
The Acido-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. It is found only in acidobacteriota, and appears to be a non-coding RNA as it does not have a consistent association with protein-coding genes.

The c4 antisense RNA is a non-coding RNA used by certain phages that infect bacteria. It was initially identified in the P1 and P7 phages of E. coli. The identification of c4 antisense RNAs solved the mystery of the mechanism for regulation of the ant gene, which is an anti-repressor.

The Downstream-peptide motif refers to a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in the cyanobacterial genera Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus and one phage that infects such bacteria. It was also detected in marine samples of DNA from uncultivated bacteria, which are presumably other species of cyanobacteria.

The glutamine riboswitch is a conserved RNA structure that was predicted by bioinformatics. It is present in a variety of lineages of cyanobacteria, as well as some phages that infect cyanobacteria. It is also found in DNA extracted from uncultivated bacteria living in the ocean that are presumably species of cyanobacteria.

The flpD RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure discovered using bioinformatics. It is detected only in methanogenic archaea, and is generally located in the apparent 5' untranslated region of genes encoding hydrogenases that are likely involved in methane metabolism. For example, the flpD gene itself encodes a subunit of methyl-viologen-reducing hydrogenase.

The Lacto-rpoB RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. It has been detected only in lactic acid bacteria, and is always located in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of rpoB genes. These genes encode a subunit of RNA polymerase, and it is hypothesized that Lacto-rpoB RNA participate in the regulation of these genes.
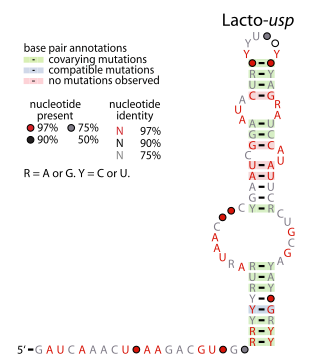
The Lacto-usp RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in bacteria by bioinformatics. Lacto-usp RNAs are found exclusively in lactic acid bacteria, and exclusively in the possible 5′ untranslated regions of operons that contain a hypothetical gene and a usp gene. The usp gene encodes the universal stress protein. It was proposed that the Lacto-usp might correspond to the 6S RNA of the relevant species, because four of five of these species lack a predicted 6S RNA, and 6S RNAs commonly occur in 5′ UTRs of usp genes. However, given that the Lacto-usp RNA motif is much shorter than the standard 6S RNA structure, the function of Lacto-usp RNAs remains unclear.
The Lnt RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure found in certain bacteria. Specifically, Lnt RNAs are known only in species within the phylum Chlorobiota, and are located in the possible 5' untranslated regions of genes that are annotated as encoding apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase enzymes. There is some doubt as to whether the indicated motif is transcribed as RNA, or whether its reverse complement is transcribed. If the reverse complement is transcribed it would potentially in 5' UTRs of genes encoding bacteriochlorophyll A, and would be close to the start codon of those genes.

The manA RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure that was identified by bioinformatics. Instances of the manA RNA motif were detected in bacteria in the genus Photobacterium and phages that infect certain kinds of cyanobacteria. However, most predicted manA RNA sequences are derived from DNA collected from uncultivated marine bacteria. Almost all manA RNAs are positioned such that they might be in the 5' untranslated regions of protein-coding genes, and therefore it was hypothesized that manA RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements. Given the relative complexity of their secondary structure, and their hypothesized cis-regulatory role, they might be riboswitches.
The wcaG RNA motif is an RNA structure conserved in some bacteria that was detected by bioinformatics. wcaG RNAs are found in certain phages that infect cyanobacteria. Most known wcaG RNAs were found in sequences of DNA extracted from uncultivated marine bacteria. wcaG RNAs might function as cis-regulatory elements, in view of their consistent location in the possible 5' untranslated regions of genes. It was suggested the wcaG RNAs might further function as riboswitches.

