See also
- Polioencephalomalacia, neurological disease in ruminants, caused by disrupted thiamine production in the body, not related to polioviruses
Polio is the common name of poliomyelitis, an acute clinical disease caused by a poliovirus. Polio (also Polios) may also refer to:

Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. In about 0.5 percent of cases, it moves from the gut to affect the central nervous system, and there is muscle weakness resulting in a flaccid paralysis. This can occur over a few hours to a few days. The weakness most often involves the legs, but may less commonly involve the muscles of the head, neck, and diaphragm. Many people fully recover. In those with muscle weakness, about 2 to 5 percent of children and 15 to 30 percent of adults die. Up to 70 percent of those infected have no symptoms. Another 25 percent of people have minor symptoms such as fever and a sore throat, and up to 5 percent have headache, neck stiffness, and pains in the arms and legs. These people are usually back to normal within one or two weeks. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to that which the person had during the initial infection.
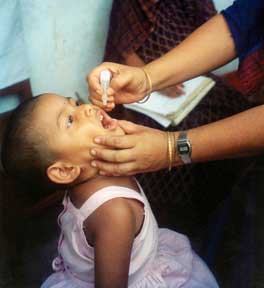
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends all children be fully vaccinated against polio. The two vaccines have eliminated polio from most of the world, and reduced the number of cases reported each year from an estimated 350,000 in 1988 to 33 in 2018.

A poliovirus, the causative agent of polio, is a serotype of the species Enterovirus C, in the family of Picornaviridae. There are three poliovirus serotypes.

Post-polio syndrome is a group of latent symptoms of poliomyelitis (polio), occurring at about a 25–40% rate. These symptoms are caused by the damaging effects of the viral infection on the nervous system. Symptoms typically occur 15 to 30 years after an initial acute paralytic attack. Symptoms include decreasing muscular function or acute weakness with pain and fatigue. The same symptoms may also occur years after a nonparalytic polio (NPP) infection.

John Franklin Enders was an American biomedical scientist and Nobel Laureate. Enders has been called "The Father of Modern Vaccines."
The oral polio vaccine (OPV) AIDS hypothesis is a now-discredited hypothesis that the AIDS pandemic originated from live polio vaccines prepared in chimpanzee tissue cultures, accidentally contaminated with simian immunodeficiency virus and then administered to up to one million Africans between 1957 and 1960 in experimental mass vaccination campaigns.

Pulse Polio is an immunisation campaign established by the government of India to eliminate poliomyelitis (polio) in India by vaccinating all children under the age of five years against the polio virus. The project fights polio through a large-scale, pulse vaccination programme and monitoring for poliomyelitis cases.

Enterovirus is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine.

Polio eradication, the permanent global cessation of circulation by the poliovirus and hence elimination of the poliomyelitis (polio) it causes, is the aim of a multinational public health effort begun in 1988, led by the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) and the Rotary Foundation. These organizations, along with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and The Gates Foundation, have spearheaded the campaign through the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI). Successful eradication of infectious diseases has been achieved twice before, with smallpox and bovine rinderpest.

The history of polio (poliomyelitis) infections began during prehistory. Although major polio epidemics were unknown before the 20th century, the disease has caused paralysis and death for much of human history. Over millennia, polio survived quietly as an endemic pathogen until the 1900s when major epidemics began to occur in Europe. Soon after, widespread epidemics appeared in the United States. By 1910, frequent epidemics became regular events throughout the developed world primarily in cities during the summer months. At its peak in the 1940s and 1950s, polio would paralyze or kill over half a million people worldwide every year.

Isabel Merrick Morgan was an American virologist at Johns Hopkins University who prepared an experimental vaccine that protected monkeys against polio in a research team with David Bodian and Howard A. Howe.

Mikhail Petrovich Chumakov was a Soviet microbiologist and virologist most famous for conducting pivotal large-scale clinical trials that led to licensing of the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) developed by Albert B. Sabin.

John Rodman Paul was an American virologist whose research focused on the spread of polio and the development of treatments for the disease.

Bernice Eddy (1903–1989) was an American virologist and epidemiologist. She and Sarah Elizabeth Stewart are known for their discoveries related to polyomavirus and SV40 in particular, a cancer-causing monkey virus that millions of children were exposed to through contaminated polio vaccines.
Polioencephalitis is a viral infection of the brain, causing inflammation within the grey matter of the brain stem. The virus has an affinity for neuronal cell bodies and has been found to affect mostly the midbrain, pons, medulla and cerebellum of most infected patients. The infection can reach up through the thalamus and hypothalamus and possibly reach the cerebral hemispheres. The infection is caused by the poliomyelitis virus which is a single-stranded, positive sense RNA virus surrounded by a non-enveloped capsid. Humans are the only known natural hosts of this virus. The disease has been eliminated from the U.S. since the mid-twentieth century, but is still found in certain areas of the world such as Africa.

The Global Polio Eradication Initiative is an initiative created in 1988, just after the World Health Assembly resolved to eradicate the disease poliomyelitis. Led by the World Health Organization, it is the largest international public health initiative in history.
DTaP-IPV/Hib vaccine is a 5-in-1 combination vaccine that protects against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio, and Haemophilus influenzae type B.
DTaP-IPV-HepB vaccine is a combination vaccine whose generic name is diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis adsorbed, hepatitis B (recombinant) and inactivated polio vaccine or DTaP-IPV-Hep B. It protects against the infectious diseases diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, poliomyelitis, and hepatitis B.
Herdis von Magnus was a Danish virologist and polio expert. After working with Jonas Salk, she and her husband directed the first polio vaccination program in Denmark. She also researched encephalitis.
The Global Commission for the Certification of the Eradication of Poliomyelitis was formed in 1995 by the World Health Organization (WHO) to independently verify the eradication of wild poliovirus around the world. The commission has been able to certify five WHO regions as having eradicated wild poliovirus, with the Eastern Mediterranean Region being the sole remaining region yet to gain certification. The Global Polio Eradication Initiative, a related initiative begun by the WHO in 1988, has been able to reduce wild poliovirus cases by 99.99% through vaccination.