Notes
- ↑ Simpson, T.L. (2012-12-06). The Cell Biology of Sponges. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 256. ISBN 9781461252146 . Retrieved 9 November 2017.
Porocytes are tubular cells which make up the pores of a sponge known as ostia. [1]
Covering the sponge is a layer of cells known as the pinacoderm, which is composed of pinacocytes. In a sponge, pinacocytes are a thin, elastic layer which keeps water out. Between the pinacocytes, there are the porocytes that allow water into the sponge. Myocytes are small muscular cells that open and close the porocytes. They also form a circular ring around the osculum and help in closing and opening of it. Once through the pores, water travels down canals. The opening to a porocyte is a pore known as an ostium.
In sponges, like Scypha, there are some cells that have an intracellular pore. These cells are known as porocytes. They are present in the Leucosolenia (an asconoid sponge) in the body wall through which water enters the body or they are present in Scypha (a syconoid sponge) as a connection between incurrent canal and radial canal. The pore is called an ostia in asconoid type sponges as it serves as the connection between the outside of the body and the spongocoel but called a prosopyle in syconoid sponges. They are modified pinacocytes.

Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera, are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells.

Ctenophora comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming, and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia.

In biology, tissue is an assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same embryonic origin that together carry out a specific function. Tissues occupy a biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. Accordingly, organs are formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.
An ascocarp, or ascoma, is the fruiting body (sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia).

The Venus' flower basket is a glass sponge in the phylum Porifera. It is a marine sponge found in the deep waters of the Pacific ocean, usually at depths below 500 m (1,600 ft). Like other sponges, they feed by filtering sea water to capture plankton and marine snow. Similar to other glass sponges, they build their skeletons out of silica, which forms a unique lattice structure of spicules. The sponges are usually between 10 cm (3.9 in) and 30 cm (12 in) tall, and their bodies act as refuge for their mutualist shrimp partners. This body structure is of great interest in materials science as the optical and mechanical properties are in some ways superior to man-made materials. Little is known regarding their reproduction habits, however fluid dynamics of their body structure likely influence reproduction and it is hypothesized that they may be hermaphroditic.
A spongocoel, also called paragaster, is the large, central cavity of sponges. Water enters the spongocoel through hundreds of tiny pores (ostia) and exits through the larger opening (osculum). Depending on the body plan of the sponge, the spongocoel could be a simple interior space of the sponge or a complexly branched inner structure. Regardless of body plan or class, the spongocoel is lined with choanocytes, which have flagella that push water through the spongocoel, creating a current.
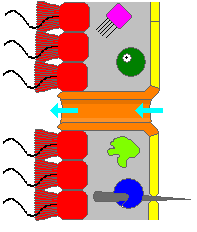
Choanocytes are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or cilium, surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a thin membrane.

A contractile vacuole (CV) is a sub-cellular structure (organelle) involved in osmoregulation. It is found predominantly in protists and in unicellular algae. It was previously known as pulsatile or pulsating vacuole.

Anheteromeyenia argyrosperma is a freshwater sponge found across North America.

Xestospongia testudinaria is a species of barrel sponge in the family Petrosiidae. More commonly known as Giant Barrel Sponges, they have the basic structure of a typical sponge. Their body is made of a reticulation of cells aggregate on a siliceous scaffold composed of small spikes called spicules. Water is taken into the inner chamber of the sponge through ostia. Flagellated choanocytes line the inner chamber and help generate water currents through the sponge.
The choanoderm is a type of cell layer composed of flagellated collar cells, or choanocytes, found in sponges. The sponge body is mostly a connective tissue; the mesohyl, over which are applied epithelioid monolayers of cells, the outer pinacoderm and the inner choanoderm.

Tethya aurantium, also known as the golf ball sponge or orange puffball sponge, is a species of sea sponge belonging to the family Tethyidae. It is spherical in shape, with a warty surface, and grows to about 10 cm in diameter. Oscula are present on the upper surface. The surface has sharp protruding spicules which can cause skin irritation if touched.
Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of sponges, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes suggest that pinacocytes had evolved before the metazoan time period, which is, before porifera had evolved.

Spongilla lacustris is a species of freshwater sponge from the family Spongillidae. It inhabits freshwater rivers and lakes, often growing under logs or rocks. Lacustris is a Latin word meaning "related to or associated with lakes". The species ranges from North America to Europe and Asia. It is the most common freshwater sponge in central Europe. It is the most widespread sponge in Northern Britain, and is one of the most common species of sponges in lakes and canals. Spongilla lacustris have the ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. They become dormant during winter. The growth form ranges from encrusting, to digitate, to branched, depending upon the quality of the habitat.
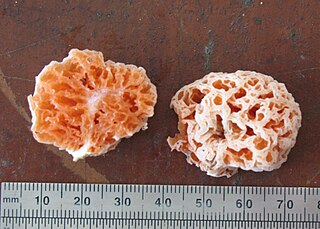
Spongiforma is a genus of sponge-like fungi in the family Boletaceae. Newly described in 2009, the genus contains two species: S. thailandica and S. squarepantsii. The type species S. thailandica is known only from Khao Yai National Park in central Thailand, where it grows in soil in old-growth forests dominated by dipterocarp trees. The rubbery fruit bodies, which has a strong odour of coal-tar similar to Tricholoma sulphureum, consists of numerous internal cavities lined with spore-producing tissue. S. squarepantsii, described as new to science in 2011, is found in Malaysia. It produces sponge-like, rubbery orange fruit bodies with a fruity or musky odour. These fruit bodies will—like a sponge—resume their original shape if water is squeezed out. The origin of the specific name derives from its perceived resemblance to the cartoon character SpongeBob SquarePants. Apart from differences in distribution, S. squarepantsii differs from S. thailandica in its colour, odour, and spore structure.

The anal pore or cytoproct is a structure in various single-celled eukaryotes where waste is ejected after the nutrients from food have been absorbed into the cytoplasm.

Tectitethya crypta is a species of demosponge belonging to the family Tethyidae. Its classified family is characterized by fourteen different known genera, one of them being Tectitethya. It is a massive, shallow-water sponge found in the Caribbean Sea. This sponge was first discovered by Werner Bergmann in 1945 and later classified by de Laubenfels in 1949. It is located in reef areas situated on softer substrates such as sand or mud. Oftentimes, it is covered in sand and algae. This results in an appearance that is cream colored/ gray colored; however, when the animal is washed free of its sediment coverings, its body plan appears more green and gray. It's characterized with ostia peaking out of its body cavity, with the ability to abruptly open or close, changing its desired water flow rate through its mesohyl.
Neofibularia nolitangere, commonly known as the touch-me-not sponge, is a species of sea sponge in the family Biemnidae. It is found in shallow waters in the Western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.

Callyspongia truncata is a species of marine sea sponge. Like all marine sponges, C. truncata is a member of phylum Porifera and is defined by its filter-feeding lifestyle and flagellated choanocytes, or collar cells, that allow for water movement and feeding. It is a species of demosponge and a member of Demospongiae, the largest class of sponges as well as the family Callyspongiidae. C. truncata is most well known for being the organism from which the polyketide Callystatin A was identified. Callystatin A is a polyketide natural product from the leptomycin family of antibiotics. It was first isolated in 1997 from this organism, which was collected from the Goto Islands in the Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan by the Kobayashi group. Recent studies have revealed numerous other bioactive compounds that have been found in this species.

Haliclona caerulea is a species of marine sponge in the family Chalinidae. It is an encrusting tubular sponge that grows anchored on rocky surfaces of coral reefs.