
Dacia was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to the present-day countries of Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine.

Moesia was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. Moesian Province was first administered by governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballia'. It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia, Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine.

Limes is a term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of Ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire. The term has been extended in modern times to refer to the frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa.

Trajan's Bridge, also called Bridge of Apollodorus over the Danube, was a Roman segmental arch bridge, the first bridge to be built over the lower Danube and one of the greatest achievements in Roman architecture. Though it was only functional for 165 years, it is often considered to have been the longest arch bridge in both total and span length for more than 1,000 years.

Novae was initially one of the few great Roman legionary fortresses along the empire's border, forming part of the defences along the Danube in northern Bulgaria. The settlement later expanded into a town in the Roman province of Moesia Inferior, later Moesia Secunda.

Singidunum was an ancient city which later evolved into modern Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. The name is of Celtic origin, going back to the time when Celtic tribe Scordisci settled the area in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans. Later on, the Roman Republic conquered the area in 75 BC and incorporated it into the province of Moesia. It was an important fort of the Danubian Limes and Roman Legio IV Flavia Felix was garrisoned there since 86 AD. Singidunum was the birthplace of the Roman Emperor Jovian. It was sacked by Huns in 441, and by Avars and Slavs in 584. At the beginning of the 7th century, the Singidunum fort was finally destroyed.

Đerdap National Park stretches along the right bank of the Danube River from the Golubac Fortress to the dam near Novi Sip, Serbia. It was established in 1974 and spreads on 63,786.5 ha. The park management office is in the town of Donji Milanovac on the Danube. Across the river is the Parcul Natural Porțile de Fier in Romania.
The Limes Germanicus, or 'Germanic Limes', is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsubdued Germanic tribes from the years 83 to about 260 AD. The frontier used either a natural boundary such as a river or typically an earth bank and ditch with a wooden palisade and watchtowers at intervals, and a system of linked forts was built behind them.

Kladovo is a town and municipality located in the Bor District of eastern Serbia. It is situated on the right bank of the Danube river.

Oescus, Palatiolon or Palatiolum was an important ancient city on the Danube river in Roman Moesia. It later became known as Ulpia Oescus. It lay northwest of the modern Bulgarian city of Pleven, near the village of Gigen.

Roman military borders and fortifications were part of a grand strategy of territorial defense in the Roman Empire, although this is a matter of debate. By the early 2nd century, the Roman Empire had reached the peak of its territorial expansion and rather than constantly expanding their borders as earlier in the Empire and Republic, the Romans solidified their position by fortifying their strategic position with a series of fortifications and established lines of defense. Historian Adrian Goldsworthy argues that the Romans had reached the natural limits which their military traditions afforded them conquest over and that beyond the borders of the early-to-mid Empire lay peoples whose military traditions made them militarily unconquerable, despite many Roman battle victories. In particular, Goldsworthy argues that the cavalry-based warfare of the Parthians, Sarmatians and Persians presented a major challenge to the expansion of Rome's infantry-based armies.

The Moesian Limes is the modern term given to a linked series of Roman forts on the northern frontier of the Roman province of Moesia along the Danube between the Black Sea shore and Pannonia and dating from the 1st century AD. It was the eastern section of the so-called Danubian Limes and protected the Roman provinces of Upper and Lower Moesia south of the river. The eastern section is often called the limes Scythiae minoris as it was located in the late Roman province of Scythia Minor.

Diana Fort is a Roman fort located near the hamlet of Karataš, 8 km northwest of Kladovo, in eastern Serbia in the Karataš archaeological site. It is located on cliffs of the Đerdap, above the Danube, on a strategic location overlooking the Danube frontier. It has been extensively excavated, is one of the best explored forts of the Moesian Limes, and can be visited today.

Capidava was an important Geto-Dacian centre on the right bank of the Danube. After the Roman conquest, it became a civil and military centre, as part of the province of Moesia Inferior and was part of the defensive frontier system of the Limes Moesiae along the Danube.

Slovakia was partly occupied by Roman legions for a short period of time. Marcomannia was a proposed province of the Roman Empire that Emperor Marcus Aurelius planned to establish in this territory. It was inhabited by the Germanic tribes of Marcomanni and Quadi, and lay in the western parts of the modern states and Slovakia and the Czech Republic (Moravia). Part of the area was occupied by the Romans under Marcus Aurelius between 174 AD and 180 AD. His successors abandoned the project, but the people of the area became steadily Romanized during the next two centuries. The Roman influence was disrupted with the invasions of Attila starting around 434 AD and as Slavic people later began to move into the area.
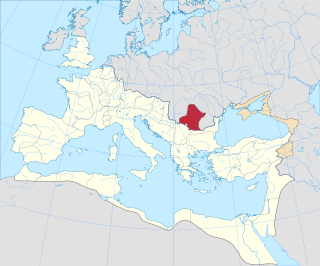
Roman Dacia was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat. During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians.
Dolni Tsibar is a village in Valchedram Municipality, Montana Province, northwestern Bulgaria.
The Danubian Limes, or Danube Limes, refers to the Roman military frontier or limes which lies along the River Danube in the present-day German state of Bavaria, in Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Bulgaria and Romania.

The Pannonian Limes is part of the old Roman fortified frontier known as the Danubian Limes that runs for approximately 420 km (260 mi) from the Roman camp of Klosterneuburg in the Vienna Basin in Austria to the castrum in Singidunum (Belgrade) in present-day Serbia. The garrisons of these camps protected the Pannonian provinces against attacks from the north from the time of Augustus (31 BC–14 AD) to the beginning of the 5th century. In places this section of the Roman limes also crossed the river into the territory of the barbarians (Barbaricum).

The Dacian Limes is the generic modern term given to a collection of ramparts and linked series of Roman forts on the frontiers of the Roman province of Dacia dating from the 1st century AD. They ran for about 1,000 km and included the:



















