See also
- Ponente, regional term for a westerly wind that blows in the Mediterranean
In French, ponant is the western cardinal point. It is an archaic French naval term for West, the opposite of Levant .
By extension :
The meaning 1. gave its name or a nickname :

The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about 85,133,000 km2 (32,870,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe, and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World.

The Levant is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of West Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in western Asia: i.e. the historical region of Syria, which includes present-day Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, the Palestinian territories and most of Turkey southwest of the middle Euphrates. Its overwhelming characteristic is that it represents the land bridge between Africa and Eurasia. In its widest historical sense, the Levant included all of the Eastern Mediterranean with its islands; that is, it included all of the countries along the Eastern Mediterranean shores, extending from Greece to Cyrenaica in eastern Libya.

The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant in West Asia. The Mediterranean has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago.

Morocco is the northwesternmost country which spans from the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean on the north and the west respectively, into large mountainous areas in the interior, to the Sahara desert in the far south. Morocco is a Northern African country, located in the extreme northwest of Africa on the edge of continental Europe. The Strait of Gibraltar separates Spain from Morocco with a 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) span of water. Morocco borders the North Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the western Mediterranean Sea to the north, and has borders with Algeria and disputed Western Sahara.
The Mediterranean Sea is a major body of water south of Europe, west of Asia and north of Africa.

In geography and geology, a cliff is an area of rock which has a general angle defined by the vertical, or nearly vertical. Cliffs are formed by the processes of weathering and erosion, with the effect of gravity. Cliffs are common on coasts, in mountainous areas, escarpments and along rivers. Cliffs are usually composed of rock that is resistant to weathering and erosion. The sedimentary rocks that are most likely to form cliffs include sandstone, limestone, chalk, and dolomite. Igneous rocks such as granite and basalt also often form cliffs.
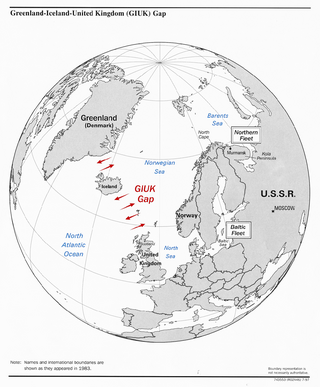
The GIUK gap is an area in the northern Atlantic Ocean that forms a naval choke point. Its name is an acronym for Greenland, Iceland, and the United Kingdom, the gap being the two stretches of open ocean between these three landmasses. It separates the Norwegian Sea and the North Sea from the open Atlantic Ocean. The term is typically used in relation to military topics. The area has for some nations been considered strategically important since the beginning of the 20th century.

USS Damato (DD-871) was a Gearing-class destroyer of the United States Navy. She was named for Corporal Anthony P. Damato USMC (1922–1944), who was killed in action during the Battle of Eniwetok in the Marshall Islands and posthumously awarded the Medal of Honor.

Metropolitan France, also known as European France, is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European regions of France is used in everyday life in France but has no administrative meaning. Indeed, the overseas regions have exactly the same administrative status as the metropolitan regions. Metropolitan France comprises mainland France and Corsica, as well as nearby islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the English Channel, and the Mediterranean Sea.

Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French as le Midi, is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin, Spain, the Mediterranean Sea and Italy. It includes southern Nouvelle-Aquitaine in the west, Occitanie in the centre, the southern parts of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes in the northeast, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur in the southeast, as well as the island of Corsica in the southeast. Southern France is generally included into Southern Europe because of its association with the Mediterranean Sea.
The Levant is a region in the eastern Mediterranean, including the Southern Levant.

Ras Nouadhibou is a 60-kilometre (37 mi) peninsula or headland divided by the border between Mauritania and Western Sahara on the African coast of the Atlantic Ocean. It is internationally known as Cabo Blanco in Spanish or Cap Blanc in French.

The Ottoman Navy, also known as the Ottoman Fleet, was the naval warfare arm of the Ottoman Empire. It was established after the Ottomans first reached the sea in 1323 by capturing Praenetos, the site of the first Ottoman naval shipyard and the nucleus of the future Navy.

Iroise or the Iroise Sea is the part of the Atlantic Ocean which stretches from the Ile de Sein to Ushant off the coast of Brittany in north-western France. It is contained within the Celtic Sea, bordering the remainder of the Celtic Sea to the north and west, and the Bay of Biscay to the south. It is one of the most dangerous seas in Europe for sea-going vessels. In winter, there are often violent storms with huge waves. It is also one of the richest areas for marine life and was designated as one of UNESCO's biosphere reserves in 1988 and as France's first marine park in October 2007.

The Flotte du Ponant was the designation under the Ancien Regime for the naval vessels of the Royal French Navy in the English Channel, Atlantic Ocean and Americas, the latter principally in the French West Indies and New France. The fleet carried out operations such as asserting naval supremacy and protecting convoys. Its counterpart was the Levant Fleet, based in the Mediterranean Sea.
Ponant is a French cruise ship operator. It was founded in April 1988 by Philippe Videau, Jean-Emmanuel Sauvé, and other officers of the French Merchant Navy and launched the first French cruise ship. The company operates eleven ships, all of which operate under the French flag.
Paul Gauguin Cruises is a cruise line that was owned by Beachcomber Croisieres Limited until 2019, when it was purchased by French company Compagnie du Ponant. Paul Gauguin Cruises operates cruises with one ship, the Paul Gauguin, to Tahiti, French Polynesia and the South Pacific.

The Levant Fleet was the designation under the Ancien Regime for the naval vessels of the Royal French Navy in the Mediterranean. The fleet carried out operations such as asserting naval supremacy and protecting convoys. Its counterpart was the Flotte du Ponant, which saw service in the English Channel and in the Atlantic Ocean.

Imperial fortress was the designation given in the British Empire to four colonies that were located in strategic positions from each of which Royal Navy squadrons could control the surrounding regions and, between them, much of the planet.