The Moco-II RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. However, only 8 examples of the RNA motif are known. The RNAs are potentially in the 5' untranslated regions of genes related to molybdenum cofactor (Moco), specifically a gene that encodes a molybdenum-binding domain and a nitrate reductase, which uses Moco as a cofactor. Thus the RNA might be involved in the regulation of genes based on Moco levels. Reliable predictions of Moco-II RNAs are restricted to deltaproteobacteria, but a Moco-II RNA might be present in a betaproteobacterial species. The Moco RNA motif is another RNA that is associated with Moco, and its complex secondary structure and genetic experiments have led to proposals that it is a riboswitch. However, the simpler structure of the Moco-II RNA motif is less typical of riboswitches. Moco-II RNAs are typically followed by a predicted rho-independent transcription terminator.
The nuoG RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure detected by bioinformatics. It is located in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of nuoG genes. This gene and the downstream genes probably comprise an operon that encodes various subunits of ubiquinone reductase enzyme.

PhotoRC RNA motifs refer to conserved RNA structures that are associated with genes acting in the photosynthetic reaction centre of photosynthetic bacteria. Two such RNA classes were identified and called the PhotoRC-I and PhotoRC-II motifs. PhotoRC-I RNAs were detected in the genomes of some cyanobacteria. Although no PhotoRC-II RNA has been detected in cyanobacteria, one is found in the genome of a purified phage that infects cyanobacteria. Both PhotoRC-I and PhotoRC-II RNAs are present in sequences derived from DNA that was extracted from uncultivated marine bacteria.

The rmf RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was originally detected using bioinformatics. rmf RNAs are consistently foundwithin species classified into the genus Pseudomonas, and is located potentially in the 5′ untranslated regions of rmf genes. These genes encodes the ribosome modulation factor protein, which affects the translation of genes by modifying ribosome structure in response to stress such as starvation. This ribosome modulation is a part of the stringent response in bacteria. The likely biological role of rmf RNAs is ambiguous. Since the RNA could be in the 5′ UTRs of protein-coding genes, it was hypothesized that it functions as a cis-regulatory element. This hypothesis is bolstered by the observation that ribosome modulation factor binds ribosomal RNA, and many cis-regulatory RNAs called ribosomal protein leaders participate in a feedback regulation mechanism by binding to proteins that normally bind to ribosomal RNA. However, since rmf RNAs are not very close to the rmf genes, they might function as non-coding RNAs.
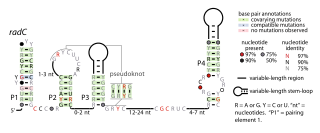
The radC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. The radC RNA motif is found in certain bacteria where it is consistent located in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of genes whose encoded proteins bind DNA are interact with other proteins that bind DNA. These proteins include integrases, methyltransferases that might methylate DNA, proteins that inhibit restriction enzymes and radC genes. Although radC genes were thought to encode DNA repair proteins, this conclusion was based on mutation data that was later shown to affect a different gene. However, it is still possible that radC genes play some DNA-related role. No radC RNAs have been detected in any purified phage whose sequence was available as of 2010, although integrases are often used by phages.

The rne-II RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified using bioinformatics. It is detected only in species classified within the family Pseudomonadaceae, a group of gammaproteobacteria. rne-II RNAs are consistently located in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of genes that encode Ribonuclease E. The RNase E 5' UTR element is a previously identified RNA structure that is also found in the 5' UTRs of RNase E genes. However, the latter motif is found only in enterobacteria, and the two motifs have apparently unrelated structure. In view of their differences, it was hypothesized that rne-II RNAs fulfill the same functional role as RNase E 5' UTR elements, which is to regulate the levels of RNase E proteins by acting as a substrate for RNase E. Thus, when concentrations of RNase E are high, they will degrade their own messenger RNA.

The sbcD RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified using bioinformatics. sbc RNAs are found some species of bacteria classified under the family Burkholderiaceae, and usually reside in plasmids. They are always located in what might be the 5' untranslated regions of operons that include sbcD genes. sbcD genes are involved in DNA repair.
Yfr2 is a family of non-coding RNAs. Members of the Yrf2 family have been identified in almost all studied species of cyanobacteria. The family was identified through a bioinformatics screen of published cyanobacterial genomes, having previously been grouped in a family of Yfr2–5.

RNAs Associated with Genes Associated with Twister and Hammerhead ribozymes (RAGATH) refers to a bioinformatics strategy that was devised to find self-cleaving ribozymes in bacteria. It also refers to candidate RNAs, or RAGATH RNA motifs, discovered using this strategy.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.

















