
In male human anatomy, the glans penis or penile glans, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and primary anatomical source of sexual pleasure. The glans penis is present in the male reproductive organs of humans and most other mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is located over the distal ends of the corpora cavernosa and is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by a fold of skin called the foreskin. In adults, the foreskin can generally be retracted over and past the glans manually or sometimes automatically during an erection.

Paraphimosis is an uncommon medical condition in which the foreskin of a penis becomes trapped behind the glans penis, and cannot be reduced. If this condition persists for several hours or there is any sign of a lack of blood flow, paraphimosis should be treated as a medical emergency, as it can result in gangrene.
Phimosis is a condition in which the foreskin of the penis cannot stretch to allow it to be pulled back past the glans. A balloon-like swelling under the foreskin may occur with urination. In teenagers and adults, it may result in pain during an erection, but is otherwise not painful. Those affected are at greater risk of inflammation of the glans, known as balanitis, and other complications.
Vaginitis, also known as vulvovaginitis, is inflammation of the vagina and vulva. Symptoms may include itching, burning, pain, discharge, and a bad smell. Certain types of vaginitis may result in complications during pregnancy.
Penile cancer, or penile carcinoma, is a cancer that develops in the skin or tissues of the penis. Symptoms may include abnormal growth, an ulcer or sore on the skin of the penis, and bleeding or foul smelling discharge.

Cervicitis is inflammation of the uterine cervix. Cervicitis in women has many features in common with urethritis in men and many cases are caused by sexually transmitted infections. Non-infectious causes of cervicitis can include intrauterine devices, contraceptive diaphragms, and allergic reactions to spermicides or latex condoms. Cervicitis affects over half of all women during their adult life.

Chancroid is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection characterized by painful sores on the genitalia. Chancroid is known to spread from one individual to another solely through sexual contact. However, there have been reports of accidental infection through the hand.

Balanitis is inflammation of the glans penis. Balanoposthitis is the proper term when the foreskin is also affected. Balanitis on persons in diapers must be distinguished from redness caused by ammoniacal dermatitis.

Hand washing, also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to the hands. Drying of the washed hands is part of the process as wet and moist hands are more easily recontaminated. If soap and water are unavailable, hand sanitizer that is at least 60% (v/v) alcohol in water can be used as long as hands are not visibly excessively dirty or greasy. Hand hygiene is central to preventing the spread of infectious diseases in home and everyday life settings.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.
Vulvitis is inflammation of the vulva, the external female mammalian genitalia that include the labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and introitus. It may co-occur as vulvovaginitis with vaginitis, inflammation of the vagina, and may have infectious or non-infectious causes. The warm and moist conditions of the vulva make it easily affected. Vulvitis is prone to occur in any female especially those who have certain sensitivities, infections, allergies, or diseases that make them likely to have vulvitis. Postmenopausal women and prepubescent girls are more prone to be affected by it, as compared to women in their menstruation period. It is so because they have low estrogen levels which makes their vulvar tissue thin and dry. Women having diabetes are also prone to be affected by vulvitis due to the high sugar content in their cells, increasing their vulnerability. Vulvitis is not a disease, it is just an inflammation caused by an infection, allergy or injury. Vulvitis may also be symptom of any sexually transmitted infection or a fungal infection.
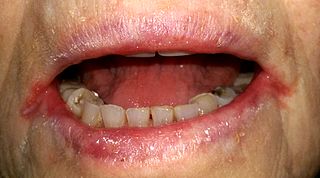
Angular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of cheilitis.

Balanitis circinata is a skin condition comprising a serpiginous ring-shaped dermatitis of the glans penis. While circinate balanitis is one of the most common cutaneous manifestations of reactive arthritis, it can also occur independently. Topical corticosteroid therapy is the most commonly used treatment, and topical calcineurin inhibitors have also been used successfully.

In human anatomy, the penis is an external sex organ through which males urinate and ejaculate. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system.
Eyelid dermatitis is commonly related to atopic dermatitis or allergic contact dermatitis. Volatile substances, tosylamide, epoxy hardeners, insect sprays, and lemon peel oil may be implicated, with many cases of eyelid contact dermatitis being caused by substances transferred by the hands to the eyelids.

Balanitis plasmacellularis, also known as balanitis circumscripta plasmacellularis, Zoon balanitis, or plasma cell balanitis, is a cutaneous condition characterized by a benign inflammatory skin lesion characterized histologically by a plasma cell infiltrate.
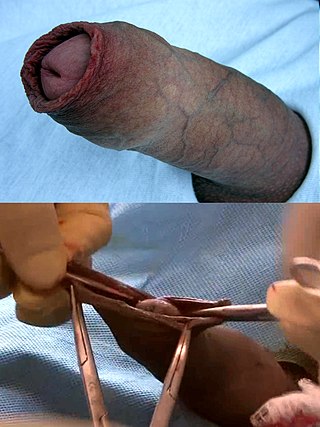
A dorsal slit is a single incision along the upper length of the foreskin from the tip to the corona, exposing the glans without removing any tissue. An ancient practice, it has been a traditional custom among a number of peoples, particularly Filipinos and Pacific Islanders, probably for thousands of years.
Perianal cellulitis, also known as perianitis or perianal streptococcal dermatitis, is a bacterial infection affecting the lower layers of the skin (cellulitis) around the anus. It presents as bright redness in the skin and can be accompanied by pain, difficulty defecating, itching, and bleeding. This disease is considered a complicated skin and soft tissue infection (cSSTI) because of the involvement of the deeper soft tissues.

In male human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce, is the double-layered fold of skin, mucosal and muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans and the urinary meatus. The foreskin is attached to the glans by an elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum. The outer skin of the foreskin meets with the inner preputial mucosa at the area of the mucocutaneous junction. The foreskin is mobile, fairly stretchable and sustains the glans in a moist environment. Except for humans, a similar structure known as a penile sheath appears in the male sexual organs of all primates and the vast majority of mammals.
In the event of a flood, many residents and emergency personal are exposed to unclean water, which can result in several different types of skin conditions. Flood waters contain pathogens and chemicals from coming in contact with raw sewage, oil, gasoline, and household chemicals such as paints and insecticides. A major concern is large scale, unintentional release of contaminants from industrial, superfund, or agricultural sites. The unknown severity of floodwater contamination can raise concerns for skin infections, inflammation, as well as psychological stress-related skin diseases.













