in the form of neutrons, aneutronic reactions release energy in the form of charged particles, typically protons or alpha particles. Successful aneutronic fusion would greatly reduce problems associated with neutron radiation such as damaging ionizing radiation, neutron activation, reactor maintenance, and requirements for biological shielding, remote handling and safety.

Magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of controlled fusion research, along with inertial confinement fusion.
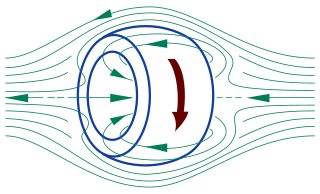
A field-reversed configuration (FRC) is a type of plasma device studied as a means of producing nuclear fusion. It confines a plasma on closed magnetic field lines without a central penetration. In an FRC, the plasma has the form of a self-stable torus, similar to a smoke ring.

A spheromak is an arrangement of plasma formed into a toroidal shape similar to a smoke ring. The spheromak contains large internal electric currents and their associated magnetic fields arranged so the magnetohydrodynamic forces within the spheromak are nearly balanced, resulting in long-lived (microsecond) confinement times without external fields. Spheromaks belong to a type of plasma configuration referred to as the compact toroids. A spheromak can be made and sustained using magnetic flux injection, leading to a dynomak.
The Madison Symmetric Torus (MST) is a reversed field pinch (RFP) physics experiment with applications to both fusion energy research and astrophysical plasmas.
The tokamak à configuration variable is an experimental tokamak located at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Swiss Plasma Center (SPC) in Lausanne, Switzerland. As the largest experimental facility of the Swiss Plasma Center, the TCV tokamak explores the physics of magnetic confinement fusion. It distinguishes itself from other tokamaks with its specialized plasma shaping capability, which can produce diverse plasma shapes without requiring hardware modifications.
The polywell is a design for a fusion reactor based on two ideas: heating ions by concentrating (-) charge to accelerate the ions and trapping a diamagnetic plasma inside a cusp field.

The Helically Symmetric Experiment, is an experimental plasma confinement device at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, with design principles that are intended to be incorporated into a fusion reactor. The HSX is a modular coil stellarator which is a toroid-shaped pressure vessel with external electromagnets which generate a magnetic field for the purpose of containing a plasma. It began operation in 1999.
The Columbia Non-neutral Torus (CNT) is a small stellarator at the Columbia University Plasma Physics Laboratory designed by Thomas Sunn Pedersen with the aid of Wayne Reiersen and Fred Dahlgren of the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory to conduct the first investigation of non-neutral plasmas confined on magnetic surfaces. The experiment, which began operation in November 2004, is funded by the National Science Foundation and the United States Department of Energy in the form of a Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) award.
Magnetized Target Fusion (MTF) is a fusion power concept that combines features of magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) and inertial confinement fusion (ICF). Like the magnetic approach, the fusion fuel is confined at lower density by magnetic fields while it is heated into a plasma. As with the inertial approach, fusion is initiated by rapidly squeezing the target to greatly increase fuel density and temperature. Although the resulting density is far lower than in ICF, it is thought that the combination of longer confinement times and better heat retention will let MTF operate, yet be easier to build. The term magneto-inertial fusion (MIF) is similar, but encompasses a wider variety of arrangements. The two terms are often applied interchangeably to experiments.
The Lithium Tokamak Experiment (LTX), and its predecessor, the Current Drive Experiment-Upgrade (CDX-U), are devices dedicated to the study of liquid lithium as a plasma-facing component (PFC) at Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory.
The Lockheed Martin Compact Fusion Reactor (CFR) is a fusion power project at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works. Its high-beta configuration, which implies that the ratio of plasma pressure to magnetic pressure is greater than or equal to 1, allows a compact design and expedited development. The project was active between 2010 and 2019, after that date there have been no updates and it appears the division has shut down.

TJ-II is a flexible Heliac installed at Spain's National Fusion Laboratory.