
Communications in Gibraltar comprise a wide range of telephony systems, Internet access, broadcasting and satellite control. There is also printed and online media. Regulation of telecommunications and broadcasting are the responsibility of the Gibraltar Regulatory Authority (GRA), established by means of the Gibraltar Regulatory Authority Act in 2000.

In digital radio, packet radio is the application of packet switching techniques to digital radio communications. Packet radio uses a packet switching protocol as opposed to circuit switching or message switching protocols to transmit digital data via a radio communication link.

Radioteletype (RTTY) is a telecommunications system consisting originally of two or more electromechanical teleprinters in different locations connected by radio rather than a wired link. Radioteletype evolved from earlier landline teleprinter operations that began in the mid-1800s. The US Navy Department successfully tested printing telegraphy between an airplane and ground radio station in 1922. Later that year, the Radio Corporation of America successfully tested printing telegraphy via their Chatham, Massachusetts, radio station to the R.M.S. Majestic. Commercial RTTY systems were in active service between San Francisco and Honolulu as early as April 1932 and between San Francisco and New York City by 1934. The US military used radioteletype in the 1930s and expanded this usage during World War II. From the 1980s, teleprinters were replaced by personal computers (PCs) running software to emulate teleprinters.

Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz ; above the medium frequency band (MF), to the bottom of the VHF band.

Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that conventionally have been implemented in analog hardware are instead implemented by means of software on a computer or embedded system. While the concept of SDR is not new, the rapidly evolving capabilities of digital electronics render practical many processes which were once only theoretically possible.

Citizens band radio is a land mobile radio system, a system allowing short-distance one-to-many bidirectional voice communication among individuals, using two-way radios operating near 27 MHz in the high frequency or shortwave band. Citizens band is distinct from other personal radio service allocations such as FRS, GMRS, MURS, UHF CB and the Amateur Radio Service. In many countries, CB operation does not require a license and may be used for business or personal communications.

High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters. Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted medium frequency (MF), while the next band of higher frequencies is known as the very high frequency (VHF) band. The HF band is a major part of the shortwave band of frequencies, so communication at these frequencies is often called shortwave radio. Because radio waves in this band can be reflected back to Earth by the ionosphere layer in the atmosphere – a method known as "skip" or "skywave" propagation – these frequencies are suitable for long-distance communication across intercontinental distances and for mountainous terrains which prevent line-of-sight communications. The band is used by international shortwave broadcasting stations (3.95–25.82 MHz), aviation communication, government time stations, weather stations, amateur radio and citizens band services, among other uses.

Digital Radio Mondiale is a set of digital audio broadcasting technologies designed to work over the bands currently used for analogue radio broadcasting including AM broadcasting—particularly shortwave—and FM broadcasting. DRM is more spectrally efficient than AM and FM, allowing more stations, at higher quality, into a given amount of bandwidth, using xHE-AAC audio coding format. Various other MPEG-4 codecs and Opus are also compatible, but the standard now specifies xHE-AAC.
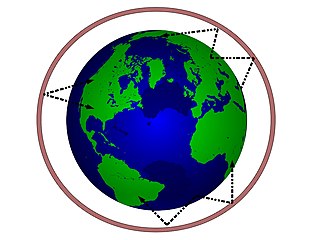
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, skywave propagation can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is mostly used in the shortwave frequency bands.

Shortwave listening, or SWLing, is the hobby of listening to shortwave radio broadcasts located on frequencies between 1700 kHz and 30 MHz (30 000 kHz). Listeners range from casual users seeking international news and entertainment programming, to hobbyists immersed in the technical aspects of long-distance radio reception and sending and collecting official confirmations that document their reception of remote broadcasts (DXing). In some developing countries, shortwave listening enables remote communities to obtain regional programming traditionally provided by local medium wave AM broadcasters. In 2002, the number of households that were capable of shortwave listening was estimated to be in the hundreds of millions.
Shortwave bands are frequency allocations for use within the shortwave radio spectrum. Radio waves in these frequency ranges can be used for very long distance (transcontinental) communication because they can reflect off layers of charged particles in the ionosphere and return to Earth beyond the horizon, a mechanism called skywave or “skip” propagation. They are allocated by the ITU for radio services such as maritime communications, international shortwave broadcasting and worldwide amateur radio. The bands are conventionally named by their wavelength in metres, for example the ‘20 meter band’. Radio propagation and possible communication distances vary depending on the time of day, the season and the level of solar activity.
DXing, taken from DX, the telegraphic shorthand for "distance" or "distant", is the hobby of receiving and identifying distant radio or television signals, or making two-way radio contact with distant stations in amateur radio, citizens band radio or other two-way radio communications. Many DXers also attempt to obtain written verifications of reception or contact, sometimes referred to as "QSLs" or "veries".

Contesting is a competitive activity pursued by amateur radio operators. In a contest, an amateur radio station, which may be operated by an individual or a team, seeks to contact as many other amateur radio stations as possible in a given period of time and exchange information. Rules for each competition define the amateur radio bands, the mode of communication that may be used, and the kind of information that must be exchanged. The contacts made during the contest contribute to a score by which stations are ranked. Contest sponsors publish the results in magazines and on web sites.

An amateur radio station is a radio station designed to provide radiocommunications in the amateur radio service for an amateur radio operator. Radio amateurs build and operate several types of amateur radio stations, including fixed ground stations, mobile stations, space stations, and temporary field stations. A slang term often used for an amateur station's location is the shack, named after the small enclosures added to the upperworks of naval ships to hold early radio equipment and batteries.

A QSL card is a written confirmation of either a two-way radiocommunication between two amateur radio or citizens band stations; a one-way reception of a signal from an AM radio, FM radio, television or shortwave broadcasting station; or the reception of a two-way radiocommunication by a third party listener. A typical QSL card is the same size and made from the same material as a typical postcard, and most are sent through the mail as such.
William Ittner Orr (1919–2001) was an engineer, educator, communicator, and ham radio operator. He was the American author of numerous amateur radio and radio engineering texts. He is best known as the author of The W6SAI Antenna Handbook and fondly remembered for the 1959 Radio Handbook.

Vintage amateur radio is a subset of amateur radio hobby where enthusiasts collect, restore, preserve, build, and operate amateur radio equipment from bygone years, such as those using vacuum tube technology. Popular modes of operation include speaking over amplitude modulation (AM), and communicating using Morse code through continuous wave (CW) radiotelegraphy. Some enthusiasts have interest in owning, restoring and operating vintage military and commercial radio equipment such as those from 1940s to 1960s. Some undertake to construct their own gear, known in ham slang as homebrewing, using vintage parts and designs. A number of amateur radio clubs and organizations sponsor contests, events, and swap meets that cater to this specialized aspect of the hobby.

Worldradio was a monthly amateur radio enthusiast magazine published in Sacramento, CA, United States from July 1971 to January 2009. The magazine was published in English and drew its subscription base primarily from the United States and Canada, although it had subscribers around the world. The staff of the magazine had an Amateur Radio club that was assigned the call sign WR6WR. This magazine is unrelated to a magazine called "World-Radio" published in the United Kingdom before World War II.

CQ VHF was a magazine that served the ham radio operators whose operational and technical interests lie above 50 MHz.
The Yaesu VX series is a line of two sequences of compact amateur radio handheld transceivers produced by Yaesu. There is a line of ultra-compact lower-power dual-band transceivers that started with the VX-1R and was later updated with the VX-2R and VX-3R. There is also a line of 5W tri-band transceivers that started with the VX-5R and was later updated with the VX-6R, VX-7R and VX-8R.














