
Kitsap County is located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, its population was 275,611. Its county seat is Port Orchard, and its largest city is Bremerton. The county was formed out of King County and Jefferson County on January 16, 1857, and is named for Chief Kitsap of the Suquamish Tribe. Originally named Slaughter County, it was soon renamed.

Indianola is a census-designated place (CDP) in Kitsap County, Washington, United States, located on the north shore of Port Madison on the Port Madison Indian Reservation, home of the Suquamish Indian Tribe. The population was 3,500 at the 2010 census. It was originally established as a summer community and was a stop for Mosquito Fleet ferries until the 1950s.

Poulsbo is a city on Liberty Bay in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. It is the smallest of the four cities in Kitsap County. The population was 9,200 at the 2010 census and an estimated 10,927 in 2018.

Suquamish is a census-designated place (CDP) in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. The population was 4,140 at the 2010 census. Comprising the Port Madison Indian Reservation, it is the burial site of Chief Seattle and the site of the Suquamish tribe winter longhouse known as Old Man House.

The Suquamish are a Lushootseed-speaking Native American people, located in present-day Washington in the United States. They are a southern Coast Salish people. Today, most Suquamish people are enrolled in the federally recognized Suquamish Tribe, a signatory to the 1855 Treaty of Point Elliott. Chief Seattle, the famous leader of the Suquamish and Duwamish Tribes for which the City of Seattle is named, signed the Point Elliot Treaty on behalf of both Tribes. The Suquamish Tribe owns the Port Madison Indian Reservation.

Washington State Ferries (WSF) is a government agency that operates automobile and passenger ferry service in the U.S. state of Washington as part of the Washington State Department of Transportation. It runs ten routes serving 20 terminals located around Puget Sound and in the San Juan Islands, designated as part of the state highway system. The agency maintains the largest fleet of ferries in the United States at 21 vessels. In 2021, the system had a ridership of about 56,800 per weekday as of the third quarter of 2022. As of 2016, it was the largest ferry operator in the United States and the second-largest vehicular ferry system in the world.
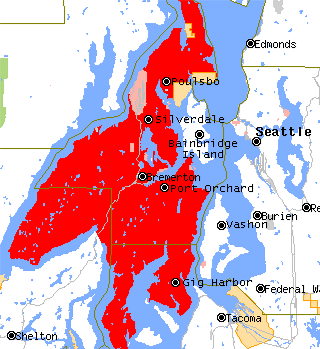
The Kitsap Peninsula lies west of Seattle across Puget Sound, in Washington state in the Pacific Northwest. Hood Canal separates the peninsula from the Olympic Peninsula on its west side. The peninsula, a.k.a. "Kitsap", encompasses all of Kitsap County except Bainbridge and Blake Islands, as well as the northeastern part of Mason County and the northwestern part of Pierce County. The highest point on the Kitsap Peninsula is Gold Mountain. The U.S. Navy's Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, and Naval Base Kitsap are on the peninsula. Its main city is Bremerton.

State Route 3 (SR 3) is a 59.81-mile-long (96.25 km) state highway in the U.S. state of Washington, serving the Kitsap Peninsula in Mason and Kitsap counties. The highway begins at U.S. Route 101 (US 101) south of Shelton and travels northeast onto the Kitsap Peninsula through Belfair to Gorst, where it intersects SR 16 and begins its freeway. SR 3 travels west of Bremerton, Silverdale and Poulsbo before it terminates at the eastern end of the Hood Canal Bridge, signed as SR 104. The highway is designated as a Strategic Highway Network (STRAHNET) corridor under the National Highway System as the main thoroughfare connecting both parts of Naval Base Kitsap and is also part of the Highways of Statewide Significance program.

Kitsap Transit is a public transit agency serving Kitsap County, Washington, part of the Seattle metropolitan area. The system is based in Bremerton and operates bus service on 40 fixed routes, a foot ferry, a vanpool system, worker-driver services, and dial-a-ride services. The Kitsap Fast Ferries are also operated by Kitsap Transit. In 2021, the system had a ridership of 1,736,100, or about 58,000 per weekday as of the third quarter of 2022.
North Kitsap School District 400 is the school district serving the northern portion of Kitsap County, including the communities of Poulsbo, Keyport, Port Gamble, Hansville, Indianola, Suquamish, and Kingston, Washington.
The M/V Kitsap was a ferry built in 1925 at the Lake Washington Shipyard in Houghton, Washington. She was 165 feet (50 m) long, and her original capacity in 1925 was 95 cars and approximately 800 passengers. By 1960, cars had become much bigger and her capacity was reduced to 32 modern automobiles and 325 passengers. A 600-horsepower Estep diesel engine allowed her to sail at 12 knots when originally built. Almost every part of her was from Washington state; her hull and superstructure were built from Washington-grown fir, and her Estep engine was built in at Washington Iron Works in Tacoma.

The Port of Poulsbo is a port serving the city of Poulsbo, Washington, United States. It is located in Liberty Bay on Puget Sound. The port includes the Poulsbo Marina, a seaplane mooring, commercial shops, residential housing, the SEA Discovery Center, and Liberty Bay Waterfront Park. The port is part of downtown Poulsbo, also known as "Little Norway".

Hyak was a wooden-hulled steamship that operated on Puget Sound from 1909 to 1941. This vessel should not be confused with the sternwheeler Hyak which ran on the extreme upper reach of the Columbia River at about the same time. The name means "swift" or "fast" in the Chinook Jargon.
The Kitsap County Transportation Company was an important steamboat and ferry company that operated on Puget Sound. The company was founded in 1898 as the Hansen Transportation Company.

Camano was a steamboat built in 1906 at Coupeville, Washington which operated on Puget Sound from 1906 to 1917. Camano was later known as Tolo. As Tolo the vessel was sunk in 1917 as a result of a collision at sea. Four people died as a result.

Alverene was a gasoline launch built in 1912 which operated on northern Puget Sound and in the San Juan Islands.
The Harper-Colby-Manchester route was a shipping route that originated from Seattle, Washington. The route included stops at Colby, Suquamish, and Manchester, Washington. As of January 1, 1917, the Kitsap County Transportation Company was operating steamboats on the route.
The YWCA-Rolling Bay route was a shipping route that originated from Seattle, Washington. The route included stops on the east side of Bainbridge Island, Washington at the YWCA summer camp and at Rolling Bay.
The Fletcher Bay–Brownsville–Manzanita route was a shipping route that originated from Seattle, Washington. The route included stops at Fletcher Bay, Brownsville, and Manzanita.

Suquamish, built in 1914, was the first diesel-engined passenger vessel in the United States. Much later Suquamish was converted to a commercial fishing vessel and was registered as a Canadian vessel under the name Terry.













