Related Research Articles

Kaliningrad Oblast is the westernmost federal subject of the Russian Federation, in Central and Eastern Europe. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The oblast is surrounded by two European Union and NATO members: Poland to the south and Lithuania to the north and east. The largest city and administrative centre of the province (oblast) is the city of Kaliningrad, formerly known as Königsberg. Half of the population of the oblast lives in Kaliningrad City proper. The port city of Baltiysk is Russia's only port on the Baltic Sea that remains ice-free in winter. Kaliningrad Oblast had a population of roughly 1 million in the Russian Census of 2021. The area of Kaliningrad oblast is 15,125 square kilometers.

Frederick Augustus I was a member of the House of Wettin who reigned as the last Elector of Saxony from 1763 to 1806 and as the first King of Saxony from 1806 to 1827. He was also Duke of Warsaw from 1807 to 1815, a short-lived disputed Grand Duke of Lithuania in 1812, and a legitimate candidate to the Polish throne.

The Kingdom of Prussia constituted the German state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1866 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin.

Prussia was a German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. The Knights had to relocate their headquarters to Mergentheim, but managed to keep land in Livonia until 1561.

The Treaties of Tilsit, also collectively known as the Peace of Tilsit, were two peace treaties signed by French Emperor Napoleon in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland, at the end of the War of the Fourth Coalition. The first was signed on 7 July, between Napoleon and Russian Emperor Alexander I, when they met on a raft in the middle of the Neman river. The second was signed with Prussia on 9 July. The treaties were made at the expense of King Frederick William III of Prussia, who had already agreed to a truce on 25 June after the Grande Armée had captured Berlin and pursued him to the easternmost frontier of his realm.
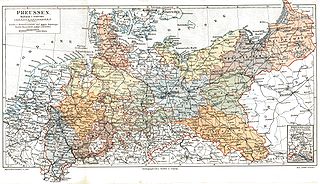
The Provinces of Prussia were the main administrative divisions of Prussia from 1815 to 1946. Prussia's province system was introduced in the Stein-Hardenberg Reforms in 1815, and were mostly organized from duchies and historical regions. Provinces were divided into several Regierungsbezirke, sub-divided into Kreise (districts), and then into Gemeinden (townships) at the lowest level. Provinces constituted the highest level of administration in the Kingdom of Prussia and Free State of Prussia until 1933, when Nazi Germany established de facto direct rule over provincial politics, and were formally abolished in 1946 following World War II. The Prussian provinces became the basis for many federal states of Germany, and the states of Brandenburg, Lower Saxony, and Schleswig-Holstein are direct successors of provinces.

Minister of the Interior is a prominent position in the Government of France. The position is equivalent to the interior minister in other countries, like the Home Secretary in the United Kingdom, the Minister of Public Safety in Canada, or the Minister of Home Affairs in Australia.

Neman, is a town and the administrative center of Nemansky District in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, located in the historic region of Lithuania Minor, on the steep southern bank of the Neman River, where it forms the Russian border with the Klaipėda Region in Lithuania, and 130 kilometers (81 mi) northeast of Kaliningrad, the administrative center of the oblast. Population figures: 11,798 (2010 Census); 12,714 (2002 Census); 13,821 (1989 Soviet census).

The Danubian Principalities was a conventional name given to the Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia, which emerged in the early 14th century. The term was coined in the Habsburg monarchy after the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (1774) in order to designate an area on the lower Danube with a common geopolitical situation. The term was largely used then by foreign political circles and public opinion until the union of the two principalities in 1859. Alongside Transylvania, the United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia became the basis for the Kingdom of Romania, and by extension the modern nation-state of Romania.

Bagrationovsk is a town and the administrative center of Bagrationovsky District in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, located close to the border with Poland, 37 kilometers (23 mi) south of Kaliningrad, the administrative center of the oblast. It has a population of 6,400 (2010 Census).

Internal troops, sometimes alternatively translated as interior troops or interior ministry forces, are a paramilitary and gendarmerie-like law enforcement services, which are found mostly in the post-Soviet states, primarily Russia. Internal troops are subordinated to the interior minister of their respective countries.

The First Partition of Poland took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that eventually ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The growth of power in the Russian Empire threatened the Kingdom of Prussia and the Habsburg monarchy and was the primary motive behind the First Partition.
Prostitution in Poland is legal, but operating brothels or other forms of pimping or coercive prostitution and prostitution of minors are prohibited.

The First French Empire or French Empire and also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 4 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815, when Napoleon was exiled to St. Helena.

The Police of Russia is the national law enforcement agency of Russia, operating under the Ministry of Internal Affairs from September 8, [O.S. 20] 1802. It was established on June 7, [O.S. 18] 1718 by decree of Peter the Great, and in 2011, it replaced the Militsiya, the former police service.

Mental health in Russia is covered by a law, known under its official name—the Law of the Russian Federation "On Psychiatric Care and Guarantees of Citizens' Rights during Its Provision", which is the basic legal act that regulates psychiatric care in the Russian Federation and applies not only to persons with mental disorders but all citizens. A notable exception of this rule is those vested with parliamentary or judicial immunity. Providing psychiatric care is regulated by a special law regarding guarantees of citizens' rights.
In the Russian Empire, government agencies exerted varying levels of control over the content and dissemination of books, periodicals, music, theatrical productions, works of art, and motion pictures. The agency in charge of censorship in the Russian Empire changed over time. In the early eighteenth century, the Russian emperor had direct control, but by the end of the eighteenth century, censorship was delegated to the Synod, the Senate, and the Academy of Sciences. Beginning in the nineteenth century, it fell under the charge of the Ministry of Education and finally the Ministry of Internal Affairs.

The Internal Russian passport is a mandatory identity document for all Russian citizens residing in Russia who are aged 14 or over. The Internal Russian passport is an internal passport used for travel and identification purposes in Russia, which is distinct from the International Russian passport used by Russian citizens to travel in and out of Russian borders.

Pavel Alexandrovich Alexandrov was a distinguished lawyer and state official of the Russian Empire, councillor of state. He investigated the most sensational crimes of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, which received wide coverage in the mass media.
Prostitution in the Soviet Union was not officially recognised domestically as a social phenomenon until 1986.