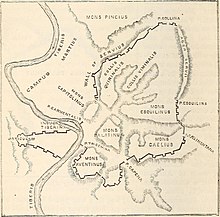
The Aventine Hill is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth rione, or ward, of Rome.

Porta Capena was a gate in the Servian Wall in Rome, Italy. The gate was located in the area of Piazza di Porta Capena, where the Caelian, Palatine and Aventine hills meet. Probably its exact position was between the entrance of Via di Valle delle Camene and the beginning of Via delle Terme di Caracalla, facing the curved side of the Circus Maximus.
The Caelian Hill is one of the famous seven hills of Rome.

The Servian Wall is an ancient Roman defensive barrier constructed around the city of Rome in the early 4th century BC. The wall was built of volcanic tuff and was up to 10 m (33 ft) in height in places, 3.6 m (12 ft) wide at its base, 11 km (6.8 mi) long, and is believed to have had 16 main gates, of which only one or two have survived, and enclosed a total area of 246 hectares. In the 3rd century AD it was superseded by the construction of the larger Aurelian Walls as the city of Rome grew beyond the boundary of the Servian Wall.

The Aurelian Walls are a line of city walls built between 271 AD and 275 AD in Rome, Italy, during the reign of the Roman Emperor Aurelian. They superseded the earlier Servian Wall built during the 4th century BC.
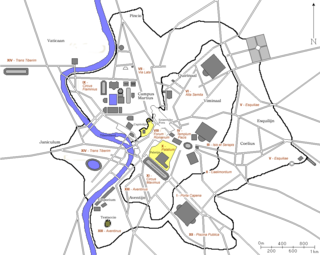
In 7 BC, Augustus divided the city of Rome into 14 administrative regions. These replaced the four regiones—or "quarters"—traditionally attributed to Servius Tullius, sixth king of Rome. They were further divided into official neighborhoods.

The Aqua Appia was the first Roman aqueduct, constructed in 312 BC by the co-censors Gaius Plautius Venox and Appius Claudius Caecus, the same Roman censor who also built the important Via Appia.

The Via Ostiensis was an important road in ancient Rome. It ran west 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the city of Rome to its important sea port of Ostia Antica, from which it took its name. The road began near the Forum Boarium, ran between the Aventine Hill and the Tiber River along its left (eastern) bank, and left the city's Servian Walls through the Porta Trigemina. When the later Aurelian Walls were built, the road left the city through the Porta Ostiensis. In the Late Roman Empire, trade suffered under an economic crisis, and Ostia declined as an important port. With the accompanying growth of importance of the Via Portuensis from the time of Constantine onwards, that of the Via Ostiensis correspondingly decreased. Modern Via Ostiense, following a similar path, is the main connection of Rome to Ostia together with the Via del Mare. On its way to Ostia, the road passes by the important basilica of Saint Paul Outside the Walls.

The Pincian Hill is a hill in the northeast quadrant of the historical centre of Rome. The hill lies to the north of the Quirinal, overlooking the Campus Martius. It was outside the original boundaries of the ancient city of Rome, and was not one of the Seven hills of Rome, but it lies within the wall built by Roman Emperor Aurelian between 270 and 273.
The Aqua Augusta, which was also called the Aqua Alsietina, was an aqueduct supplying ancient Rome. Owing to severe drought, the Emperor Augustus built the Aqua Augusta in or around 33 BC in order to supplement the Aqua Marcia, and then later the Aqua Claudia when required. However, the aqueduct was poorly designed and most of it collapsed in 27 BC.

The Aqua Julia is a Roman aqueduct built in 33 BC by Agrippa under Augustus to supply the city of Rome. It was repaired and expanded by Augustus from 11–4 BC.

In Ancient Rome, the Aqua Alsietina was the earlier of the two western Roman aqueducts, erected sometime around 2 BC, during the reign of emperor Augustus. It was the only water supply for the Transtiberine region, on the right bank of the river Tiber until the Aqua Traiana was built.

The Porta Latina is a single-arched gate in the Aurelian Walls of ancient Rome.

The Aqua Marcia is one of the longest of the eleven aqueducts that supplied the city of Rome. The aqueduct was built between 144–140 BC, during the Roman Republic. The still-functioning Acqua Felice from 1586 runs on long stretches along the route of the Aqua Marcia.

The Pons Probi was a bridge over the River Tiber in Ancient Rome, just south of Porta Trigemina.

The Porta Fontinalis was a gate in the Servian Wall in ancient Rome. It was located on the northern slope of the Capitoline Hill, probably the northeast shoulder over the Clivus Argentarius. The Via Salaria exited through it, as did the Via Flaminia originally, providing a direct link with Picene and Gallic territory. After the Aurelian Walls were constructed toward the end of the 3rd century AD, the section of the Via Flaminia that ran between the Porta Fontinalis and the new Porta Flaminia was called the Via Lata ("Broadway").
The Temple of Luna was a temple on the Aventine Hill in Rome, dedicated to Luna, the moon goddess. Its dedication was celebrated on 31 March.