
Trujillo is a city in coastal northwestern Peru and the capital of the Department of La Libertad. It is the third most populous city and center of the third most populous metropolitan area of Peru. It is located on the banks of the Moche River, near its mouth at the Pacific Ocean, in the Moche Valley. This was a site of the great prehistoric Moche and Chimu cultures before the Inca conquest and subsequent expansion.

The Plaza de Armas of Ayacucho is in the city center of Ayacucho, Peru. Central plazas in Peru are typically called the Plaza Mayor. The Plaza de Armas is so named because it was the place where the city's defenders assembled during emergencies. In Ayacucho it is known as Sucre Park.

The Angel of Independence, most commonly known by the shortened name El Ángel and officially known as Monumento a la Independencia, is a victory column on a roundabout on the major thoroughfare of Paseo de la Reforma in downtown Mexico City.

A Spanish Peruvian is a Peruvian citizen of Spanish descent. Among European Peruvians, the Spanish are the largest group of immigrants to settle in the country.

The Jirón de la Unión, or Union Street, is a pedestrian street located in the Historic Centre of Lima, part of the capital of Peru. For many decades it was the most important boulevards of the city, often described as the most aristocratic, where many of the most affluent citizens of the city and most powerful men around the world would meet. Subsequently, with the deterioration of the center of Lima, the Jirón de la Unión lost its aristocratic character and became completely commercialized.

The Plaza Mayor de Lima, or Plaza de Armas de Lima, is considered one of the birthplaces of the city of Lima, as well as the core of the city. Located in the Historic Centre of Lima, it is surrounded by the Government Palace, Lima Metropolitan Cathedral, Archbishop's Palace of Lima, the Municipal Palace, and the Palacio de la Unión.

Edmund Moeller was an early twentieth century German sculptor. He was born on 8 August 1885 in Neustadt, Bavaria and died on 19 January 1958 in Dresden, Saxony. He studied in Dresden and Düsseldorf.
The Historic Centre of Trujillo is the main urban area and the most important center of development and unfolding in the Peruvian city of Trujillo located in La Libertad Region. The whole process of its original urban fabric is in elliptical shape surrounded by España Avenue that was built in the wake of the Wall of Trujillo. It houses the seat of city government and other important entities in the locality. In the center of this historic urban area is the Plaza de Armas of Trujillo that was the scene of the Spanish founded of the city in 1534 and the proclamation of the independence of Trujillo on December 29, 1820.

The Independence of Trujillo refers to the historical events that led to the Intendancy of Trujillo, located in northern Peru of 19th century, becoming independent from the Colonialist Spanish state, during the Peruvian War of Independence 1811-1821. The fight for independence in the north began in the city of Trujillo between 1820 and 1821 and spread throughout north Peru, ending colonialism in nearly all of northern regions of Peru

The Municipality of Trujillo is the Peruvian public institution of government for Trujillo Province, Peru. It is located in the city of Trujillo and is responsible for the supply and management of the province and its districts. This includes rural and urban towns and the provision of local services within its jurisdiction. It is a politically autonomous legal entity and as such it deals with economic and administrative matters.

The Foundation of Trujillo is an example of Spanish colonial expansion that took place in the area known today as the Valley of Moche in northern Peru. The exact date of Trujillo's foundation is still in dispute; according to historian Napoleón Cieza Burga it is November 1534.

The Plazuela El Recreo is a traditional square located in the Peruvian city of Trujillo in La Libertad Region in northern Peru. Situated at the 8th block of the Pizarro street in the Historic Centre of Trujillo in this square are held cultural shows and in March 2012 was the scenery of Trujillo Book Festival. The square has high ficus around. This square has been declared Monumental Heritage of the Nation by the National Institute of Culture of Peru.

Paseo Pizarro is pedestrian walk located on the main street of Trujillo city, in Peru. Pizarro street in blocks 5,6,7 and 8 becomes exclusively a pedestrian and joins the Plaza de Armas with the Plazuela El Recreo, along its four blocks are numerous landmarks like the Palace Iturregui, the Emancipation House, etc. and businesses such as supermarkets, souvenir shops, cafes and bars, etc.
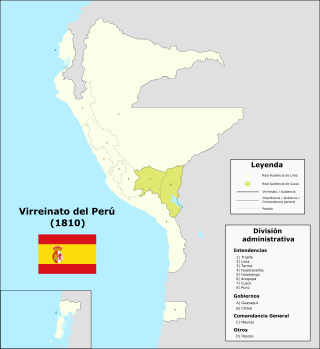
The Intendancy of Trujillo, also known informally as Trujillo Province, was one of the territorial divisions of the Viceroyalty of Peru. This territory was ruled from the city of Trujillo, located in La Libertad Region. It was created in 1784 and lasted until 12 February 1821 when General Jose de San Martin created the Department of Trujillo through the Reglamento Provisional to replace it in the new Republic of Peru.

The Plaza Independencia is a Spanish colonial era plaza in Cebu City.

The Centennial of the Independence of Peru took place on July 28, 1921, as well as in December 9, 1924. To commemorate the hundred years of the country's independence from Spain, large and lavish parties supervised by President Augusto B. Leguía were held.

The Monument to Manco Cápac is a statue located in the homonymous square in La Victoria District, Lima, the work of the Peruvian sculptor David Lozano, inaugurated in 1926.

The Statue of Liberty is a bronze sculpture located in the Plaza Francia of the historic centre of Lima, Peru. It was made in 1926 according to the design of the French sculptor René Bertrand-Boutée and cast by Eugène Soleau. It is a one-piece bronze sculpture about 2 metres high and represents a standing female figure, dressed in a light tunic and with a laurel wreath on her head. This is installed on a 4.30 m high pedestal. The sculpture and the Plaza Francia were declared a monumental urban environment in 1972. In 2018, La Libertad was declared Cultural Heritage of the Nation.

Huaura is a city in Peru. It is the capital of the homonymous district located in the province of Huaura in the department of Lima. It had an estimated population of 24,668 according to the 2017 census. It ceased to be the provincial capital in 1866 in favor of the city of Huacho and is part of the conurbation formed around the latter by means of two bridges over the Huaura River.

The Department of Trujillo was a short-lived department of the Protectorate of Peru that existed from 1821 to 1825, when it renamed into the Department of La Libertad.


































