Related Research Articles

A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is a plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.

Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.

Raffia palms (Raphia) are a genus of about twenty species of palms native to tropical regions of Africa, and especially Madagascar, with one species also occurring in Central and South America. R. taedigera is the source of raffia fibers, which are the veins of the leaves, and this species produces a fruit called "brazilia pods", "uxi nuts" or "uxi pods".

Shrink wrap, also shrink film, is a material made up of polymer plastic film. When heat is applied, it shrinks tightly over whatever it is covering. Heat can be applied with a handheld heat gun, or the product and film can pass through a heat tunnel on a conveyor.

Corrugated plastic or corriboard – also known under the tradenames of Cartonplast, Polyflute, Coroplast, FlutePlast, IntePro, Proplex, Correx, Twinplast, Corriflute or Corflute – refers to a wide range of extruded twinwall plastic-sheet products produced from high-impact polypropylene resin with a similar make-up to corrugated fiberboard. It is a light-weight tough material which can easily be cut with a utility knife. Manufacturers typically offer a wide variety of colors and thicknesses.
Strapping, also known as bundling and banding, is the process of applying a strap to an item to combine, stabilize, hold, reinforce, or fasten it. The strap may also be referred to as strapping. Strapping is most commonly used in the packaging industry.

Geotextiles are permeable fabrics which, when used in association with soil, have the ability to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain. Typically made from polypropylene or polyester, geotextile fabrics come in three basic forms: woven, needle punched, or heat bonded.

Engineering plastics are a group of plastic materials that have better mechanical and/or thermal properties than the more widely used commodity plastics.

Corona treatment is a surface modification technique that uses a low temperature corona discharge plasma to impart changes in the properties of a surface. The corona plasma is generated by the application of high voltage to an electrode that has a sharp tip. The plasma forms at the tip. A linear array of electrodes is often used to create a curtain of corona plasma. Materials such as plastics, cloth, or paper may be passed through the corona plasma curtain in order to change the surface energy of the material. All materials have an inherent surface energy. Surface treatment systems are available for virtually any surface format including dimensional objects, sheets and roll goods that are handled in a web format. Corona treatment is a widely used surface treatment method in the plastic film, extrusion, and converting industries.

Photodegradation is the alteration of materials by light. Commonly, the term is used loosely to refer to the combined action of sunlight and air, which cause oxidation and hydrolysis. Often photodegradation is intentionally avoided, since it destroys paintings and other artifacts. It is, however, partly responsible for remineralization of biomass and is used intentionally in some disinfection technologies. Photodegradation does not apply to how materials may be aged or degraded via infrared light or heat, but does include degradation in all of the ultraviolet light wavebands.
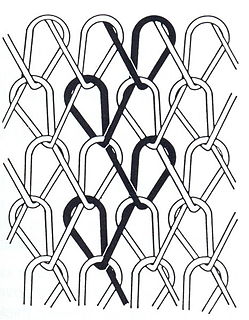
Warp knitting is a family of knitting methods in which the yarn zigzags along the length of the fabric; i.e., following adjacent columns, or wales, of knitting, rather than a single row, or course. For comparison, knitting across the width of the fabric is called weft knitting.

A plastic bottle is a bottle constructed from high-density or low density plastic. Plastic bottles are typically used to store liquids such as water, soft drinks, motor oil, cooking oil, medicine, shampoo, milk, and ink. The size ranges from very small bottles to large carboys. Consumer blow molded containers often have integral handles or are shaped to facilitate grasping.

Filler materials are particles added to resin or binders that can improve specific properties, make the product cheaper, or a mixture of both. The two largest segments for filler material use is elastomers and plastics. Worldwide, more than 53 million tons of fillers are used every year in application areas such as paper, plastics, rubber, paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants. As such, fillers, produced by more than 700 companies, rank among the world's major raw materials and are contained in a variety of goods for daily consumer needs. The top filler materials used are ground calcium carbonate (GCC), precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), kaolin, talc, and carbon black. Filler materials can affect the tensile strength, toughness, heat resistance, color, clarity etc. A good example of this is the addition of talc to polypropylene. Most of the filler materials used in plastics are mineral or glass based filler materials. Particulates and fibers are the main subgroups of filler materials. Particulates are small particles of filler which are mixed in the matrix where size and aspect ratio are important. Fibers are small circular strands that can be very long and have very high aspect ratios.
Polymer engineering is generally an engineering field that designs, analyses, and modifies polymer materials. Polymer engineering covers aspects of the petrochemical industry, polymerization, structure and characterization of polymers, properties of polymers, compounding and processing of polymers and description of major polymers, structure property relations and applications.

Commodity plastics or commodity polymers are plastics produced in high volumes for applications where exceptional material properties are not needed. In contrast to engineering plastics, commodity plastics tend to be inexpensive to produce and exhibit relatively weak mechanical properties. Some examples of commodity plastics are polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, and poly(methyl methacrylate). Globally, the most widely used thermoplastic includes both Polypropylene and Polyethylene.
Metallised films are polymer films coated with a thin layer of metal, usually aluminium. They offer the glossy metallic appearance of an aluminium foil at a reduced weight and cost. Metallised films are widely used for decorative purposes and food packaging, and also for specialty applications including insulation and electronics.

Roll slitting is a shearing operation that cuts a large roll of material into narrower rolls. There are two types of slitting: log slitting and rewind slitting. In log slitting the roll of material is treated as a whole and one or more slices are taken from it without an unrolling/re-reeling process. In rewind slitting the web is unwound and run through the machine, passing through knives or lasers, before being rewound on one or more shafts to form narrower rolls. The multiple narrower strips of material may be known as mults or pancakes if their diameter is much more than their width. For rewind slitting the machine used is called a slitter rewinder, a slitter or a slitting machine – these names are used interchangeably for the same machines. For particularly narrow and thin products, the pancakes become unstable, and then the rewind may be onto a bobbin-wound reel: the rewind bobbins are much wider than the slit width and the web oscillates across the reel as it is rewound. Apart from the stability benefit it is also then possible to put very long lengths,, onto one bobbin.

Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin plastic membranes are used to separate areas or volumes, to hold items, to act as barriers, or as printable surfaces.

Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives.

Tear tape, also known as tearstrip or tear-off ribbon, is a narrow adhesive tape used to open packaging. The backing is often a narrow oriented polymer such as polypropylene but other polymers, yarns, and filaments are also used. Many tear tapes use a pressure sensitive adhesive but others have a heat-activated adhesive system.
References
- ↑ Reisner, David E.; Pradeep, T. (24 September 2014). Aquananotechnology: Global Prospects. CRC Press. p. 589. ISBN 9781466512245 . Retrieved 14 July 2016.
Today's most widely used material for atmospheric capture is polypropylene raffia, also called “raschel,” which is a material classified under a class of mosquito netting fabric types (manufactured using Raschel knitting machines).