This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2009) |

A point machine (also known as a point motor, switch machine or switch motor) is a device for operating railway turnouts especially at a distance.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2009) |

A point machine (also known as a point motor, switch machine or switch motor) is a device for operating railway turnouts especially at a distance.
In the earliest times, points were operated manually by levers. Gradually, these were centralized and came to be operated from a signal box, either by rods, or by double wire arrangements.
Since the limitation of mechanical operation restricted the design of track layouts on the one hand, and tended to require more signal boxes, even lightly used ones, on the other hand, there has always been a desire of railway administrations to increase the distance that remote turnouts can be operated. This requires some kind of power operation of points and signals. The principal means of power operation include hydraulic, pneumatic and electric.
More recently with the increase in weight of rail, and the introduction of high speed turnouts with finer angles requiring multiple drives, points have become stiffer and beyond the capability of mechanical drives, forcing the introduction of point machines if not already done so.
Modern point machines have an electric motor and gears to convert the rotational motion of the motor into the linear motion required to switch the points. The gear assembly also provides required transmission ratio so that it can generate necessary force to move switch blades. The machine performs following functions:
A point machine conversion system consists of a remotely controlled device attached to an existing manually operated point that allows the shunter/driver to remotely operate hand points with a radio handset. Each converter can be used as a stand-alone or multiple units can be installed operating together with routing.
The latest development is to mount the switch motor inside a faux railroad tie (aka sleeper) where it is relatively hidden from damage from track maintenance machines. [1]

A relay is an electrically operated switch. It consists of a set of input terminals for a single or multiple control signals, and a set of operating contact terminals. The switch may have any number of contacts in multiple contact forms, such as make contacts, break contacts, or combinations thereof.
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contacts connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow.

A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecules, such as molecular machines. Machines can be driven by animals and people, by natural forces such as wind and water, and by chemical, thermal, or electrical power, and include a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. They can also include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, often called mechanical systems.

A starter is a device used to rotate (crank) an internal-combustion engine so as to initiate the engine's operation under its own power. Starters can be electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic. The starter can also be another internal-combustion engine in the case, for instance, of very large engines, or diesel engines in agricultural or excavation applications.

A railroad switch (AE), turnout, or [set of] points (CE) is a mechanical installation enabling railway trains to be guided from one track to another, such as at a railway junction or where a spur or siding branches off.

On a rail transport system, signalling control is the process by which control is exercised over train movements by way of railway signals and block systems to ensure that trains operate safely, over the correct route and to the proper timetable. Signalling control was originally exercised via a decentralised network of control points that were known by a variety of names including signal box, interlocking tower and signal cabin. Currently these decentralised systems are being consolidated into wide scale signalling centres or dispatch offices. Whatever the form, signalling control provides an interface between the human signal operator and the lineside signalling equipment. The technical apparatus used to control switches (points), signals and block systems is called interlocking.
An actuator is a component of a machine that produces force, torque, or displacement, usually in a controlled way, when an electrical, pneumatic or hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system. An actuator converts such an input signal into the required form of mechanical energy. It is a type of transducer. In simple terms, it is a "mover".

A pencil sharpener is a tool for sharpening a pencil's writing point by shaving away its worn surface. Pencil sharpeners may be operated manually or by an electric motor. It is common for many sharpeners to have a casing around them, which can be removed for emptying the pencil shavings debris into a bin.

A cam timer or drum sequencer is an electromechanical system for controlling a sequence of events automatically. It resembles a music box with movable pins, controlling electrical switches instead of musical notes.

A transmission is a mechanical device which uses gears to change the speed or direction of rotation in a machine. Many transmissions have multiple gear ratios, but there are also transmissions that use a single fixed gear ratio.

A rotary encoder, also called a shaft encoder, is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to analog or digital output signals.
A synchro is, in effect, a transformer whose primary-to-secondary coupling may be varied by physically changing the relative orientation of the two windings. Synchros are often used for measuring the angle of a rotating machine such as an antenna platform or transmitting rotation. In its general physical construction, it is much like an electric motor. The primary winding of the transformer, fixed to the rotor, is excited by an alternating current, which by electromagnetic induction, causes voltages to appear between the Y-connected secondary windings fixed at 120 degrees to each other on the stator. The voltages are measured and used to determine the angle of the rotor relative to the stator.

In railway signalling, an interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. In North America, a set of signalling appliances and tracks interlocked together are sometimes collectively referred to as an interlocking plant or just as an interlocking. An interlocking system is designed so that it is impossible to display a signal to proceed unless the route to be used is proven safe.

A linear actuator is an actuator that creates linear motion, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer peripherals such as disk drives and printers, in valves and dampers, and in many other places where linear motion is required. Hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor.

An axle counter is a system used in railway signalling to detect the clear or occupied status of a section of track between two points. The system generally consists of a wheel sensor and an evaluation unit for counting the axles of the train both into and out of the section. They are often used to replace a track circuit.

Mechanical railway signalling installations rely on lever frames for their operation to interlock the signals, track locks and points to allow the safe operation of trains in the area the signals control. Usually located in the signal box, the levers are operated either by the signalman or the pointsman.

An amplidyne is an obsolete electromechanical amplifier invented prior to World War II by Ernst Alexanderson. It consists of an electric motor driving a DC generator. The signal to be amplified is applied to the generator's field winding, and its output voltage is an amplified copy of the field current. The amplidyne was used in industry in high power servo and control systems, to amplify low power control signals to control powerful electric motors, for example. It is now mostly obsolete.

A valve actuator is the mechanism for opening and closing a valve. Manually operated valves require someone in attendance to adjust them using a direct or geared mechanism attached to the valve stem. Power-operated actuators, using gas pressure, hydraulic pressure or electricity, allow a valve to be adjusted remotely, or allow rapid operation of large valves. Power-operated valve actuators may be the final elements of an automatic control loop which automatically regulates some flow, level or other process. Actuators may be only to open and close the valve, or may allow intermediate positioning; some valve actuators include switches or other ways to remotely indicate the position of the valve.
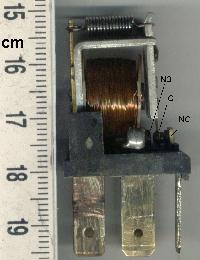
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each other. This process is especially prominent in systems such as those of DC or AC rotating electrical machines which can be designed and operated to generate power from a mechanical process (generator) or used to power a mechanical effect (motor). Electrical engineering in this context also encompasses electronics engineering.

Car controls are the components in automobiles and other powered road vehicles, such as trucks and buses, used for driving and parking.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)