
In military terminology, a squad is among the smallest of military organizations and is led by a non-commissioned officer. NATO and U.S. doctrine define a squad as an organization "larger than a team, but smaller than a section." while U.S. Army doctrine further defines a squad as a "small military unit typically containing two or more fire teams." In American usage, a squad consists of eight to fourteen soldiers, and may be further subdivided into fireteams.
Sergeant (Sgt) is a rank in use by the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services. The alternative spelling, serjeant, is used in The Rifles and other units that draw their heritage from the British light infantry. Its origin is the Latin serviens, 'one who serves', through the Old French term serjant.
Staff sergeant is a rank of non-commissioned officer used in the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services.
Gunnery Sergeant (GySgt) is the seventh enlisted rank in the United States Marine Corps, above staff sergeant and below master sergeant and first sergeant, and is a senior non-commissioned officer (SNCO). It has a pay grade of E-7.

The flag of the United States Marine Corps is the flag used to represent the U.S. Marine Corps, as well as its subsidiary units and formations.

A drill instructor is a non-commissioned officer in the armed forces, fire department, or police forces with specific duties that vary by country. Foot drill, military step, and marching are typically taught by drill instructors.
A Drill Instructor Ribbon is a military award of the United States Armed Forces which is issued by the U.S. Navy, U.S. Air Force, U.S. Space Force, and U.S. Marine Corps. The Drill Instructor Ribbon recognizes those service members who are trained and qualified as military instructors to new recruits during initial basic training.
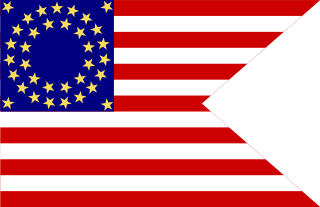
In the United States Armed Forces, a guidon is a military standard or flag that company/battery/troop or platoon-sized detachments carry to signify their unit designation and branch/corps affiliation or the title of the individual who carries it. A basic guidon can be rectangular, but sometimes has a triangular portion removed from the fly.

Alford L. McMichael is a retired United States Marine who served as the 14th Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps from 1999 to 2003. He was also the first Staff Non-Commissioned Officer for Allied Command Operations for NATO (2003–2006). McMichael retired from the Marine Corps in 2006 after 36 years of service.

Lewis G. Lee is a retired United States Marine who served as the 13th Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps from 1995 to 1999. He retired from active duty in 1999 after over 31 years of service. He was the last Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps to serve in combat in the Vietnam War.

David W. Sommers is a retired United States Marine who served as the 11th Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps from 1987 to 1991.

Staff Sergeant Ambrosio Guillen was a United States Marine who was posthumously awarded the Medal of Honor—the United States' highest military award for valor—for his heroic actions and sacrifice of life on July 25, 1953, two days before the ceasefire, during the Korean War. He was responsible for his infantry platoon's turning an overwhelming enemy attack into a defeat and disorderly retreat.

Jimmie Earl Howard was a Marine Corps staff sergeant when he led an eighteen-man reconnaissance patrol in a fierce battle against a battalion of Viet Cong in June 1966. As a result of his heroic actions, Howard became the sixth U.S. Marine to be awarded the nation's highest honor for heroism in combat in Vietnam. The Medal of Honor was presented by President Lyndon B. Johnson in White House ceremonies on August 21, 1967.

Captain John James McGinty III was a United States Marine Corps officer who received the United States militaries' highest decoration — the Medal of Honor — for heroism during July 1966 in the Vietnam War.

Karl Gorman Taylor Sr. was a United States Marine Corps staff sergeant who was killed in action during his second tour of duty in the Vietnam War. He was posthumously awarded the Medal of Honor, the nation's highest military decoration for valor, for his heroic actions on December 8, 1968.

Carlton Wayne Kent is a retired United States Marine who served as the 16th Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps. He succeeded John L. Estrada on April 25, 2007, and was succeeded by Micheal Barrett on June 9, 2011.

United States Marine Corps Recruit Training is a 13-week program, including in & out-processing, of recruit training that each recruit must successfully complete in order to serve in the United States Marine Corps.

The Young Marines is a youth program in the United States and Japan open to all youth between the ages of 8 and 18 or high school graduation. The Young Marines program is the leader in youth Drug Demand Reduction (DDR) education and has received many accolades for its DDR programs. It has been awarded the United States Department Of Defense's Fulcrum Shield Award 12 times, with the last one awarded in 2022. The program has partnered up with National Family Partnership to help keep kids off drugs. The Young Marines take part in Red Ribbon Week and hold activities and events that take place during that week in October to push drug prevention and resistance efforts nationally. A documentary released in 2019, but filmed much earlier The Recruits, has brought the Young Marines under renewed scrutiny

Justin D. LeHew is a United States Marine who served in the War on Terror. He was awarded the Navy Cross for his actions on 23 and 24 March 2003 during the initial 2003 invasion of Iraq. He was hand picked to spearhead the rescue operation and recovery of the U.S. Army's 507th Maintenance Company on 23 March and subsequently was called upon again to take part in the rescue operation of US Army Private Jessica Lynch on 1 April 2003. He is also a recipient of the Bronze Star with Combat Distinguishing Device denoting Valor for his heroic actions from 5 to 28 August 2004 during the Battle of Najaf.

Troy E. Black is a United States Marine who has served as the 5th senior enlisted advisor to the chairman since November 3, 2023. He was the 19th sergeant major of the Marine Corps from July 2019 to August 2023.